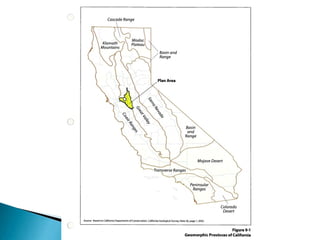
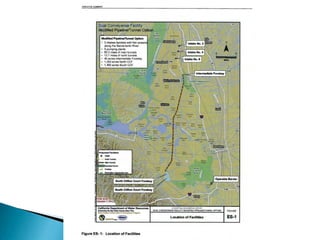
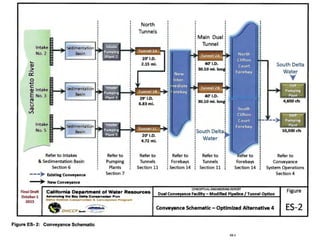
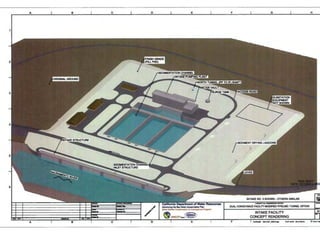
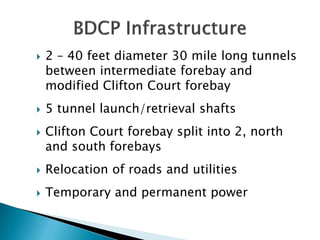
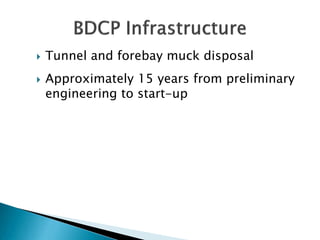
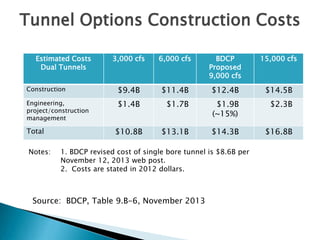
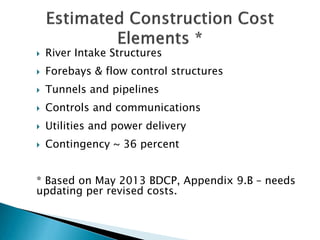
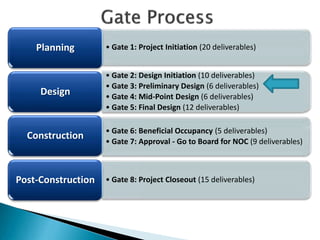
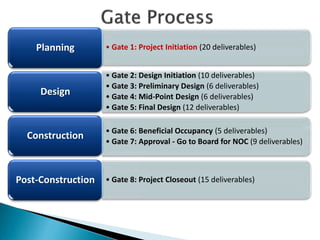
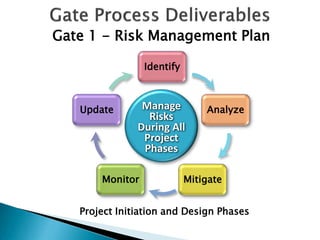
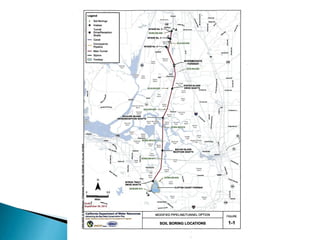
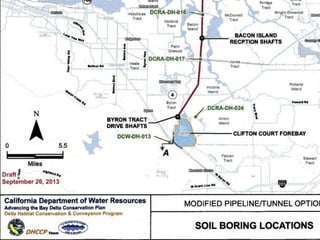
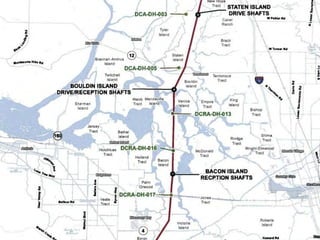
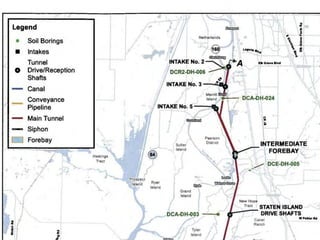
This document provides an overview and status update of the Bay Delta Conservation Plan (BDCP) design review process. It outlines the schedule for board review over the coming months, describes the proposed facilities including three intakes, tunnels and forebays, and provides cost estimates. It also introduces the gate review process and lists some initial concerns including muck removal, disposal and ventilation, contracting requirements, power needs, and unknown geotechnical conditions. Historical data and previous explorations are noted sources of geotechnical information.