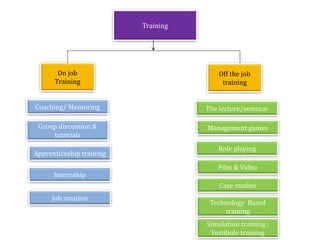
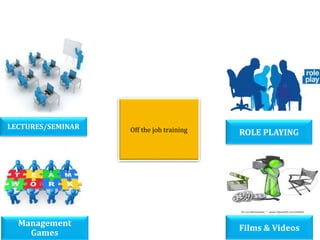
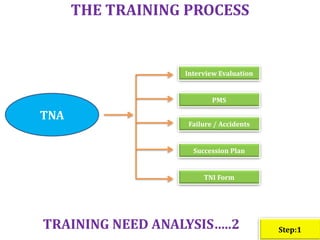
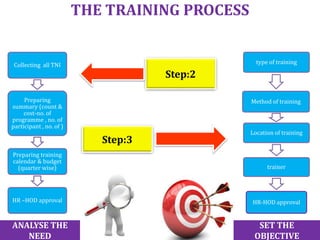
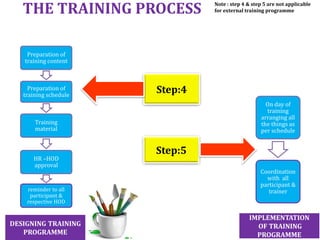
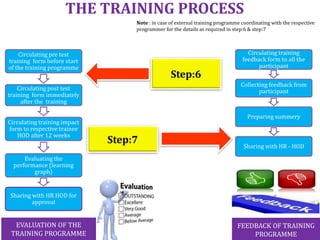
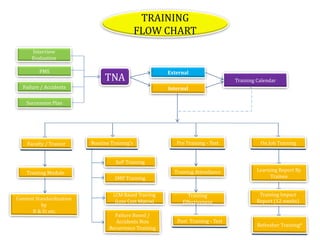
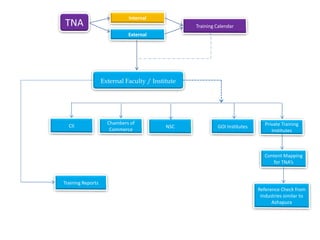
- Infosys has plans to expand its training facility in Mysore from accommodating 4,000 trainees to 10,000 trainees.
- Wipro Spectramind provides educational support called SEED to help talented employees pursue higher education so they are not lost to the business.
- LG Electronics requires its staff to complete two training modules per month with tests and provides prizes every three months to encourage learning.