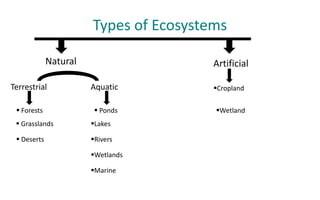
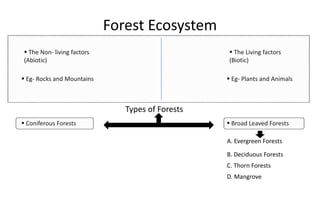
A forest ecosystem is defined as an interacting system formed by the biotic and abiotic factors in a forest region. The key components are plants and animals that depend on geographical features like climate, soil and terrain. There are several types of forests classified by leaf type and rainfall patterns - coniferous forests are found in cooler areas and have needle-like leaves, deciduous forests shed leaves seasonally, and evergreen forests retain leaves year-round. Forest ecosystems provide resources to humans but are threatened by deforestation, overexploitation, and habitat loss, so conservation efforts like protected areas and sustainable use are important to maintain balance.