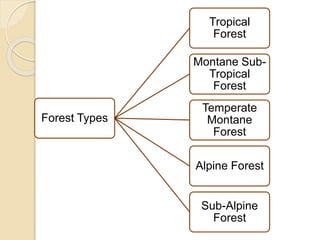
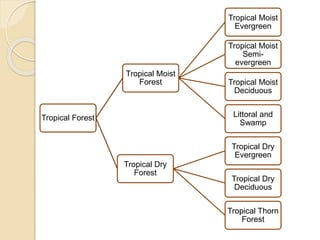
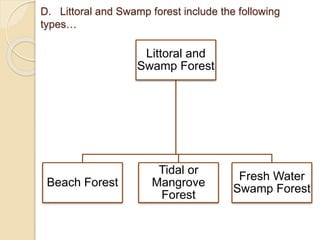
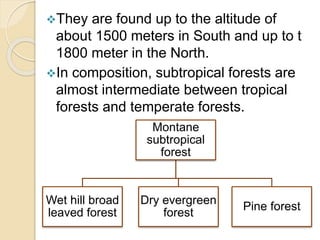
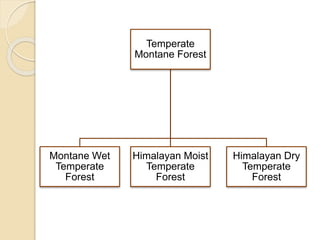
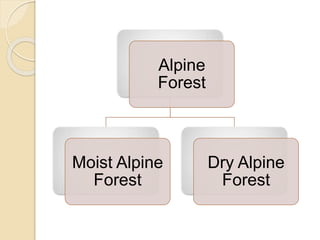
This document summarizes the major forest types found in India. It describes 5 main forest types - tropical forests, montane subtropical forests, temperate montane forests, sub-alpine forests, and alpine forests. Each forest type is further divided into subtypes based on factors like climate, rainfall, temperature, and elevation. The document provides details on the characteristic features and locations of each forest subtype.