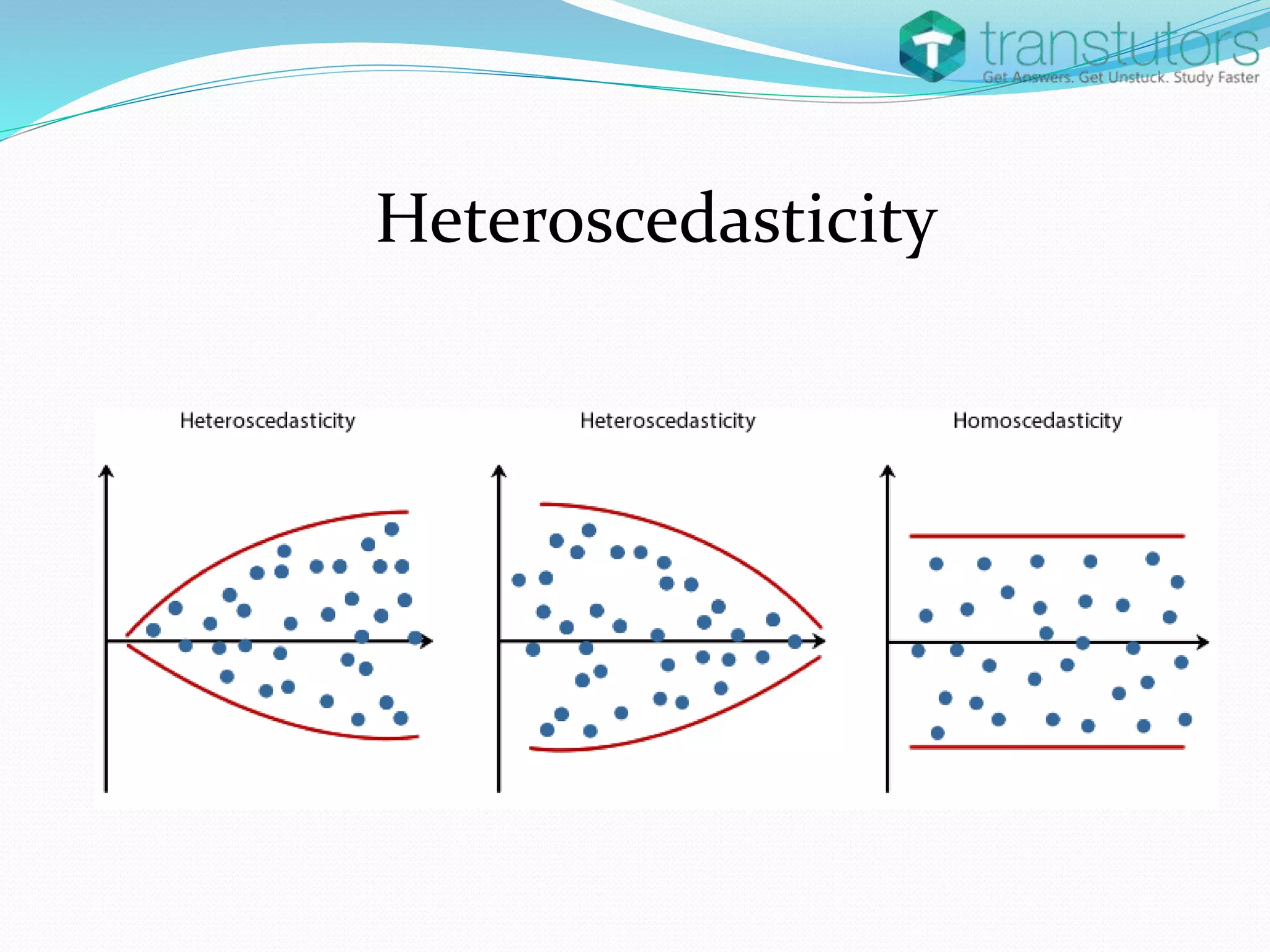
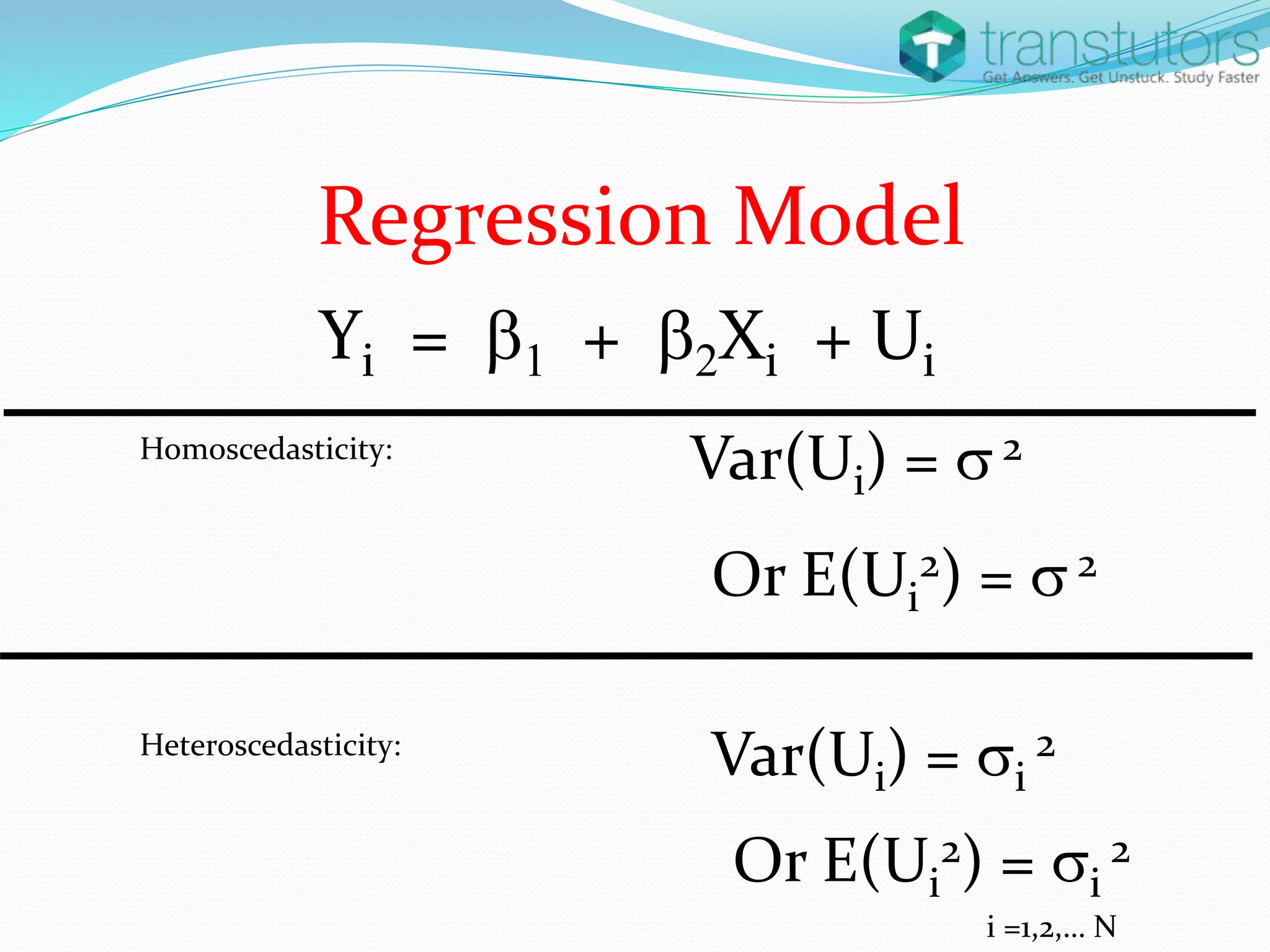
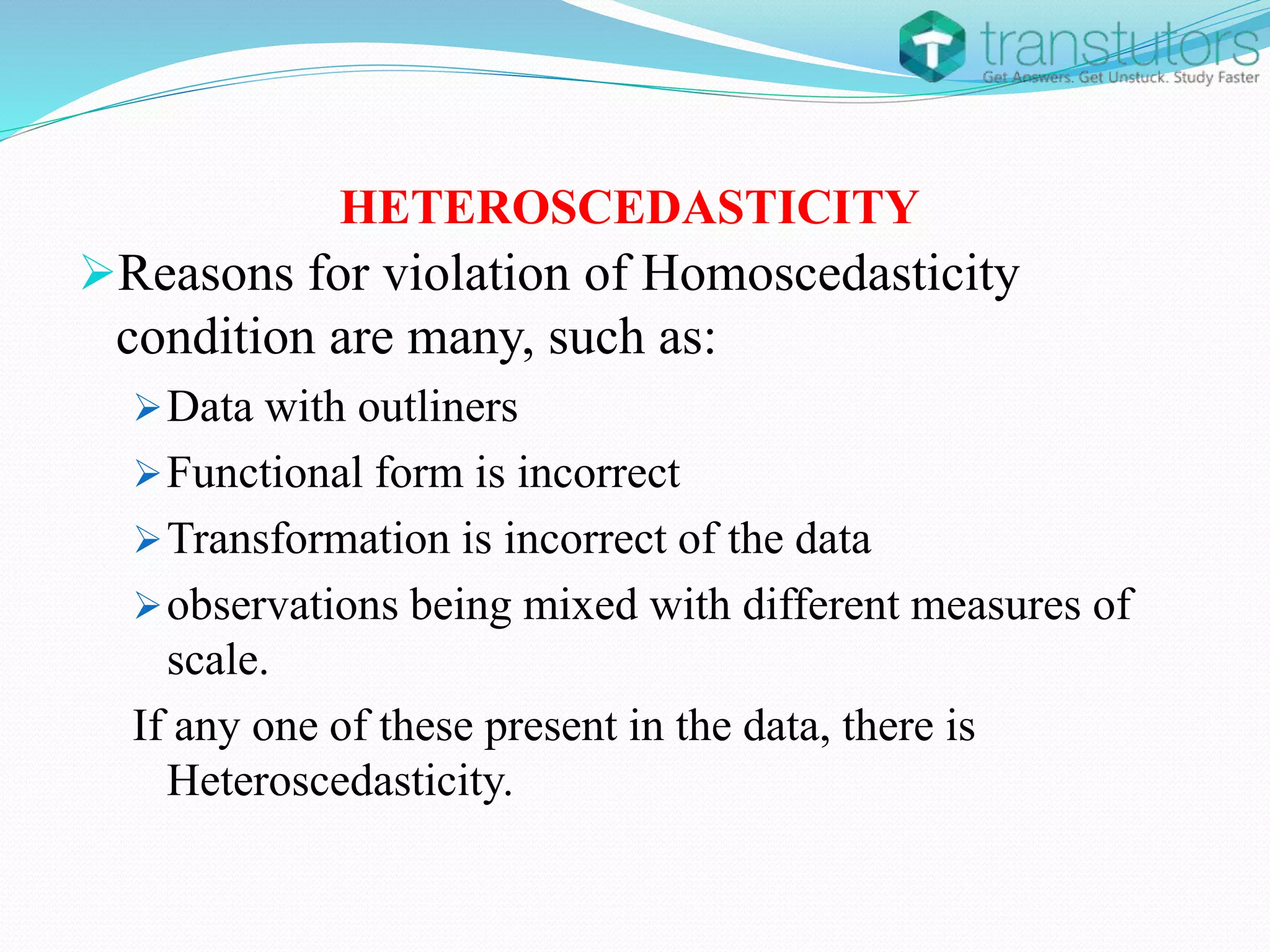
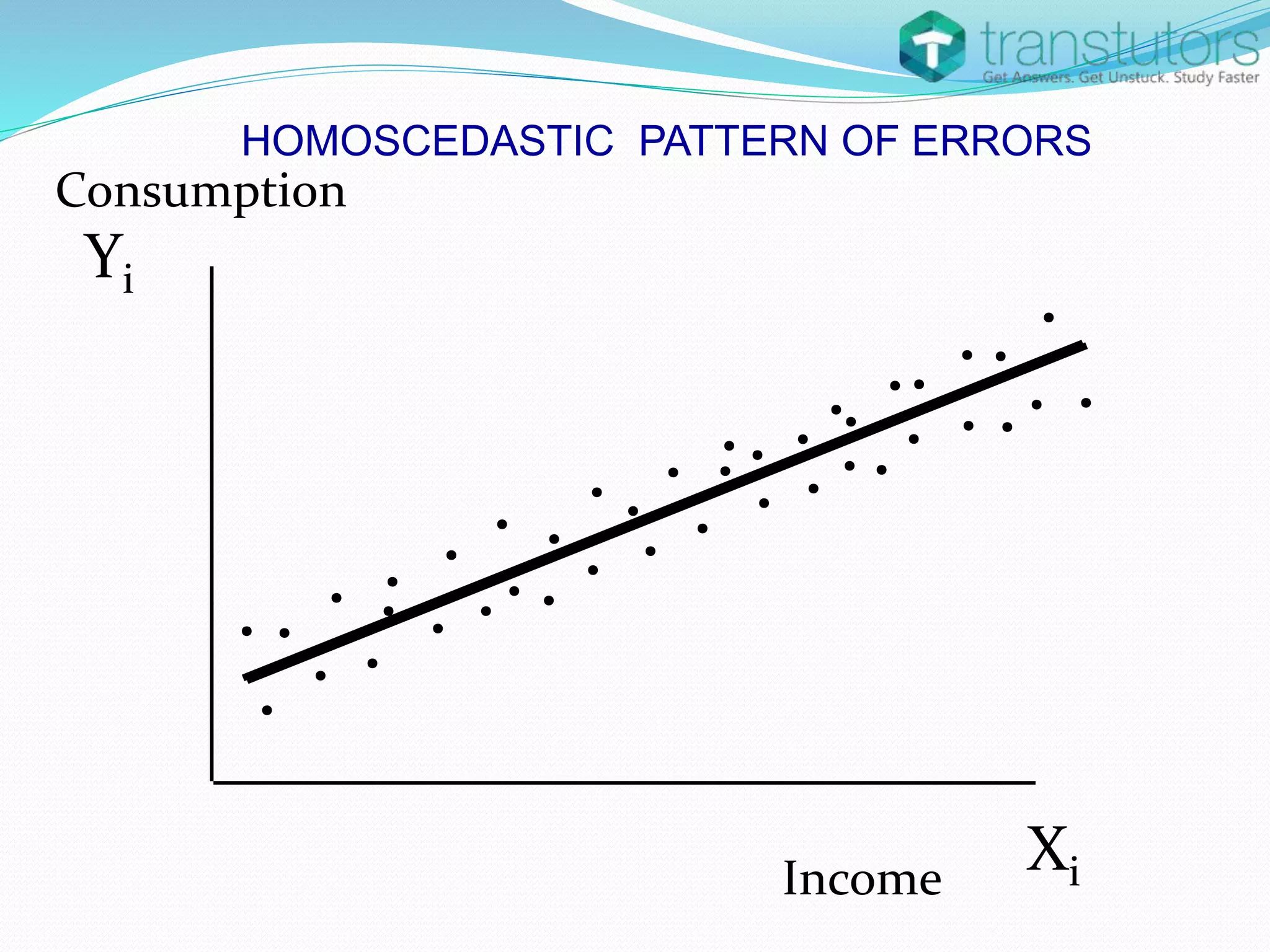
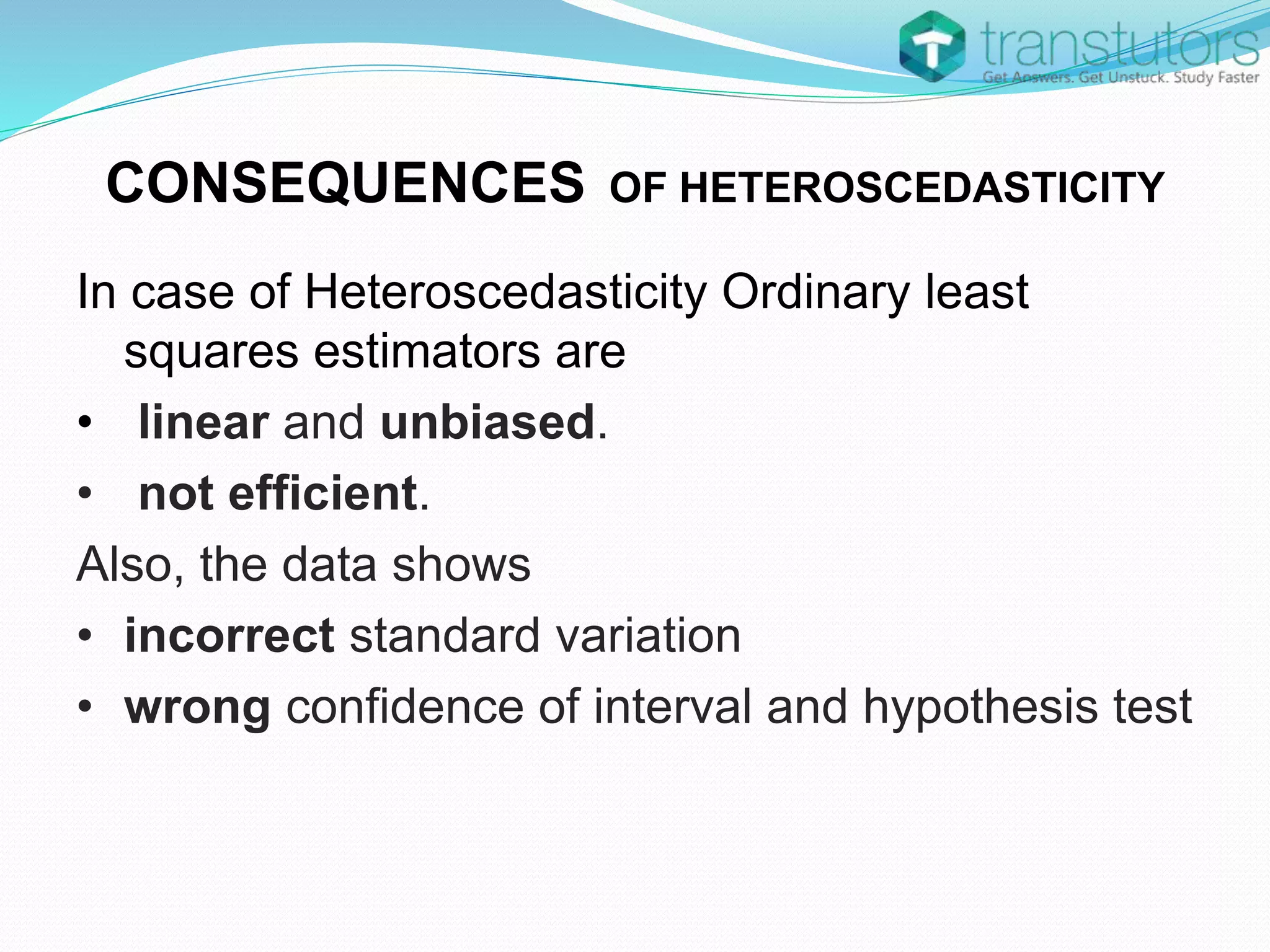
Heteroscedasticity is a violation of the regression model's assumption that error terms have constant variance, leading to inaccuracies in inference. It can arise from factors such as outliers, incorrect functional forms, or mixed measurement scales. The presence of heteroscedasticity renders ordinary least squares estimators unbiased but inefficient, resulting in incorrect standard deviations and hypothesis tests.