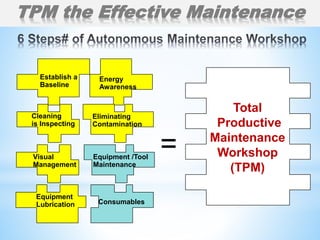
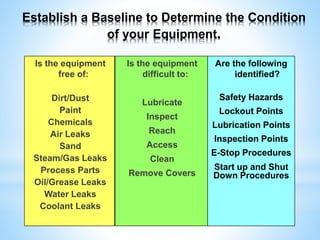
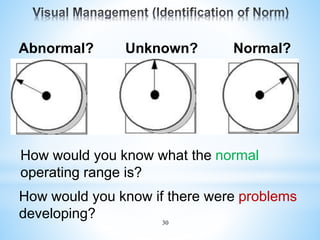
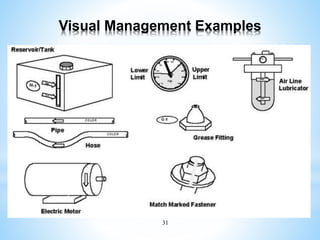
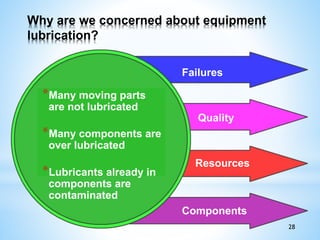
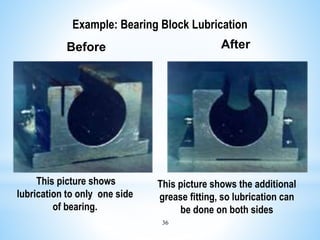
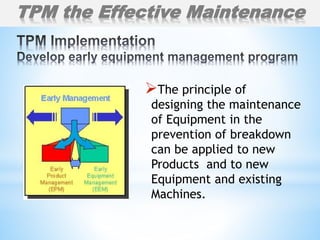
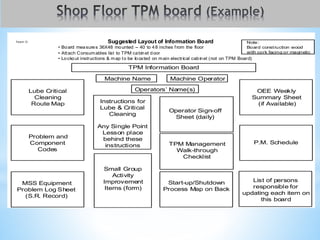
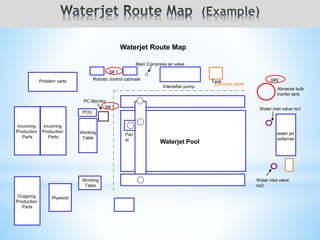
The document outlines a two-day workshop on Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) designed to help implement autonomous, preventive, and predictive maintenance strategies at Kotak Malaysia. It emphasizes the importance of employee involvement and structured maintenance protocols to achieve zero downtime and enhance equipment efficiency. Key topics include establishing maintenance schedules, conducting audits, visual management, and a systematic approach to identify and rectify equipment issues.