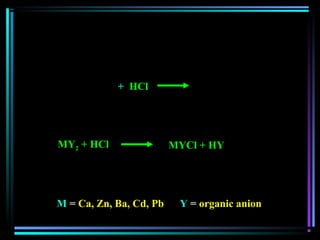
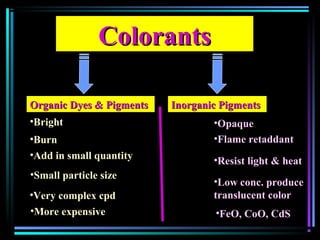
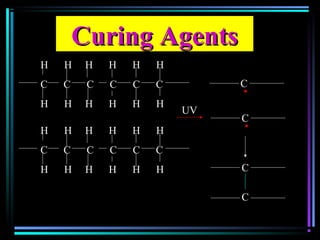
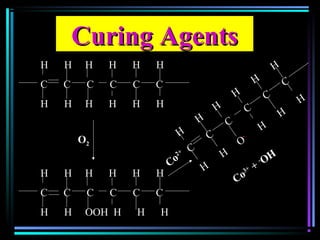
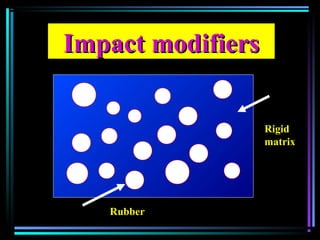
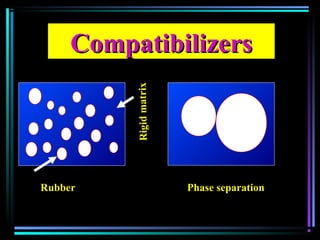
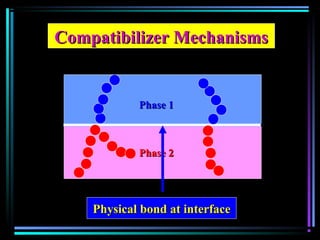
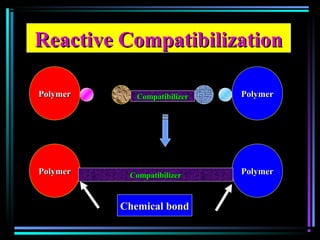
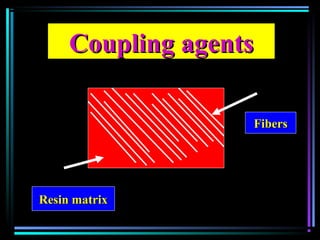
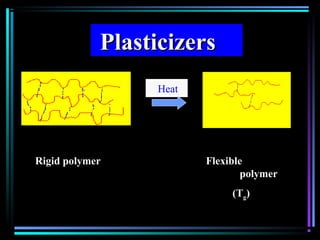
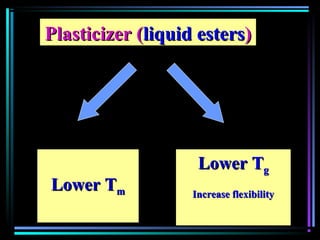
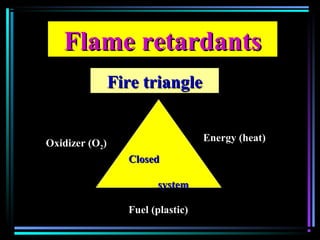
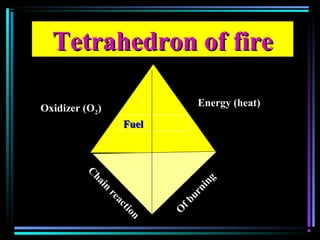
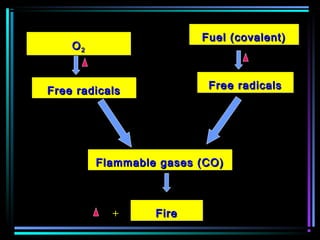
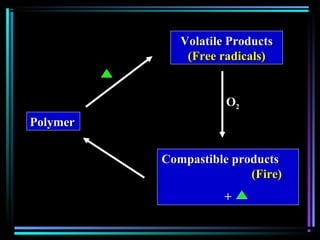
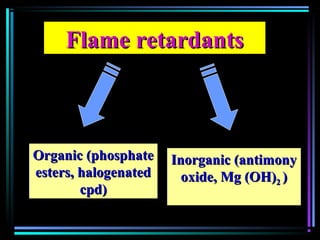
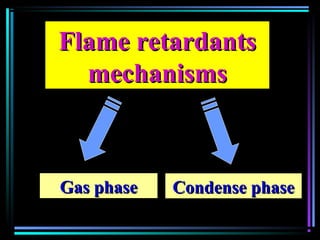
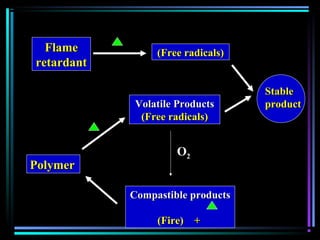
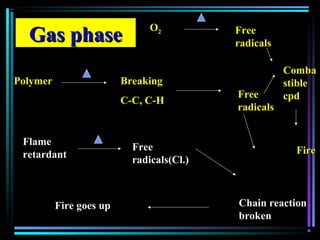
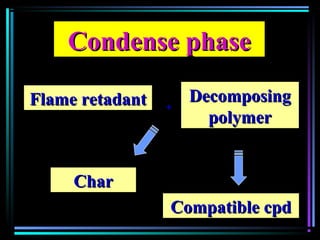
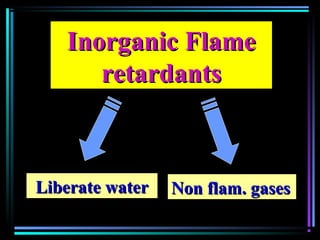
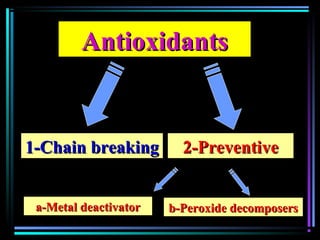
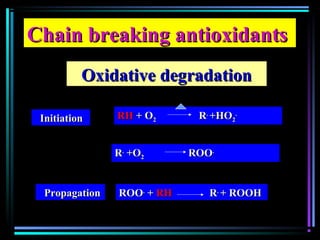
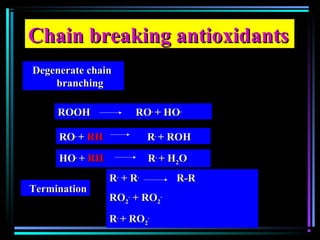
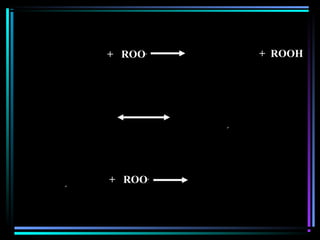
This document discusses various types of additives used in plastics including fillers, plasticizers, lubricants, flame retardants, antioxidants, photostabilizers, blowing agents, colorants, curing agents and more. It describes the functions and mechanisms of these additives such as modifying properties, retarding degradation, extending bulk at lower cost. Various examples are provided for each type of additive and factors to consider in their selection like efficiency, cost, stability under processing and service conditions.


























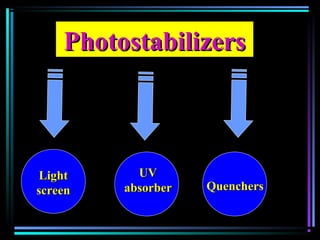


![PhotostabilizersPhotostabilizers
Quenchers [Ni(II) organic cpd]Quenchers [Ni(II) organic cpd]
Energy transfer between excitedEnergy transfer between excited
polymer and photostabilizerpolymer and photostabilizer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/additivesforplasticii3-150206120941-conversion-gate01/85/Additives-for-plastic_ii-3-53-320.jpg)
![Quencher mechanismQuencher mechanism
UVUV
AA**
QQ
A+ QA+ Q** A+ QA+ QAA
AA** + Q+ Q
UVUV
AA**AA
[A…….Q][A…….Q]** A + QA + Q
Excited complexExcited complex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/additivesforplasticii3-150206120941-conversion-gate01/85/Additives-for-plastic_ii-3-54-320.jpg)