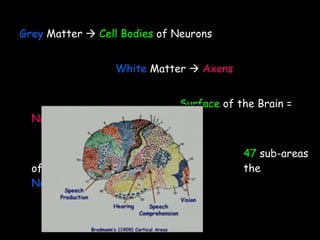
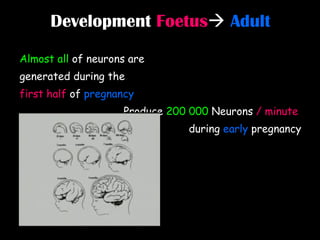
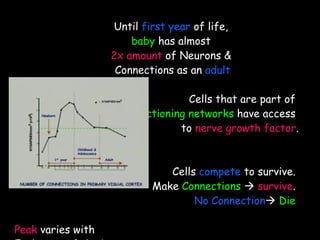
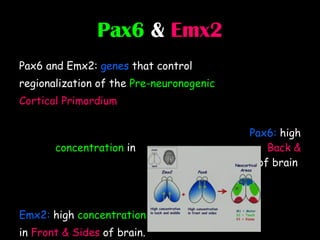
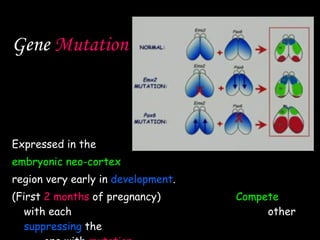
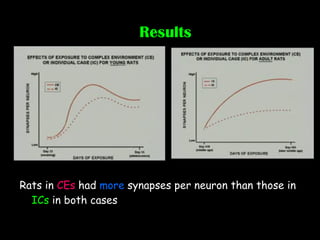
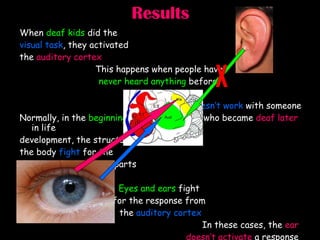
The document discusses brain development in children and the interaction between genes and environment. It notes that the brain develops rapidly in the first two years of life and that both genes and environment influence this development. Genes determine the basic structure of the brain, but the environment determines which neural connections and cells survive based on use. Early experiences and stimulation can affect the brain by strengthening certain connections.