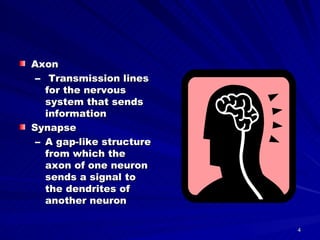
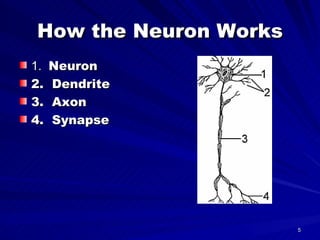
The document discusses brain development in infants. It explains that an infant's brain wiring is shaped by external experiences, and that parents can influence development by touching, talking, singing, and cuddling with the infant. It also notes that infants experience the world through their five senses, and parents can provide sensory experiences through music, colorful surroundings, aromas, and textures. Finally, it states that early relationships are important for emotional and social development, and that parents should smile, use different voice tones, and provide calm interactions and social opportunities.