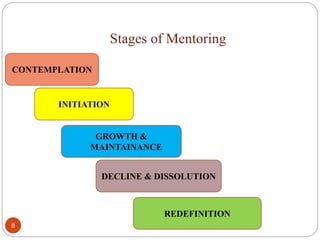
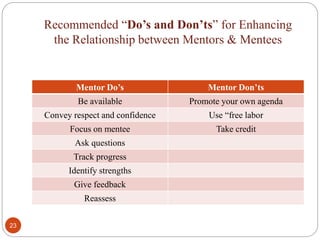
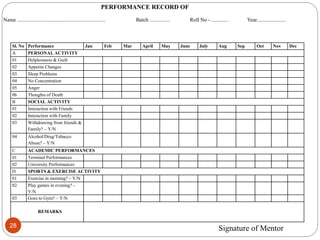
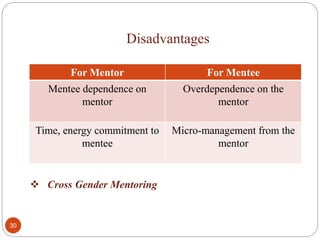
The document outlines guidelines for a mentorship program between medical students and faculty. It defines mentorship and discusses its history and benefits. The objectives of the program are to create trust between students and faculty and provide support to help students cope with academic and personal issues. Faculty mentors are expected to meet regularly with their group of students, address any concerns, and keep records of student performance and well-being. The goal is to improve the medical school experience and reduce stress and depression among students.