The document provides an overview of Marine Corps Aviation, including its mission, functions, aircraft, training process, career paths, and benefits. Some key points:
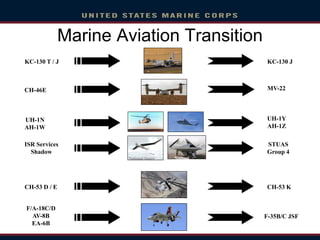
- Marine Aviation performs six essential functions including offensive air support, anti-aircraft warfare, and command and control. It equips Marines with the capability to engage on any terrain using fixed-wing, rotary-wing, tilt-rotor, and unmanned aircraft.
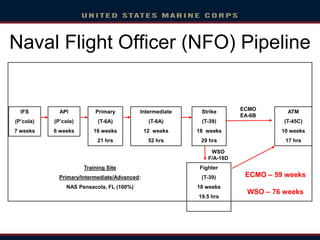
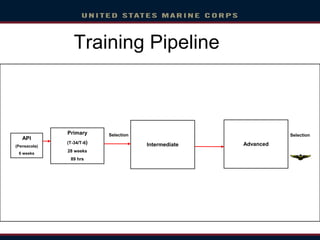
- Training takes 1.5-2 years and involves initial flight school followed by advanced training in a specific aircraft type at different bases before joining a fleet squadron. Career paths include positions in fleet squadrons, staff jobs, and instructional roles.
- The Marine Corps