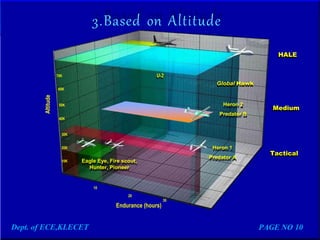
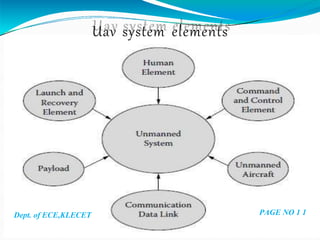
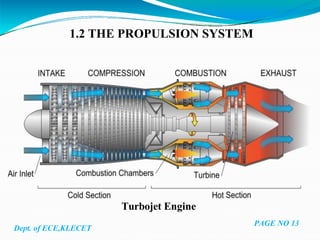
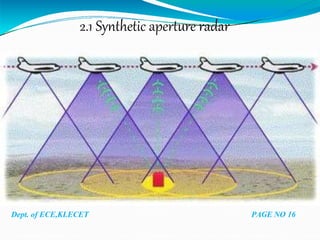
Under the guidance of Mr. Darshankumar Billur, the document discusses the history and classification of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). It provides details on the different elements of UAV systems, including the airframe, propulsion, payload and ground control systems. A case study is presented on the Predator C Avenger UAV, covering its specifications and capabilities. Advantages of UAVs include reduced risks and longer flight times compared to manned aircraft, while disadvantages include higher costs and limited abilities. Applications discussed include remote sensing, surveillance, transport, search and rescue, and armed attacks.
![Under the guidance of
Mr: Darshankumar Billur
Assistant Professor
Department of Electronics & Communication
KLECET, Chikodi
[Grab your reader’s attention with a great quote from the
document or use this space to emphasize a key point. To
place this text box anywhere on the page, just drag it.]
BY: UMESH
DADDE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myseminar-150505013854-conversion-gate01-180313044825/85/Drone-technology-UAV-1-320.jpg)