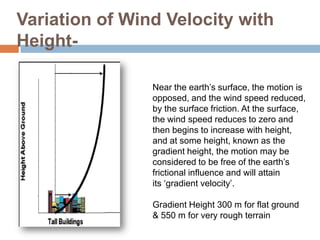
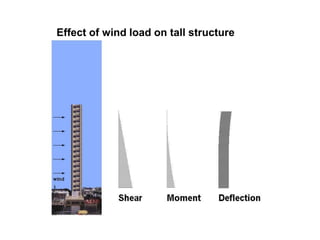
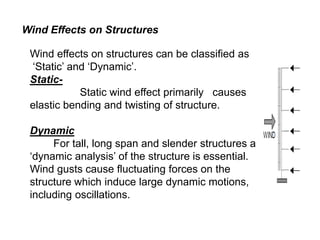
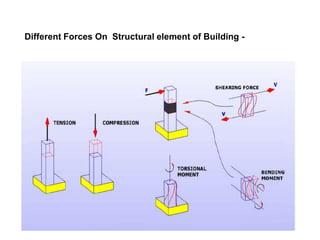
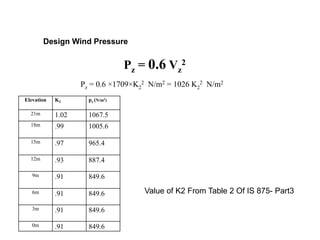
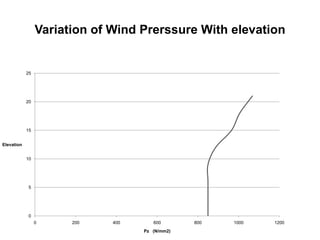
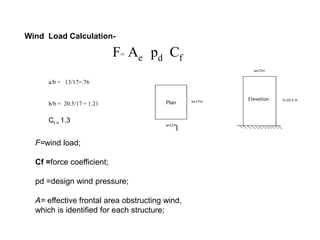
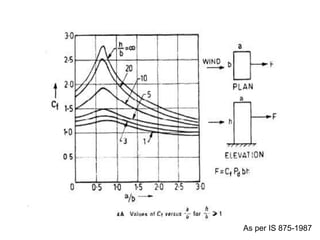
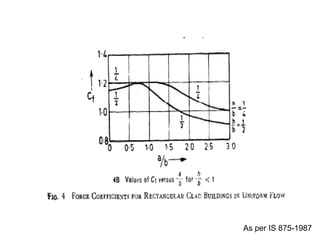
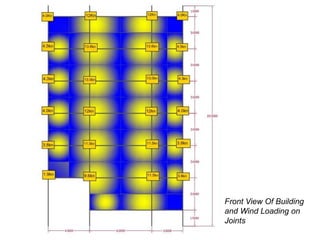
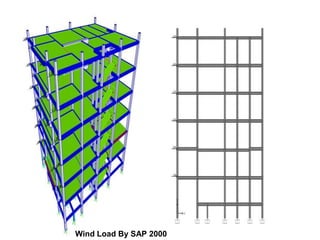
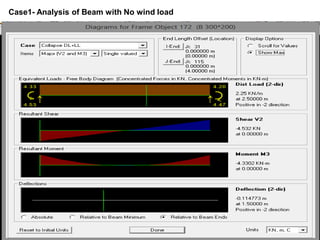
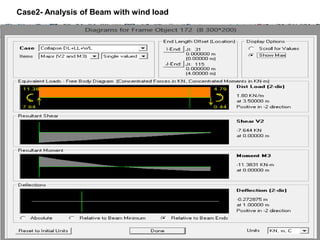
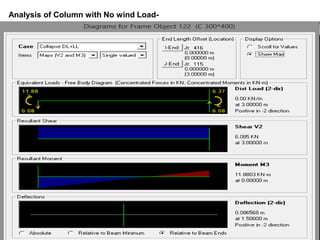
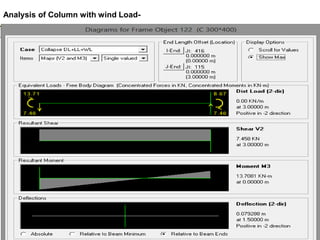
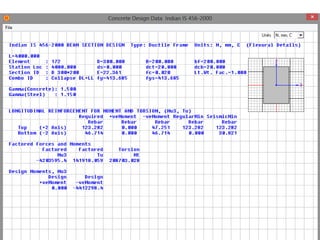
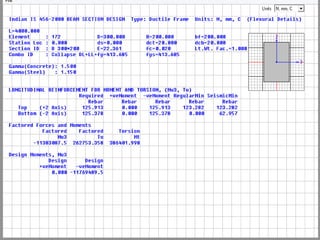
Wind load is an important design consideration for high-rise buildings due to the increasing wind forces experienced at greater heights. This document discusses wind load calculation and analysis for a 20.5m high building according to Indian code IS 875-Part 3. Static analysis of the building model in SAP2000 showed that wind load causes higher bending moments and shear forces compared to analysis without wind load. The wind pressure varies with height and building designers must account for this gradient in load to safely structure high-rise buildings.