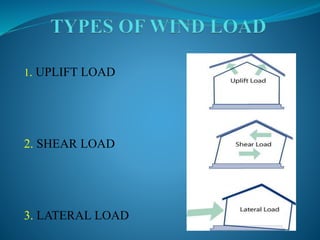
This document discusses wind loads on structures. It describes how high velocity winds create low pressure areas that exert lifting and pulling forces on buildings. Wind load is classified as static or dynamic, with static wind causing elastic bending and twisting, while dynamic wind from gusts induces oscillations. Wind load analysis is used for structures over 10-30 meters tall. Design wind speed is calculated per IS code 875 using factors for probability, terrain height/structure size, and topography. The key effects of wind load are uplift, shear, and lateral loads.