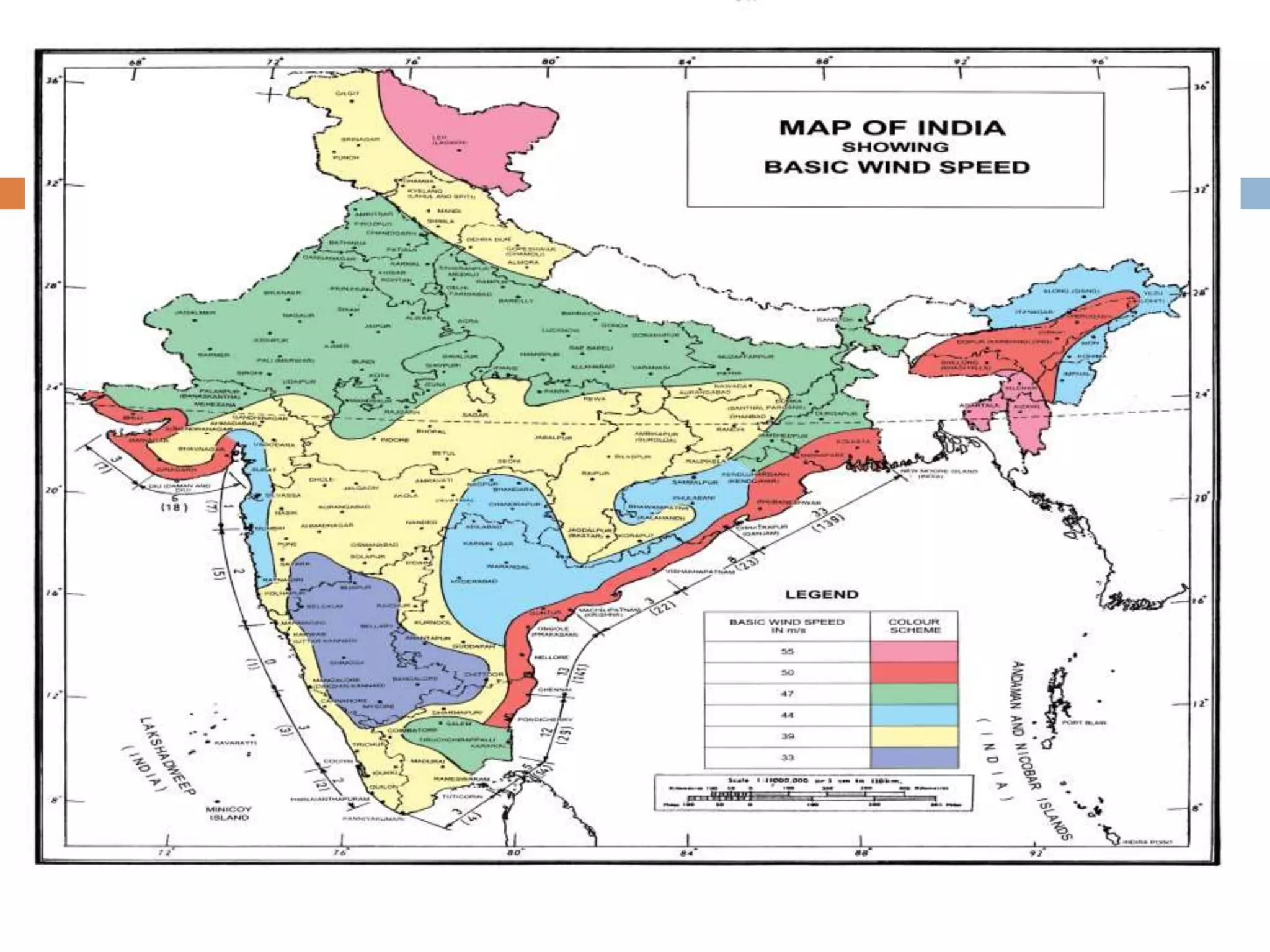
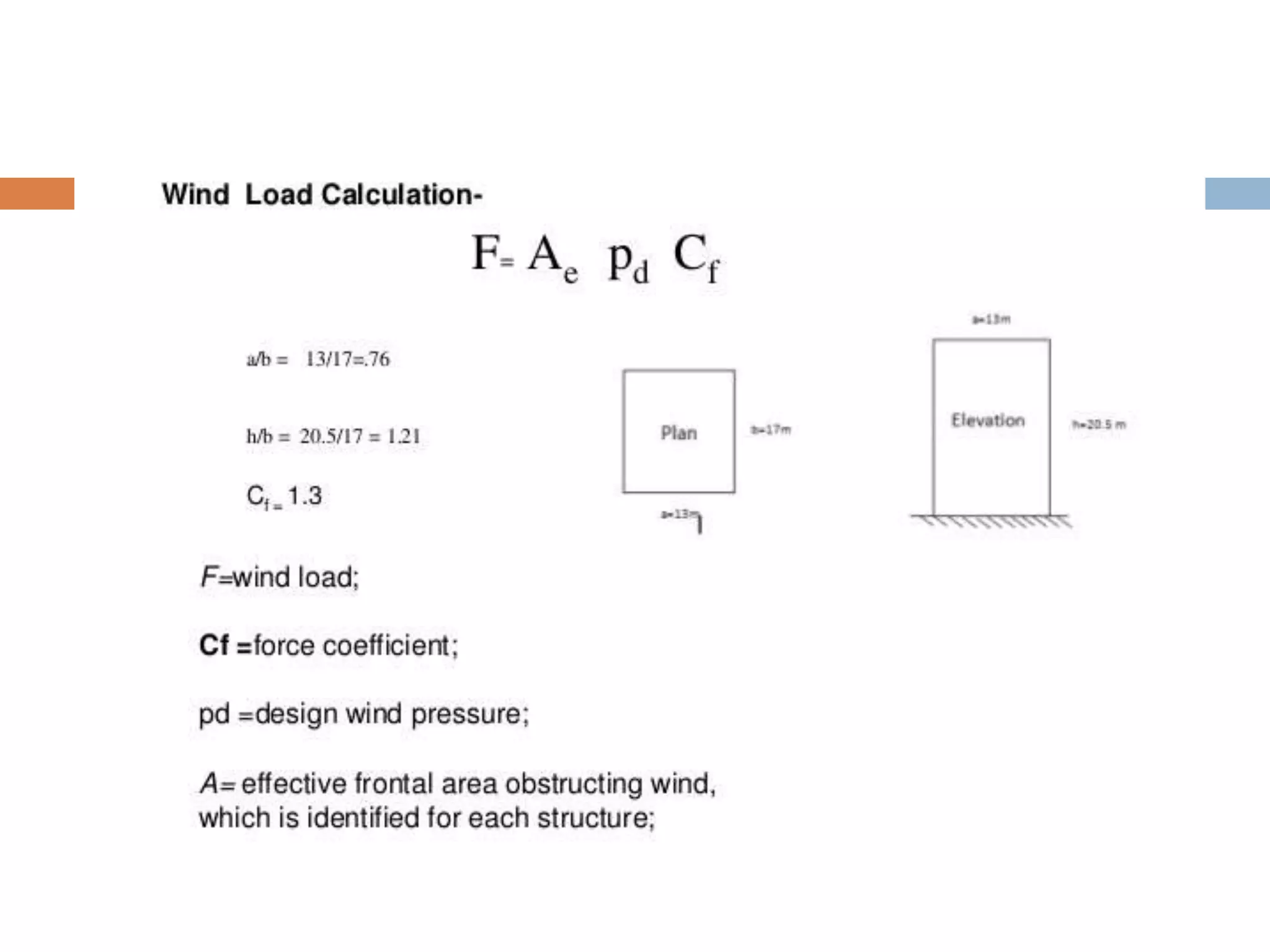
This document discusses design wind load and terminology according to Indian standard code IS 875 (III). It defines key terms like angle of attack, breadth, depth, developed height, effective frontal area, element surface area, force coefficient, gust, peak gust, fetch length, gradient height, pressure coefficient, suction, velocity profile, and topography. It also covers how to calculate design wind speed based on risk coefficient and terrain/height/structure size factor, and how to determine design wind pressure and force coefficients to calculate total wind load on a structure.