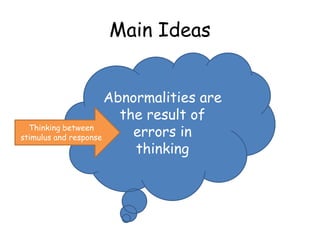
1. The cognitive approach views abnormalities as resulting from errors in thinking between a stimulus and response.
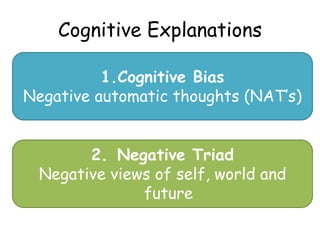
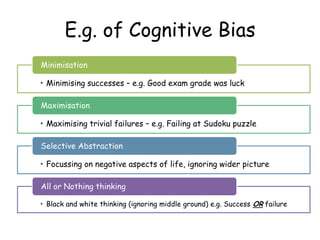
2. It posits that mental disorders stem directly from distortions in cognitive processes like thinking biases such as minimization or maximization.
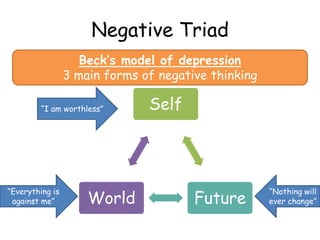
3. A key concept is Beck's negative triad - negative views of the self, world, and future - which has been shown to accurately characterize depressed thinking.