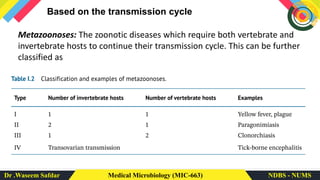
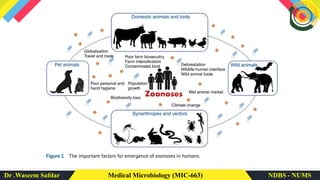
Zoonotic diseases, or zoonoses, are diseases that can be transmitted between animals and humans. They make up around 60% of emerging infectious diseases. Zoonoses can be classified in several ways, including by their causative agent (such as bacteria, viruses, parasites), reservoir host (animals that can transmit the disease to humans), and transmission cycle (direct or requiring multiple hosts). Common transmission routes include direct contact, bites, contaminated food/water, vectors like ticks and fleas, and airborne or fecal-oral transmission. Occupations like farming and veterinary work carry higher risk of exposure. Emerging infectious diseases are on the rise due to factors like environmental changes, antimicrobial resistance, and globalization