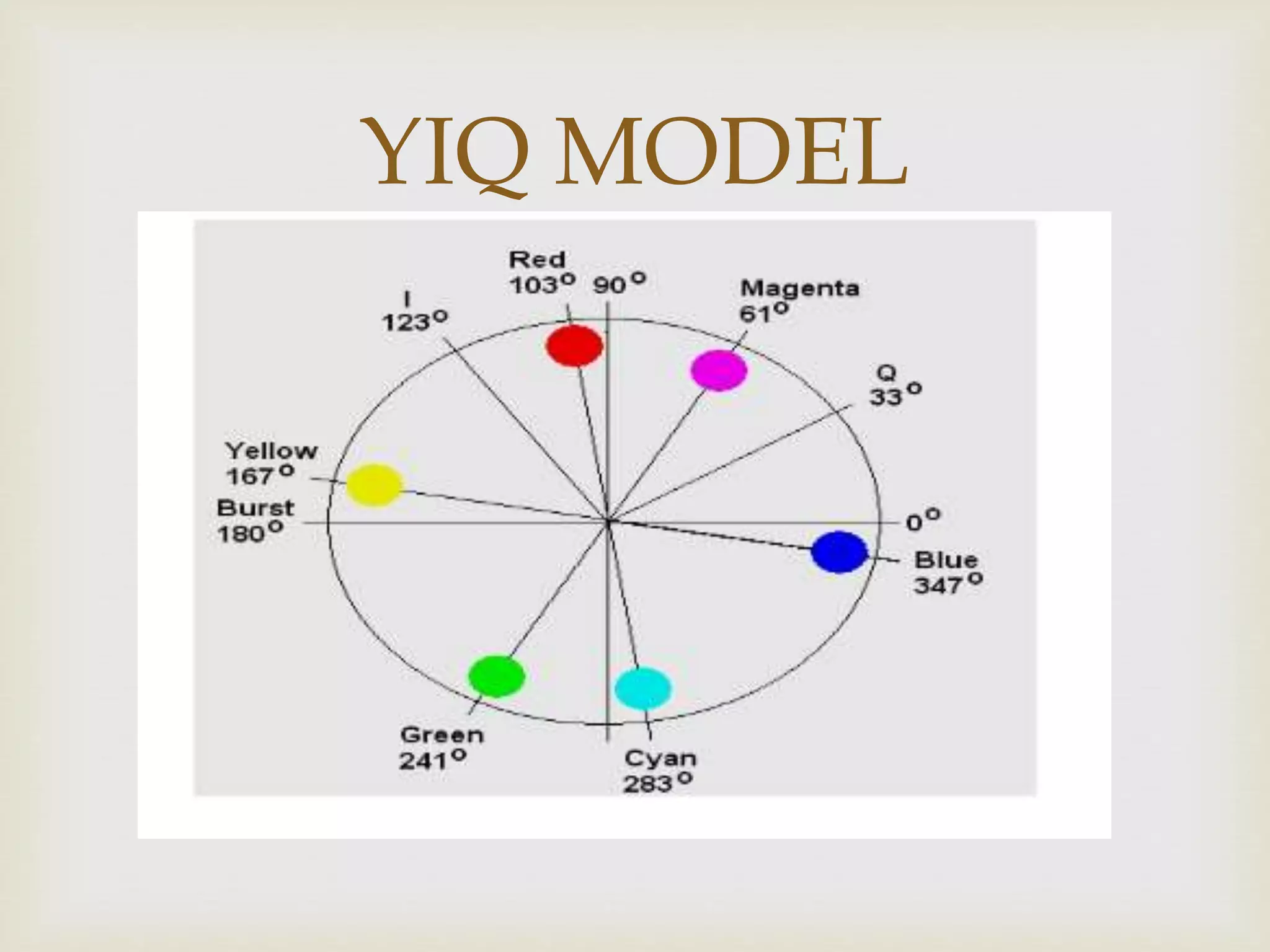
The YIQ color model is used in NTSC television broadcasting to separate luminance (Y) from chrominance (I and Q). It encodes RGB color information into Y for brightness, I for color information related to red and yellow, and Q for color information related to blue and yellow. The YIQ model allows black and white televisions to display color images based on the luminance channel alone. It is designed with human visual perception in mind, allocating more bandwidth to luminance than chrominance.