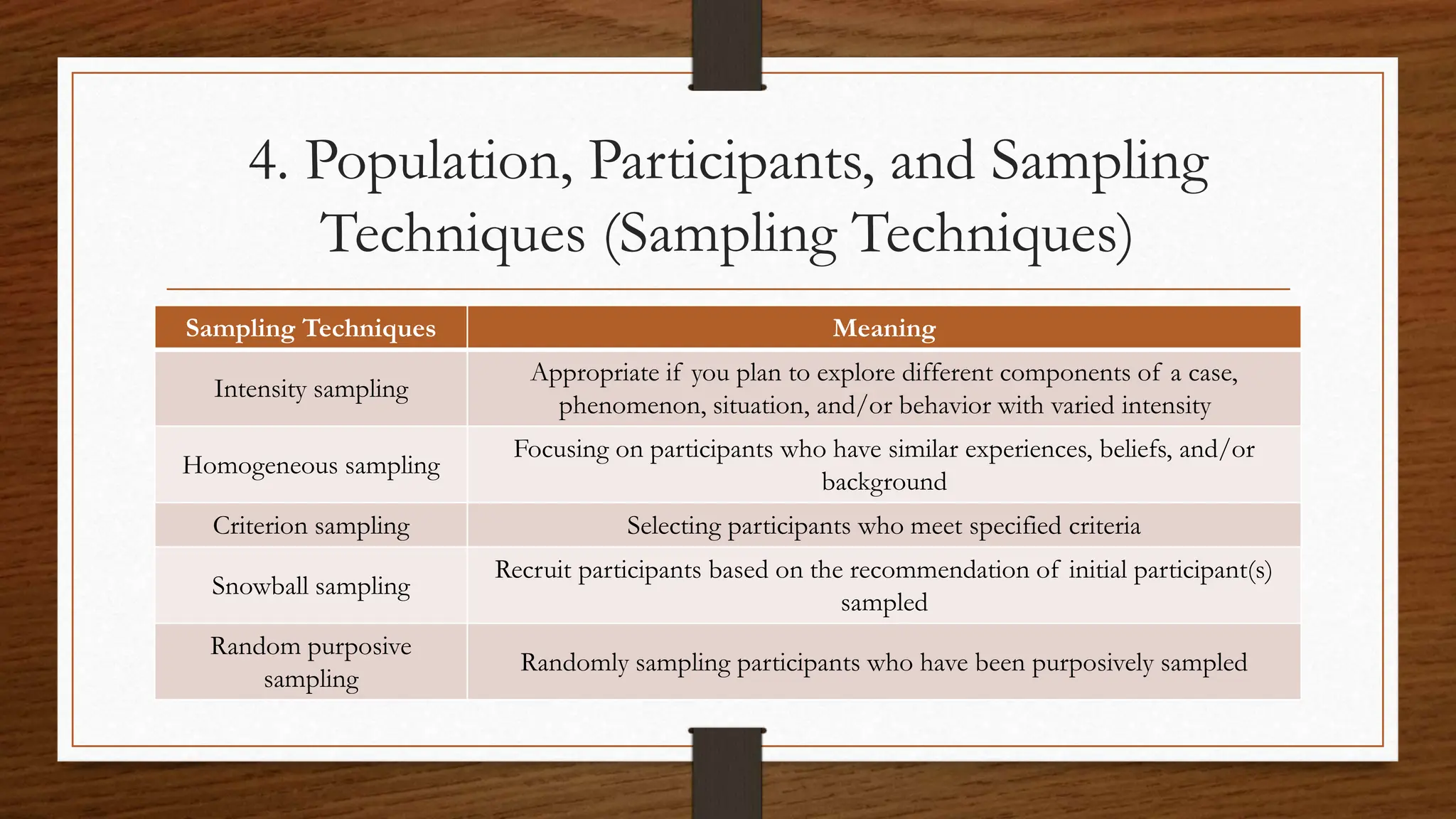
This document outlines the key components that should be included in the methodology chapter of a research paper. It discusses including: the research question; research design and approach; research environment description; population, participants, and sampling techniques; data collection procedures; and data analysis process. Specifically, it recommends stating the research question and purpose, justifying the qualitative approach chosen, describing the research setting and participants, explaining the sampling method and size, outlining the data collection strategies and characteristics, and detailing the data analysis through content or thematic analysis.