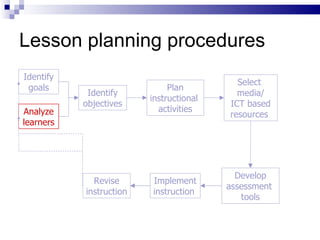
This document discusses planning a student-centered IT-based lesson using the ABCD framework for writing objectives. It covers analyzing learners' backgrounds, knowledge, and other factors. It also differentiates between goals and objectives, explaining that objectives should be specific, observable, and assessable. The ABCD model is introduced for writing objectives: Audience, Behavior, Condition, Degree. An example of a good objective following this model is provided along with critique of sample objectives.