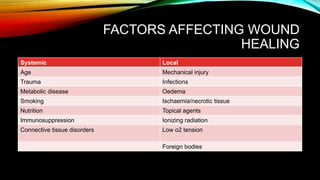
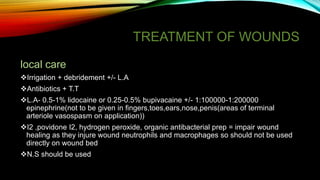
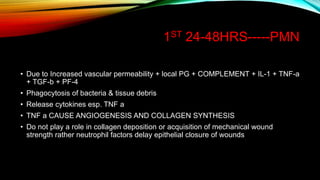
Wound healing occurs in three phases: hemostasis and inflammation, proliferation, and maturation and remodeling. During hemostasis and inflammation, platelets aggregate to form a clot and release growth factors that recruit inflammatory cells. Proliferation involves angiogenesis, collagen deposition, and re-epithelialization facilitated by macrophages, lymphocytes, fibroblasts and endothelial cells. Maturation and remodeling involves collagen remodeling and scar formation over months. Many factors can influence wound healing including infection, poor perfusion, medications, and nutrition. Treatment involves wound care, dressings, antibiotics, surgery, and growth factors depending on the type and severity of the wound.



![2ND GROUP[48-96HRS]------
MACROPHAGES
• Essential to successful healing[derived from circulating monocytes]
• Remain till healing is complete
• Phagocytosis + microbial stasis via o2 radical & NO synthesis
• Activation & recruitment of other cells via cytokines + GF+ cell to cell adhesions and
ICAM
• Release TGF-b, VEGF, IGF, EGF,LACTATE
• Macrophages play significant role in regulating angiogenesis + matrix deposition &
remodeling](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/woundhealingfullme-180401181928/85/Wound-healing-5-320.jpg)


![FIBROBLASTS
• Strongest chemo tactic factor for its release is PDGF
• Cause matrix synthesis and remodeling
• To function needs to proliferate and get activated by macrophages
• Synthesize more collagen from wound site than non wound site
• LACTATE[-10mmol] IS A POTENT REGULATOR OF COLLAGEN SYNTHESIS
THROUGH A MECHANISM OF ADP- ribosylation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/woundhealingfullme-180401181928/85/Wound-healing-8-320.jpg)

![MATRIX SYNTHESIS
• By collagen type 1[major component of ECM in skin] & type 3[important in repair process]
• Collagen has glycine in every 3rd position,2nd by proline or lysine
• 1000aa = protocollagen, goes to E.R where hydroxylation of proline & lysine take place
• Hydroxylation of proline by prolyl hydroxylase-1>o2 & Fe as cofactors
2>a-KG AS co substrate
3>Vitamin C as electron donor
• Protocollagen in ER is glycosylated by GAL & GLU
• Protocollagen is hydroxylated and glycosylated to form procollagen(a-helix)
• Registration peptides are present in the terminal ends
• Then there is extracellular crosslinking to form collagen](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/woundhealingfullme-180401181928/85/Wound-healing-10-320.jpg)