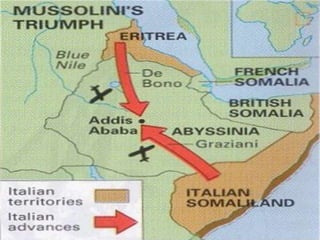
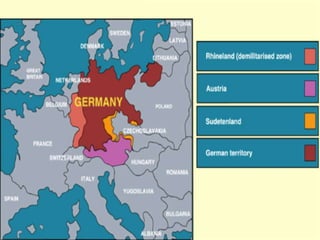
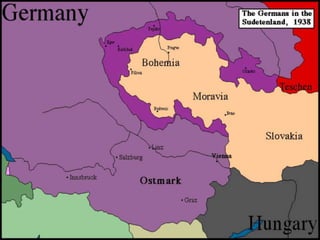
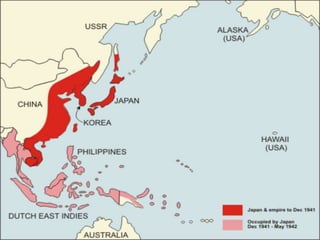
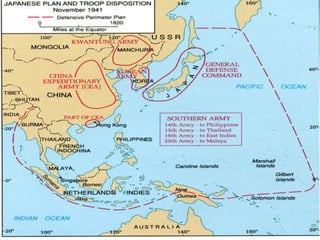
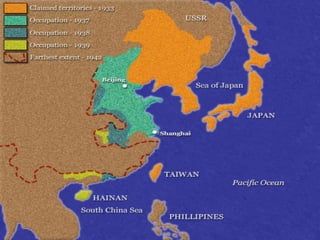
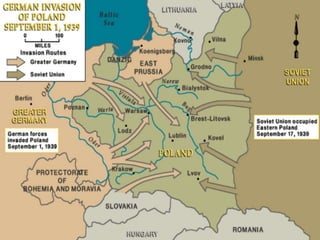
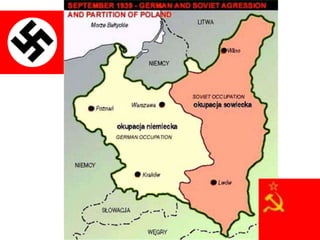
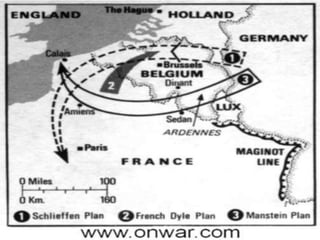
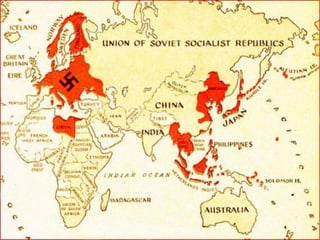
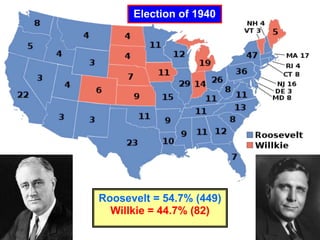
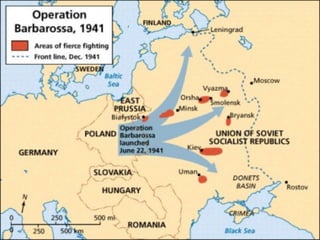
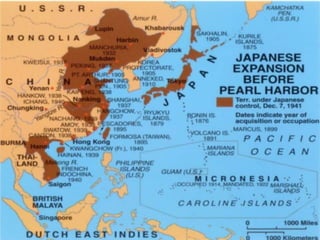
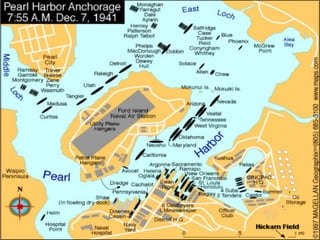
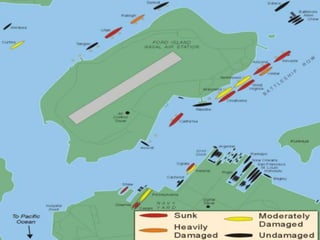
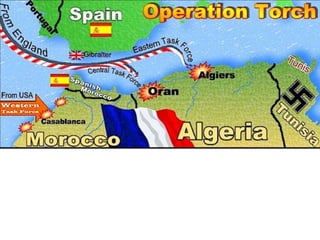
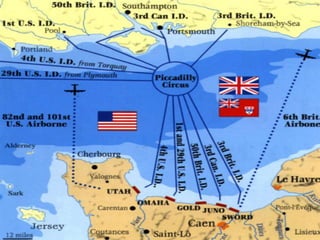
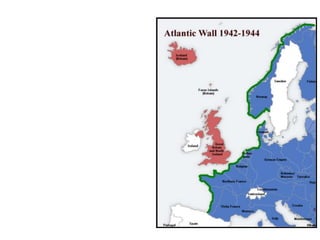
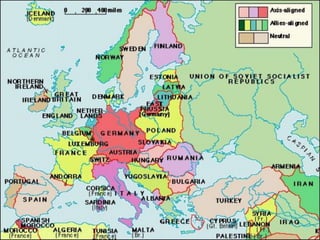
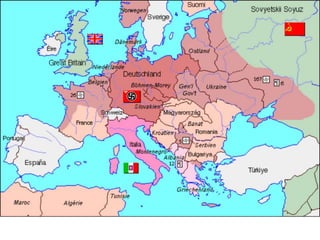
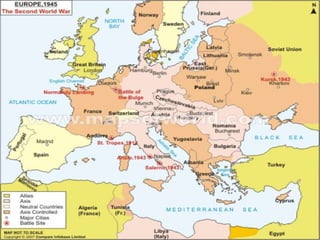
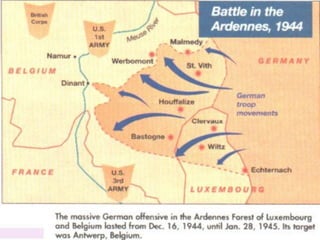
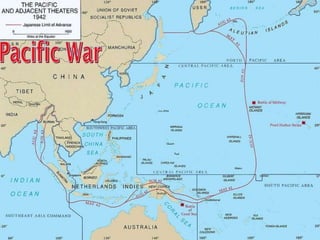
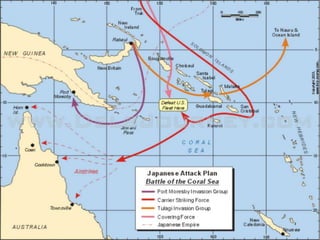
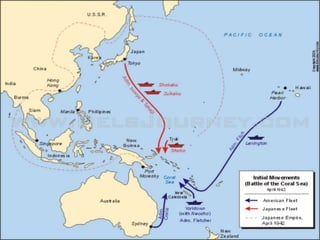
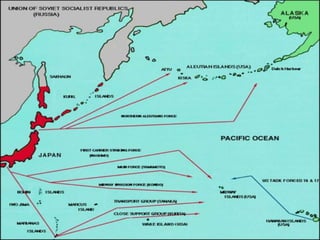
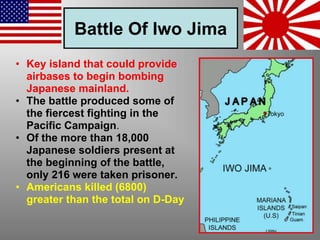
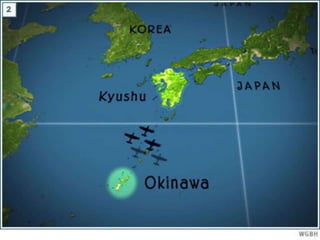
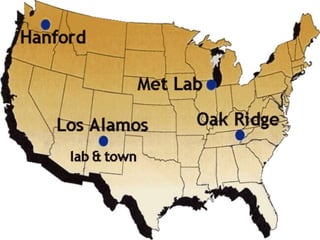
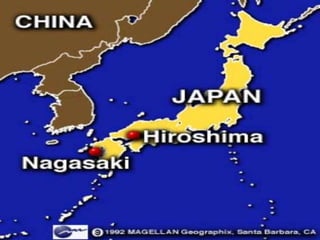
The document provides biographical information on several key World War II leaders such as Joseph Stalin, Benito Mussolini, and Adolf Hitler. It also summarizes important events and battles of World War II, including the Munich Conference, the Battle of Stalingrad, Operation Torch, the Manhattan Project which developed the atomic bomb, and the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki that led to Japan's surrender, bringing the war to an end.