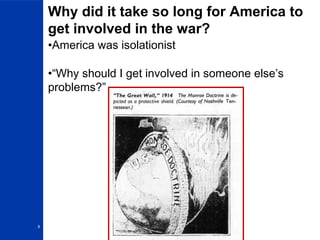
The First World War began in 1914 and lasted until 1918. It involved many of the world's major powers aligned in two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Central Powers. The US initially remained neutral, but was drawn into the war in 1917 by Germany's unrestricted submarine warfare and the Zimmerman Telegram. After four years of costly trench warfare that saw new technologies increase casualties, Germany and its allies surrendered in November 1918. The Treaty of Versailles formally ended the war the following year.