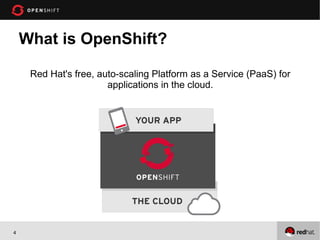
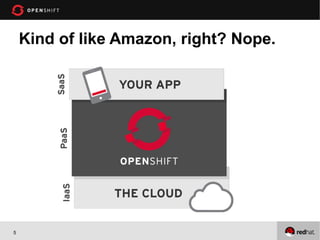
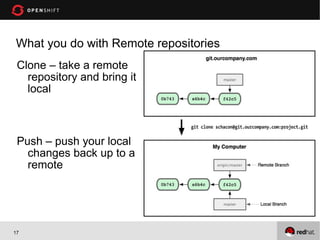
This document provides an agenda and overview for an OpenShift workshop on Python development. The workshop will introduce OpenShift and demonstrate how to create Python applications using the OpenShift platform-as-a-service. Attendees will learn to create applications from the command line and web console, add databases like MongoDB, and use tools like Git for version control. The document outlines assumptions about attendees' experience and what will be covered, including supported technologies, available resources, and terminology for the workshop.