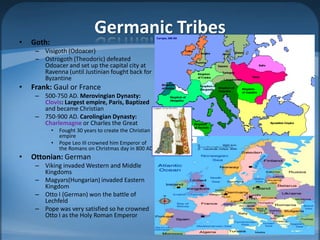
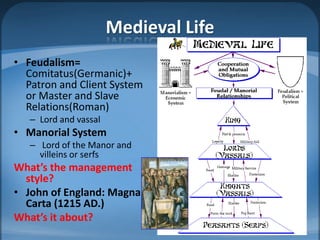
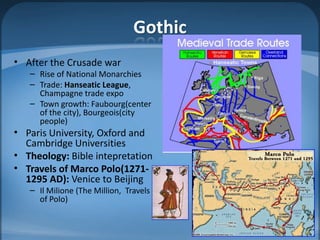
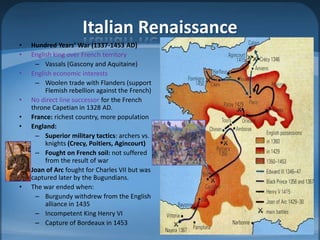
The document outlines the agenda for a class on the European Middle Ages, including assigning group projects comparing topics of religion, music, art or literature from the period, a lecture on Western Europe in the Middle Ages, and an exam on January 25th with late homework penalties. It also provides background information on the development of Europe during the Middle Ages from the influence of Greek/Roman classics and Germanic tribes to the rise of feudalism and developments in religion, knowledge, and art.