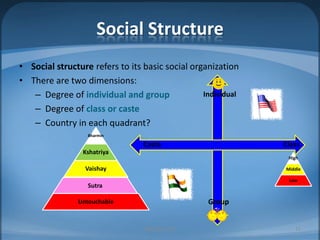
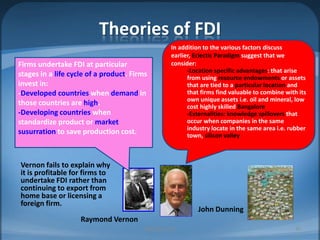
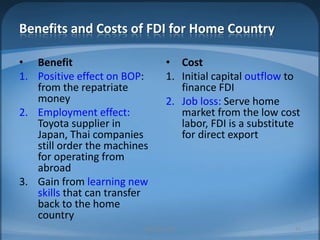
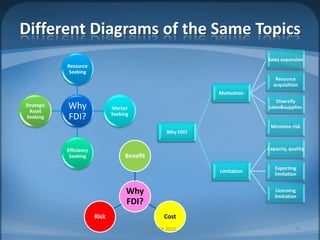
The document provides an agenda for Week 2 that includes several discussion topics: hot topics, news, Facebook, companion websites, a student survey, and readings on India vs. China, nonverbal communication, and foreign direct investment (FDI). Activities include analyzing factors that make countries attractive for FDI, comparing India and China, acting out nonverbal cues, and a group homework assignment to evaluate the best country for a business based on weighted criteria.