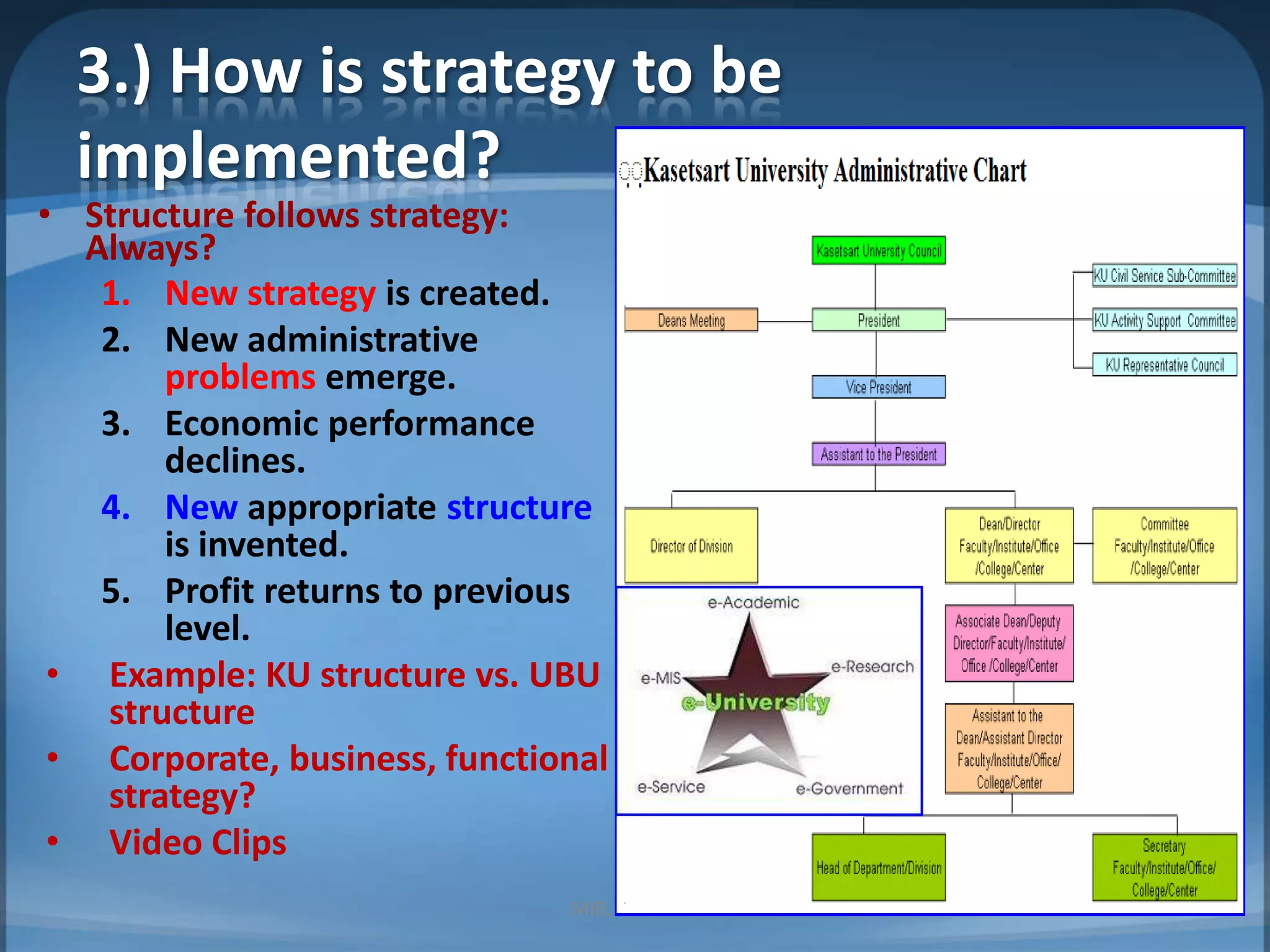
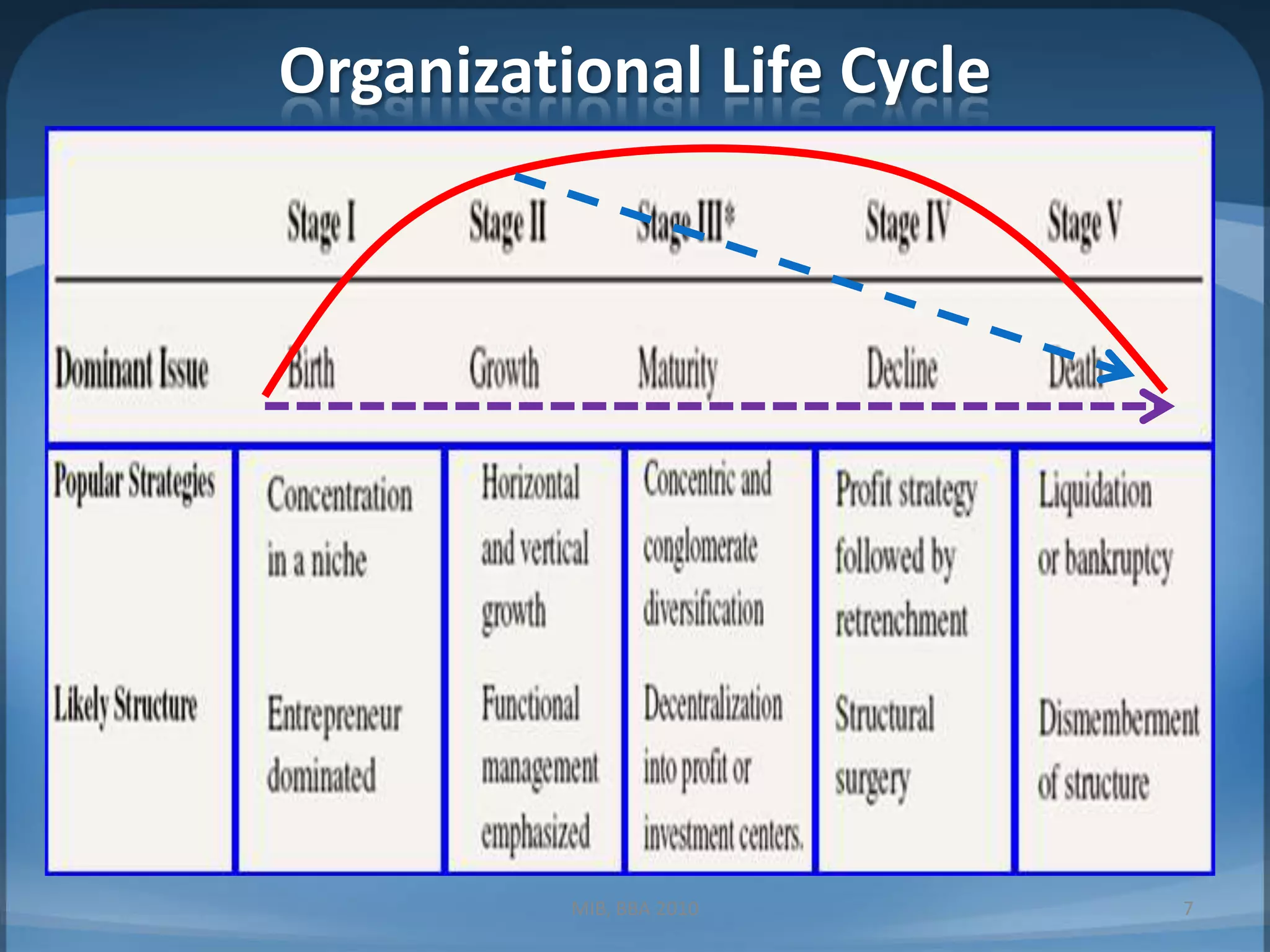
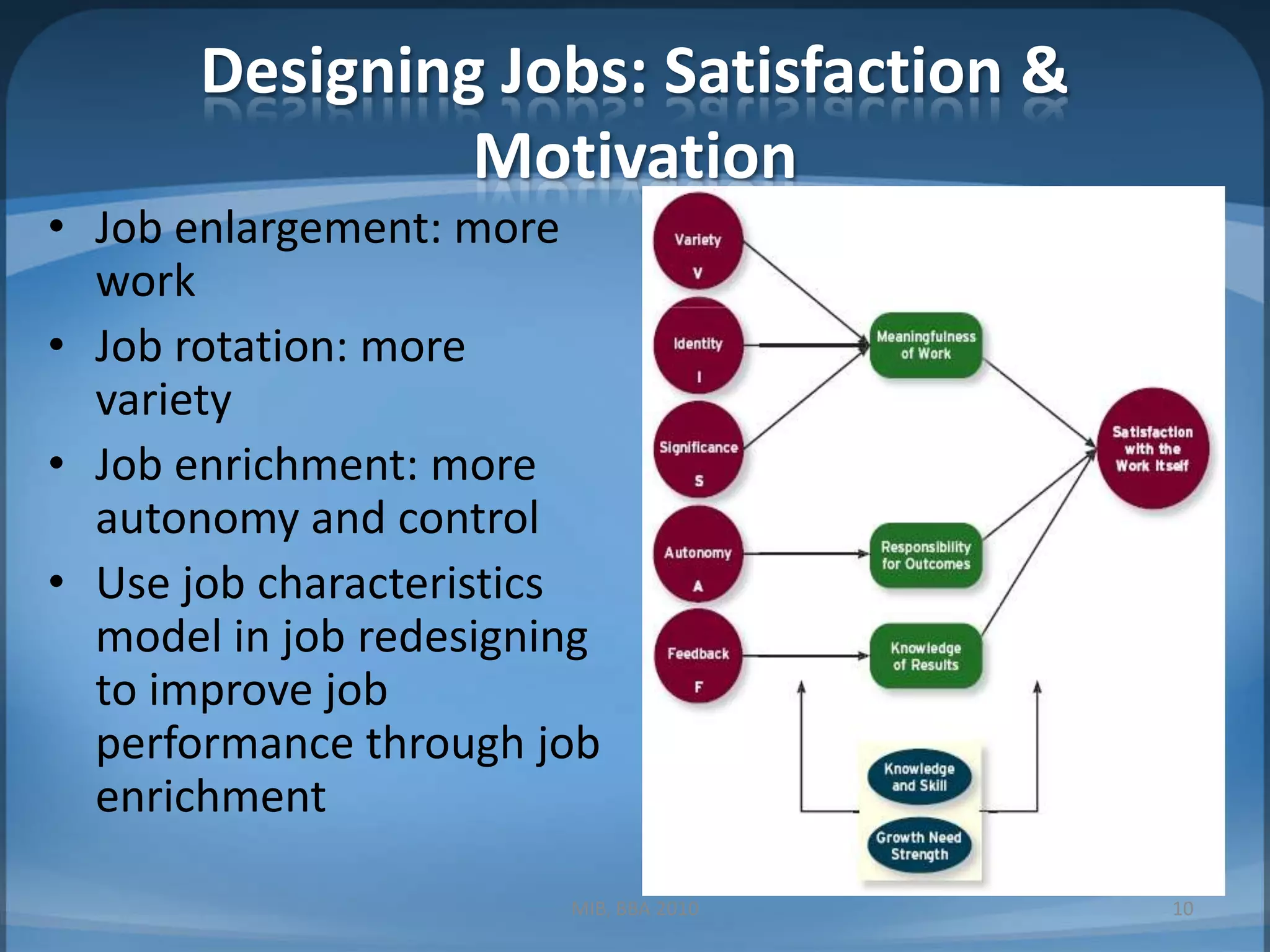
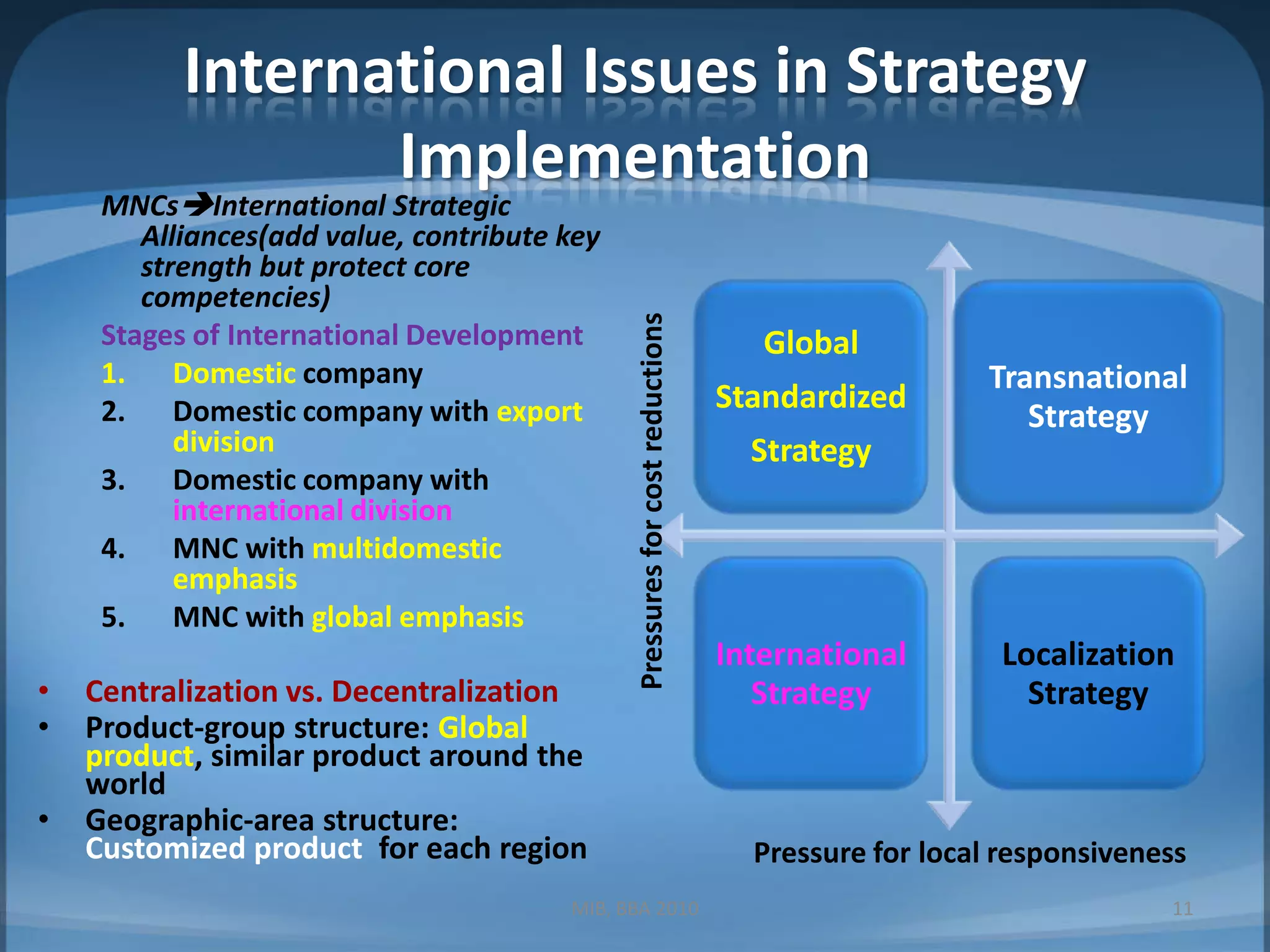
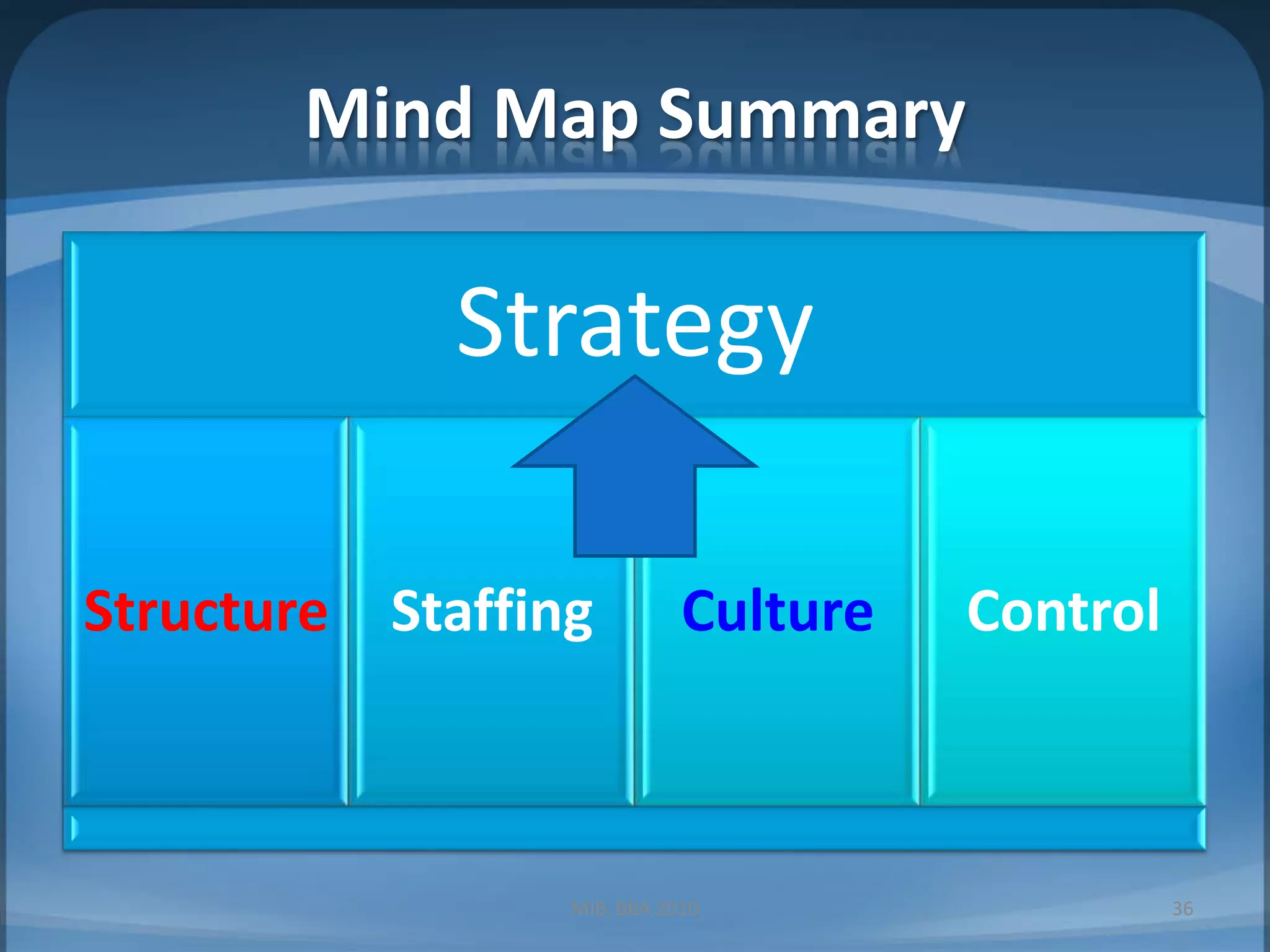
This document contains summaries of topics related to strategy implementation and evaluation including:
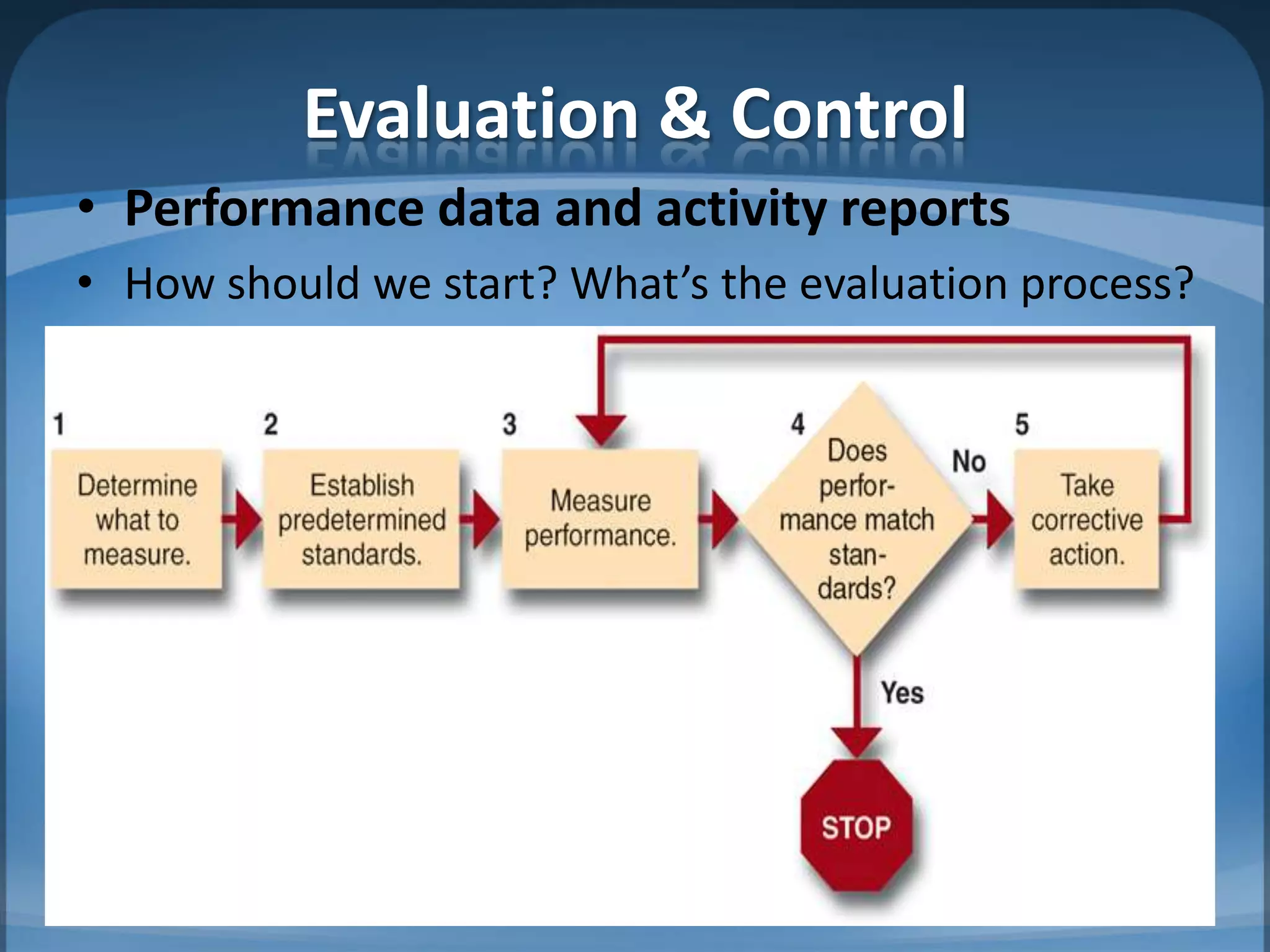
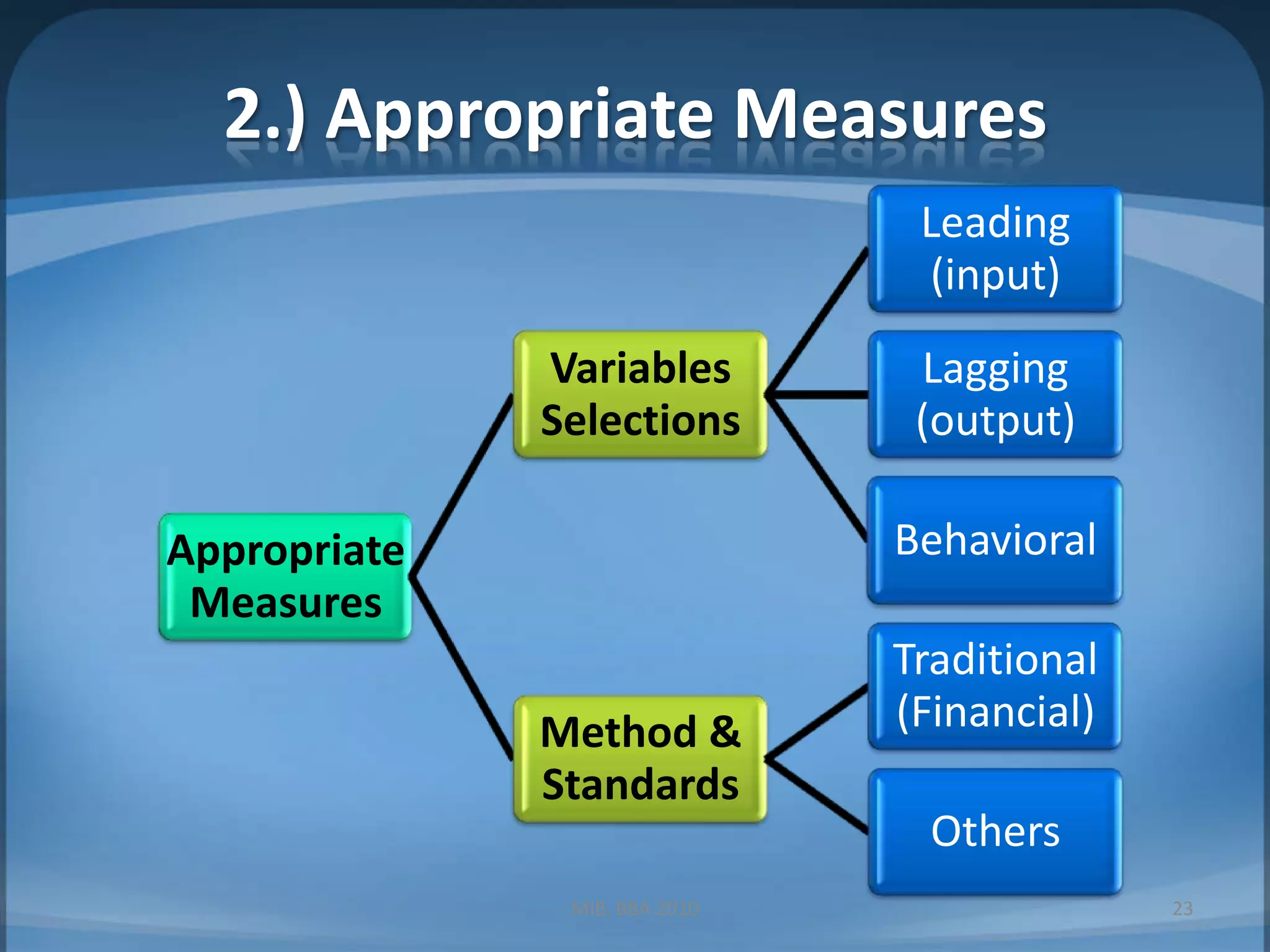
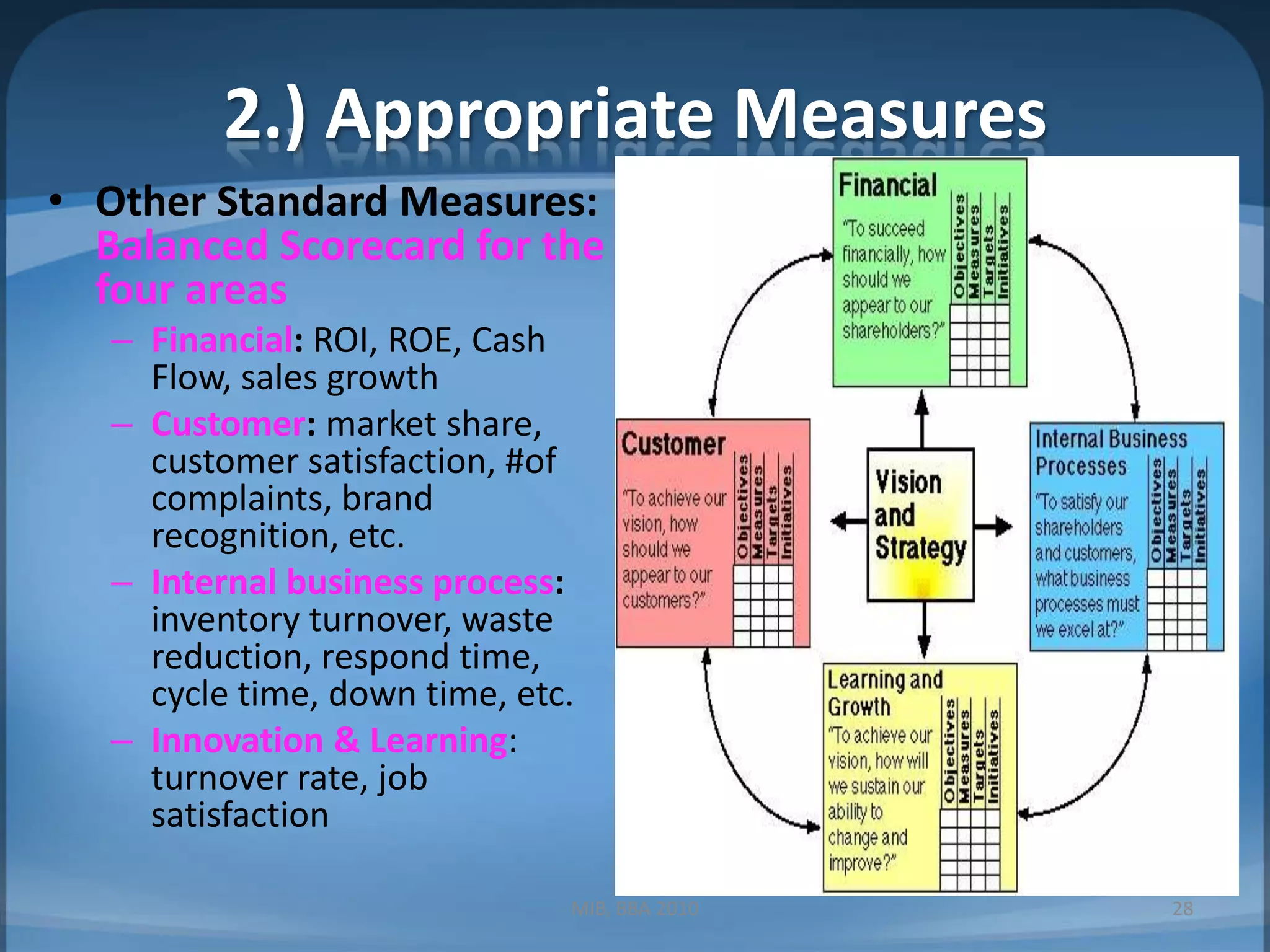
1. Measuring performance through appropriate financial and non-financial metrics at the corporate, business unit, and functional levels. Key metrics mentioned include ROI, EPS, balanced scorecard.
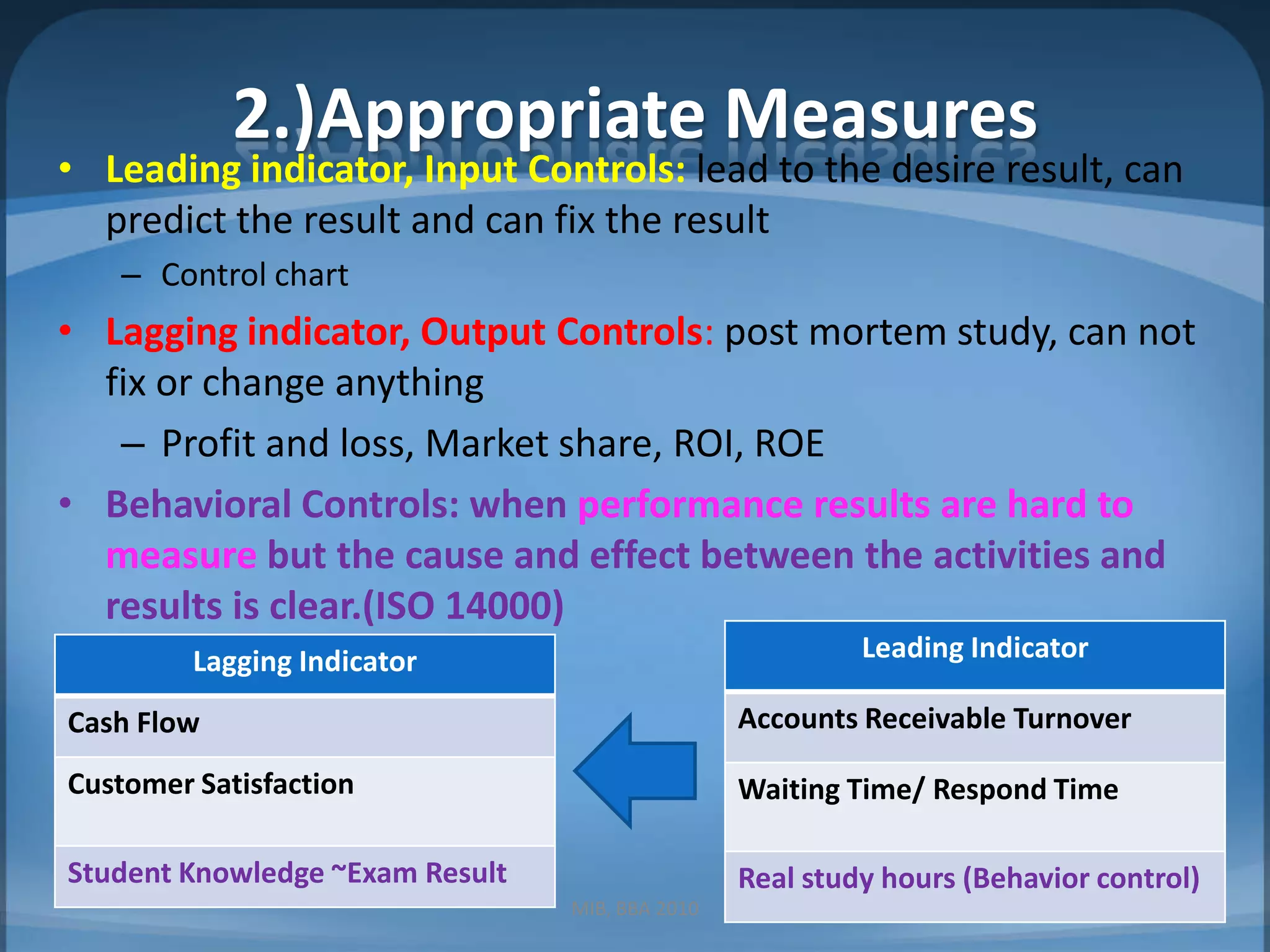
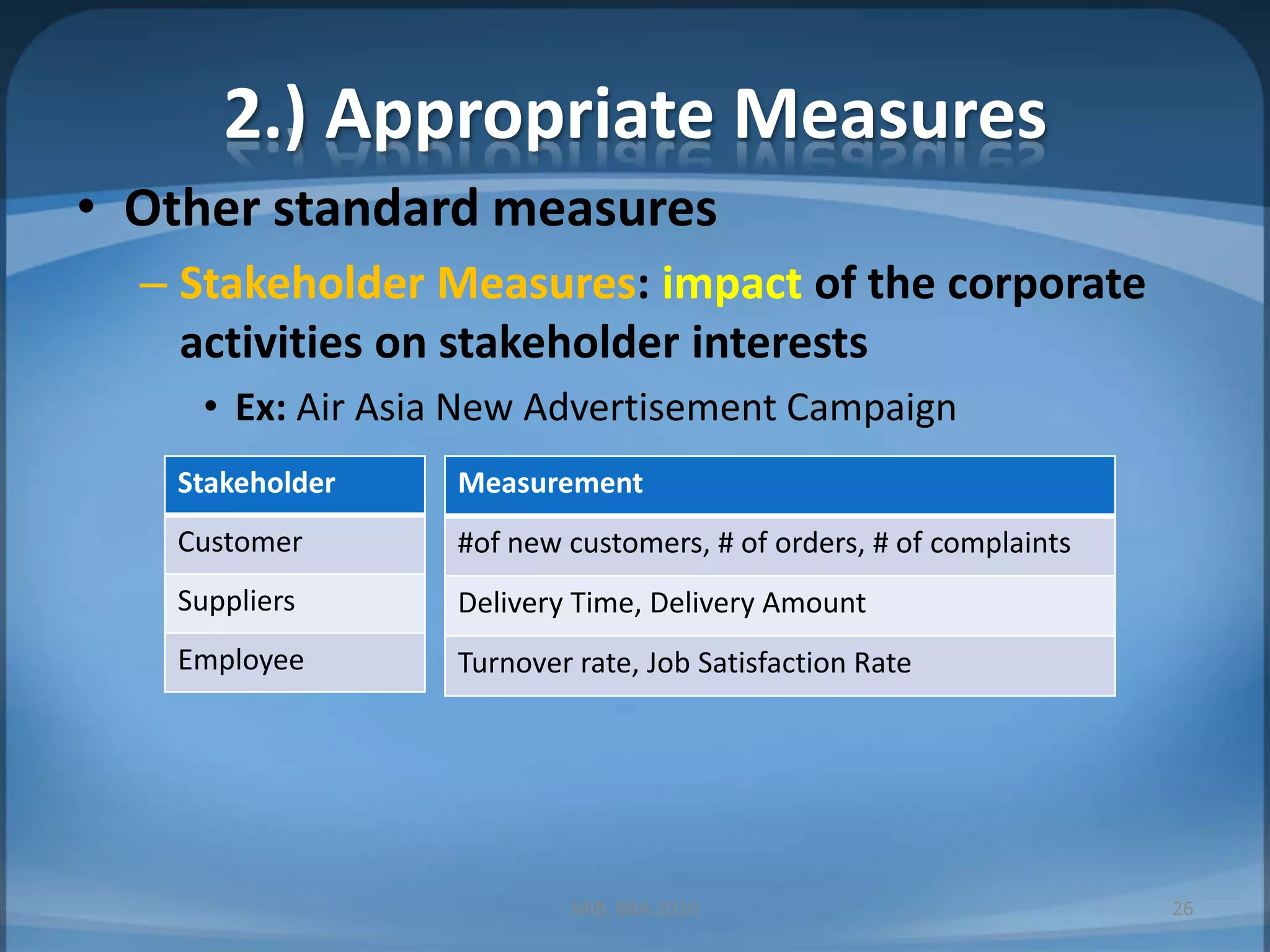
2. Guidelines for effective controls including monitoring a limited number of leading indicators, ensuring measures are timely and focus on exceptions.
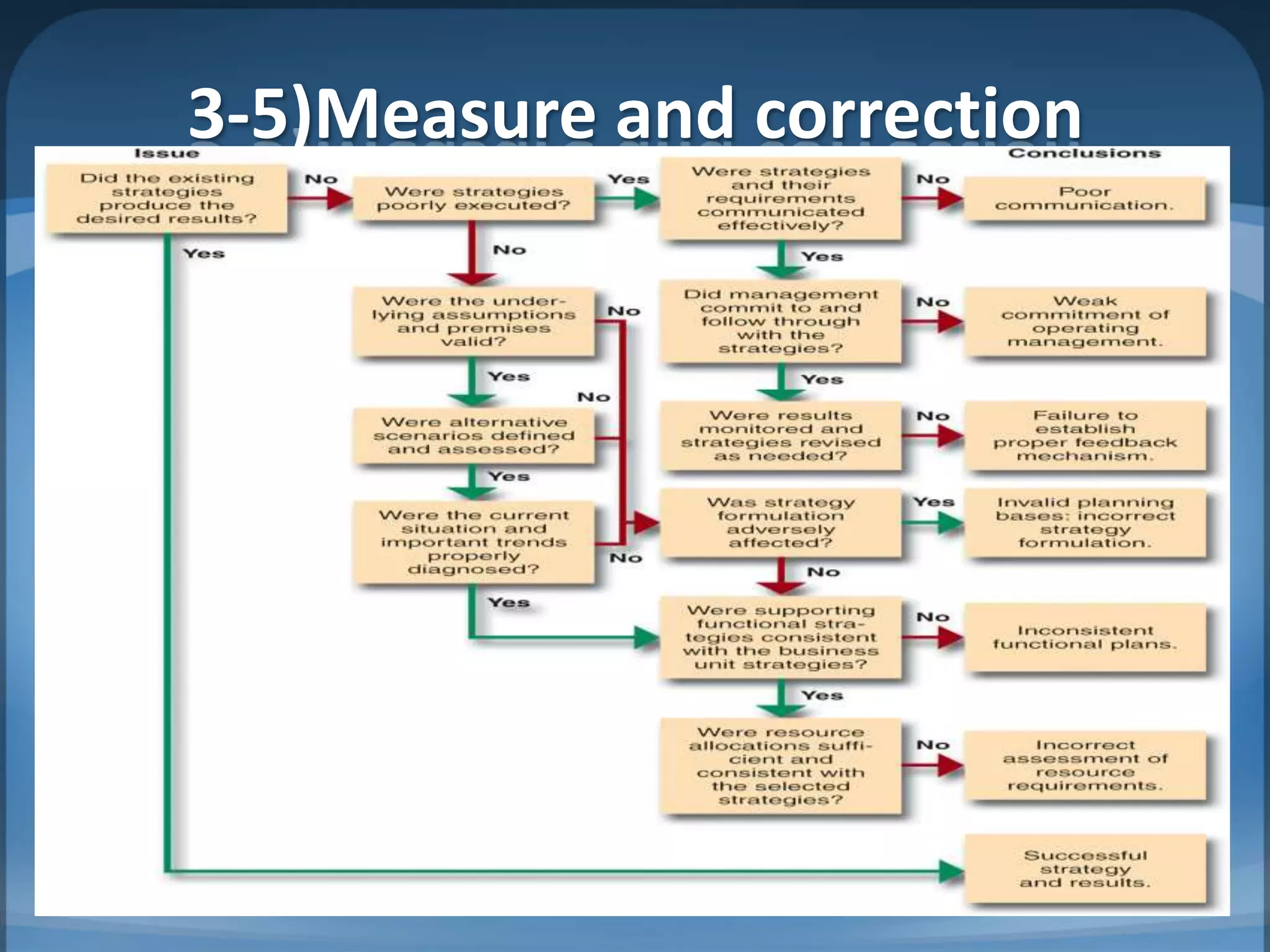
3. Issues with performance measurement including negative side effects of short-term thinking and goal displacement, as well as problems measuring intangibles.