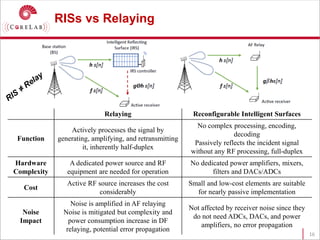
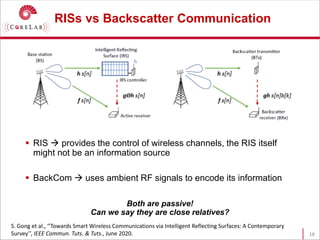
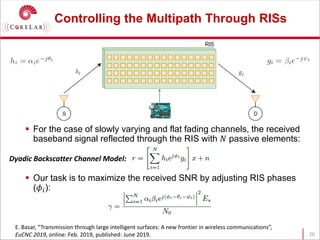
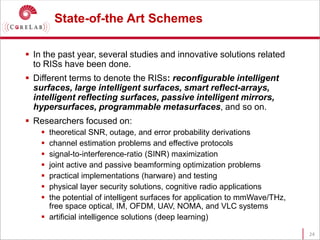
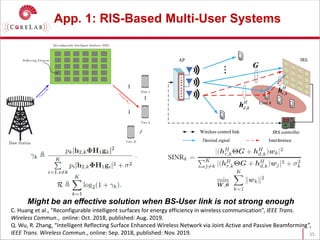
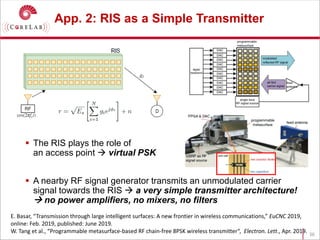
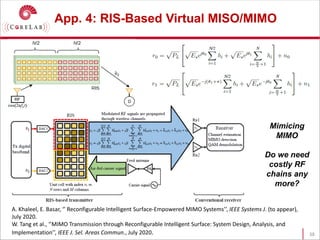
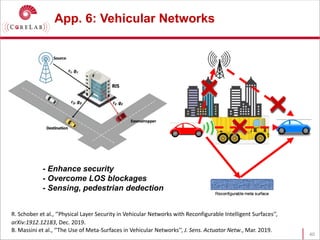
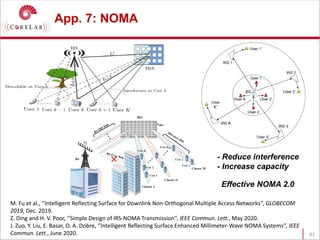
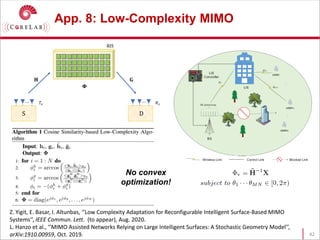
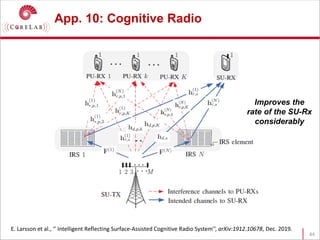
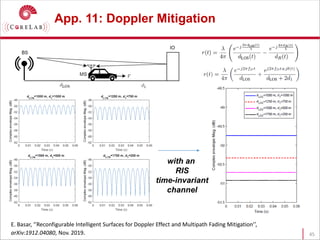
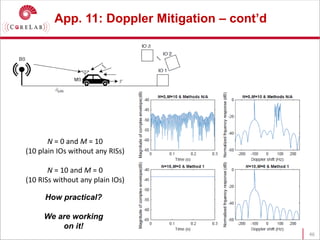
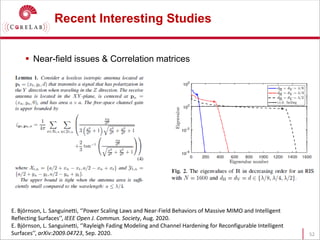
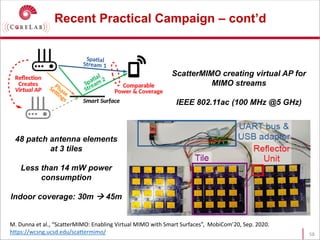
This document discusses reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) and their potential applications in future wireless networks beyond 5G. It provides an overview of RISs, which are programmable metasurfaces that can control the propagation environment by adjusting the phase of reflected signals. The document summarizes recent research on modeling RIS-assisted channels and developing systems that optimize transmission through RISs. It also describes simulation tools developed to model RIS channels and evaluate the performance of RIS-based techniques.