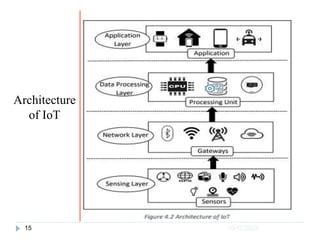
The document discusses Internet of Things (IoT), including definitions, history, how it works, architecture, and applications. It provides definitions of IoT from several groups and dictionaries. The history of IoT is traced back to the early 1800s with the development of telegraphs, and it discusses milestones in the 1980s and 1990s that led to the term "Internet of Things" being coined in 1999. The architecture of IoT devices is explained as having sensing, network, data processing, and application layers. Finally, examples of application areas like smart homes and healthcare are mentioned.