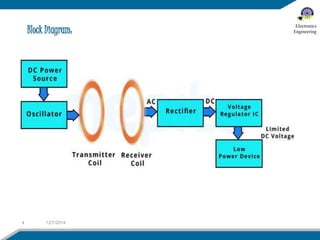
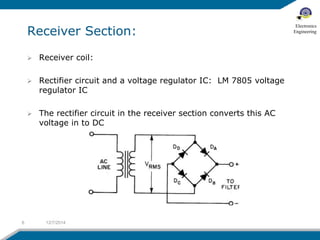
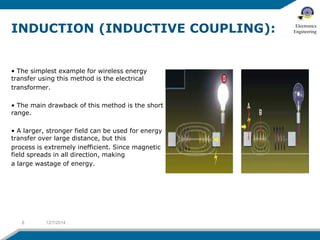
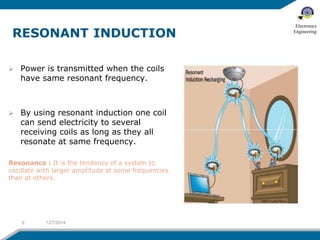
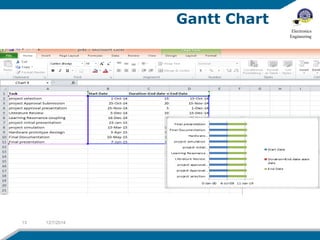
The document discusses wireless electricity transfer, also known as witricity, which utilizes coupled resonators for energy transmission without wires. It covers components like transmitter and receiver circuits, methods of wireless power transmission, and the advantages and challenges of adopting this technology. The summary highlights potential applications such as powering homes without grids and the drawbacks related to efficiency and biological concerns.