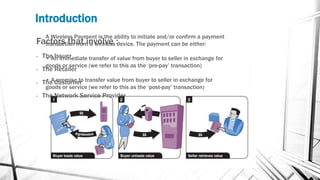
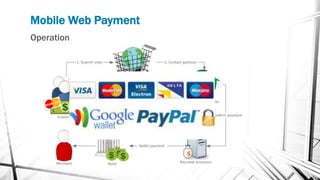
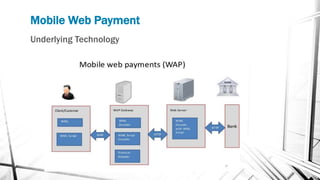
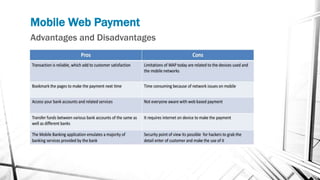
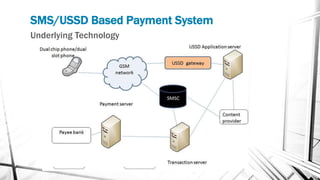
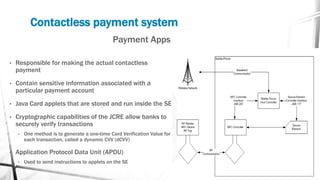
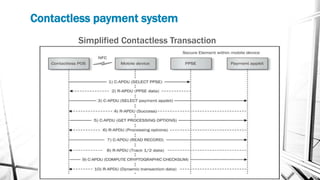
This document discusses various wireless payment systems including mobile web payments, SMS/USSD payments, and contactless payments using near-field communication (NFC). It describes the underlying technologies such as secure elements and Java Card applets. It also covers practical issues regarding compatibility, costs, security challenges and opportunities for businesses. Contactless payments are presented as facilitating fast transactions under £20 through credit cards, phones, watches and other devices equipped with NFC in the future.