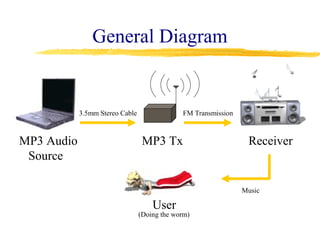
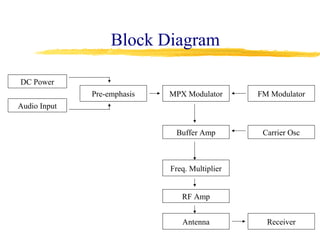
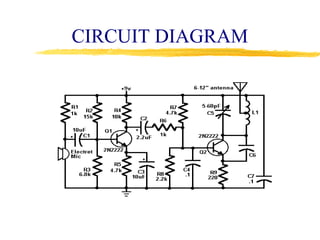
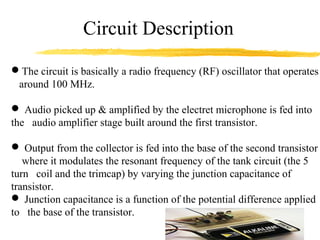
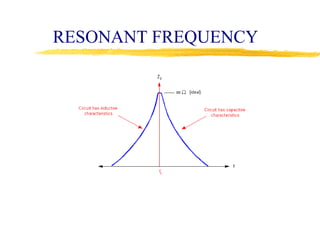
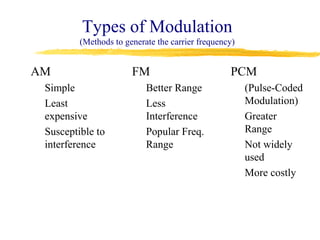
This document describes the design and operation of a simple wireless FM microphone transmitter. The transmitter uses an electret microphone, two transistors, and a tuned coil to modulate an FM carrier signal between 87-108 MHz. The audio signal from the microphone is amplified and used to vary the resonant frequency of the tuned coil, transmitting the audio over FM radio frequencies. The transmitted signal can be received on any standard FM radio within a range of over 300 meters. The wireless microphone allows for freedom of movement and avoids issues with cables. Potential applications include entertainment, broadcasting, and public speaking.