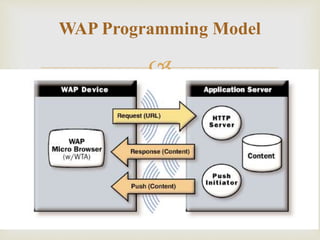
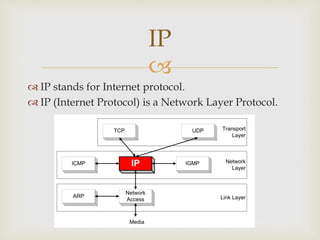
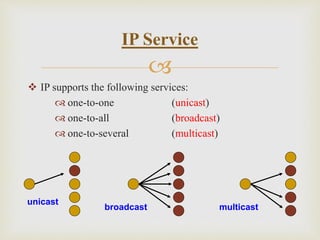
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) is a technical standard that enables mobile devices to access information over wireless networks, compatible with various operating systems. It allows for efficient service delivery to mobile users but has limitations such as small screens and speed issues. In contrast, Internet Protocol (IP) supports broader networking capabilities and is primarily used for fixed internet connections, while WAP offers more flexible access from any location.