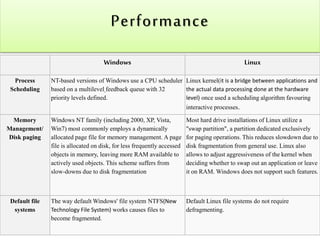
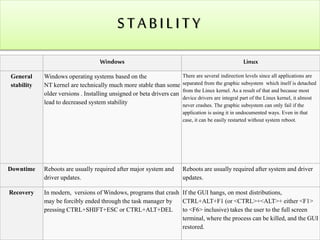
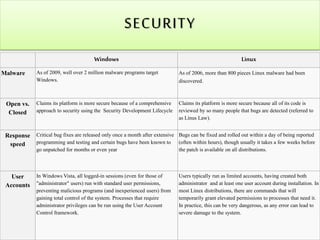
The document compares the Windows and Linux operating systems across several categories such as performance, stability, and security. Windows has traditionally dominated the personal desktop market while Linux is most prominent as a free operating system. Both systems now extend beyond personal computers and compete in other markets like servers and embedded systems. The document concludes that neither system is truly superior as it depends on the intended use, though Linux is generally better suited for servers and web development due to its security, cost-effectiveness, and open-source benefits.