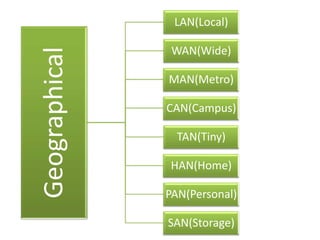
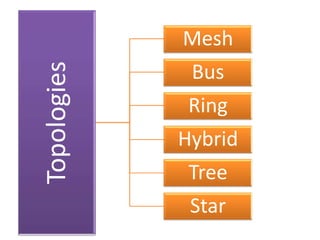
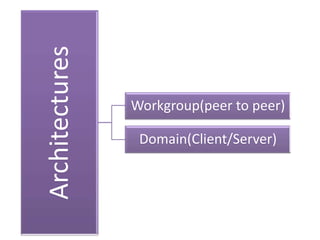
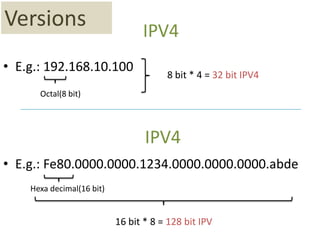
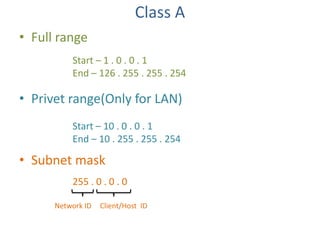
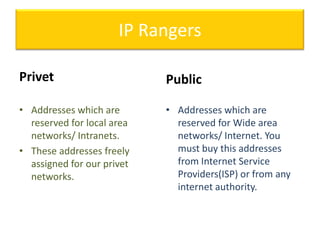
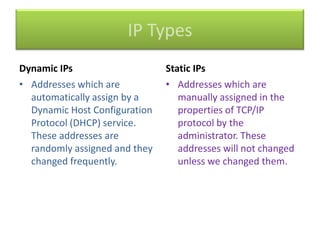
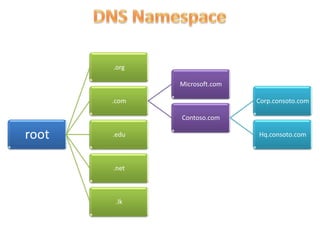
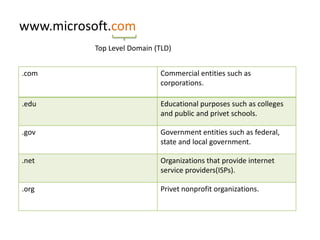
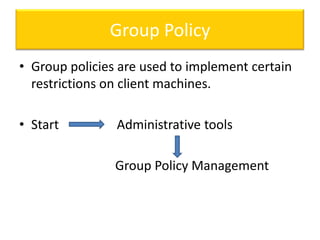
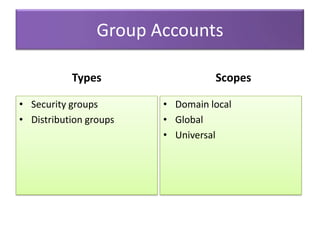
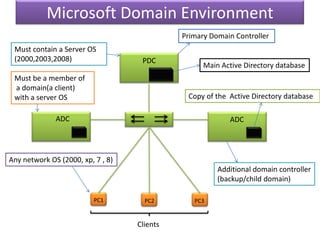
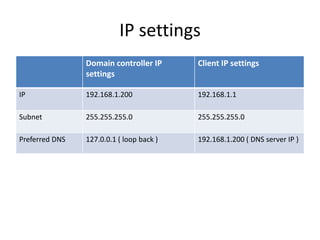
This document contains information about networking concepts including cable types, topologies, network architectures, IP addressing, and Microsoft networking tools. It defines coaxial and twisted pair cables, and lists common network topologies like mesh, bus, ring, star and hybrid. It also explains the differences between a hub and switch, and between a workgroup and domain network architecture. The document provides details on IP addressing standards including public vs private IP ranges, static vs dynamic addressing, and IPv4 and IPv6 versions. It introduces tools like DNS, MMC, Group Policy and IIS that are used to manage Microsoft networks.