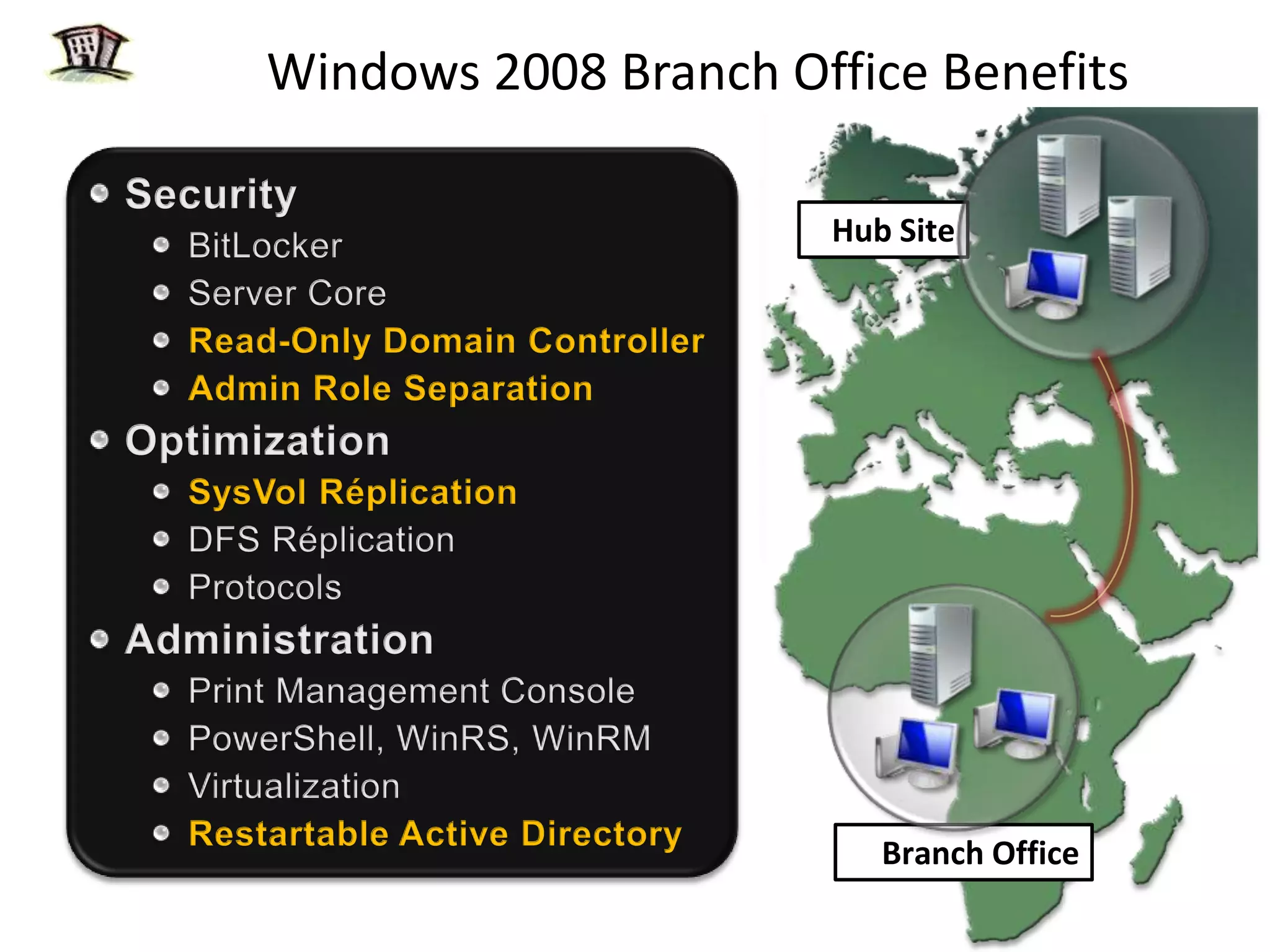
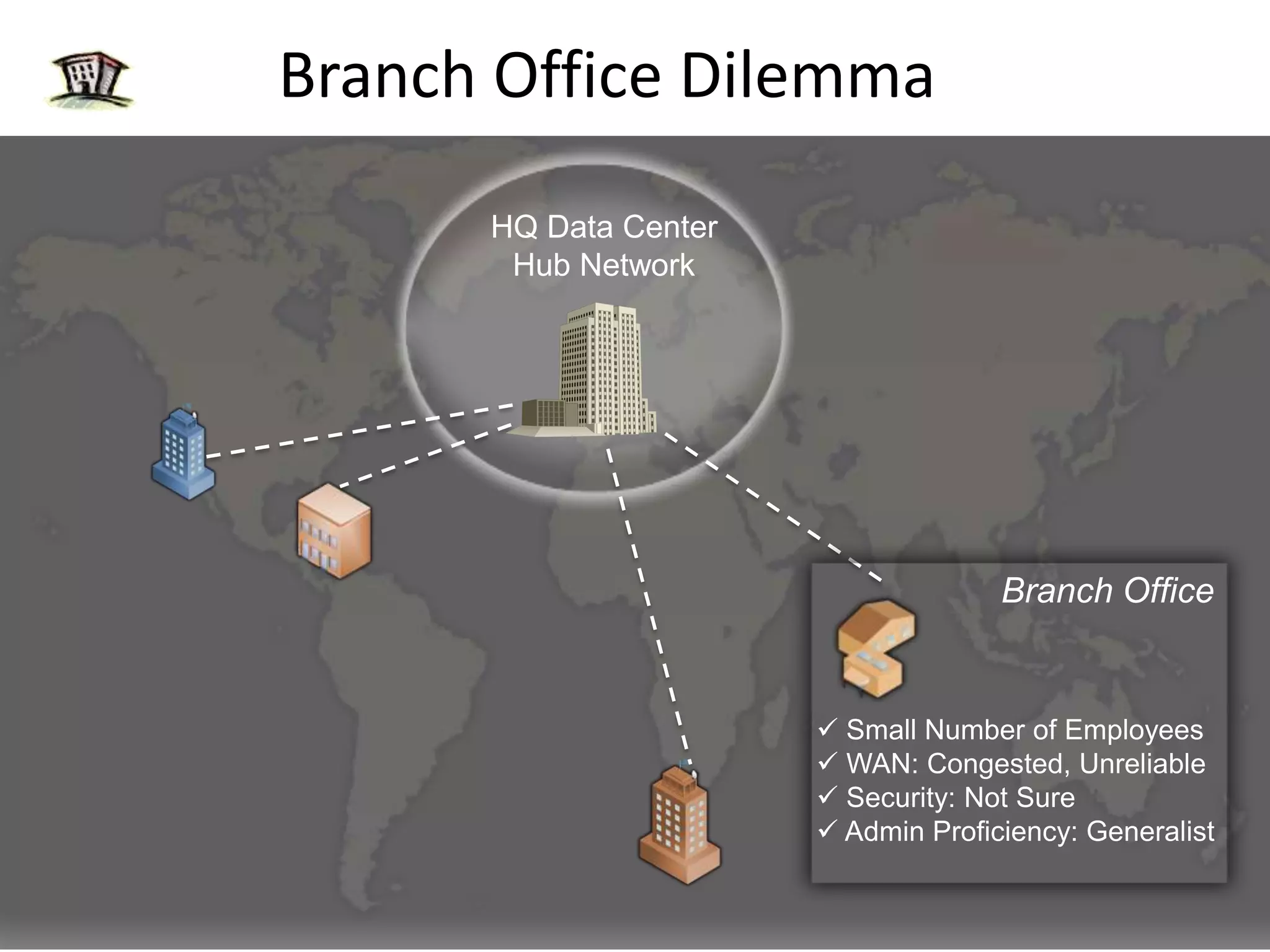
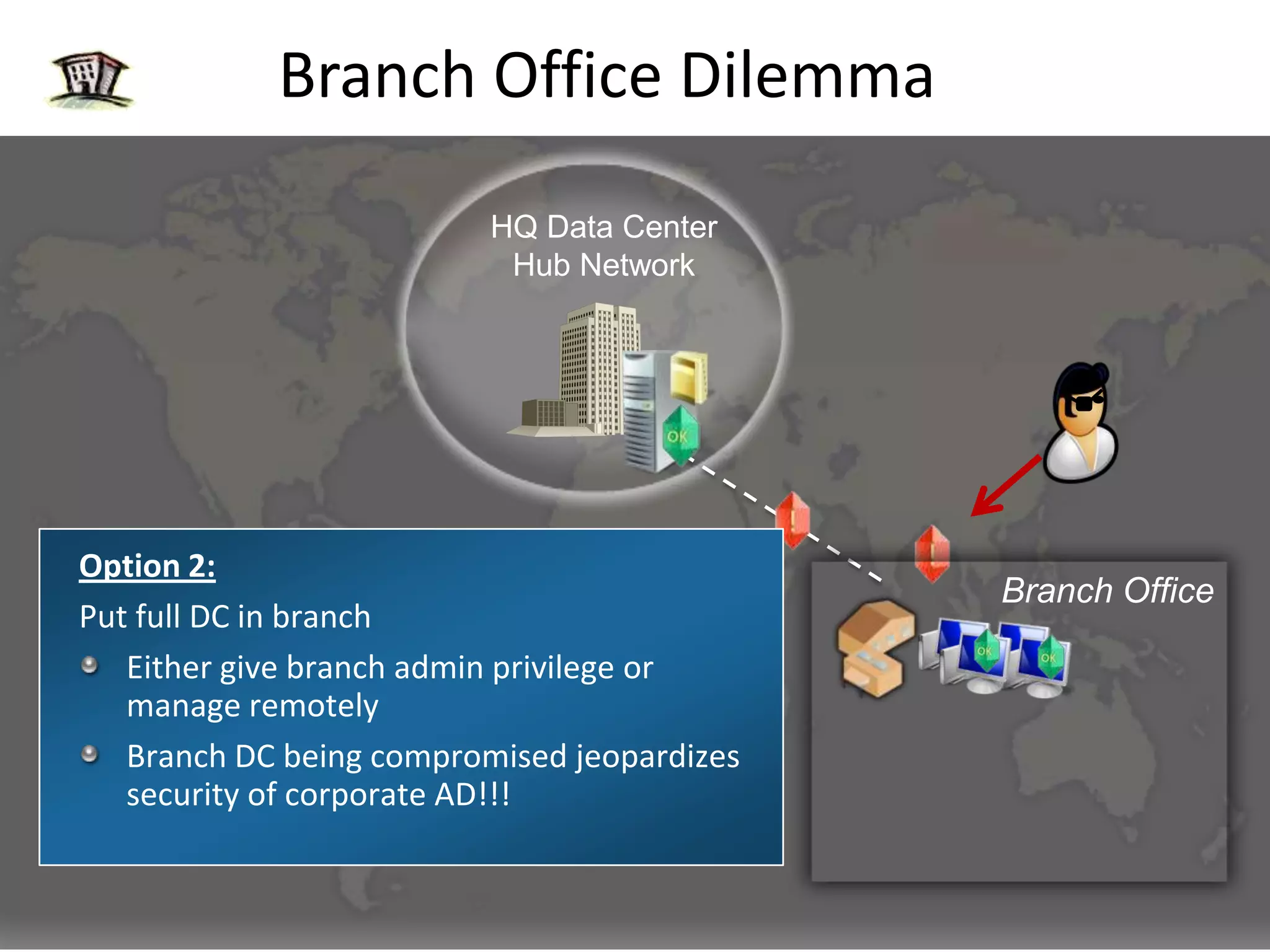
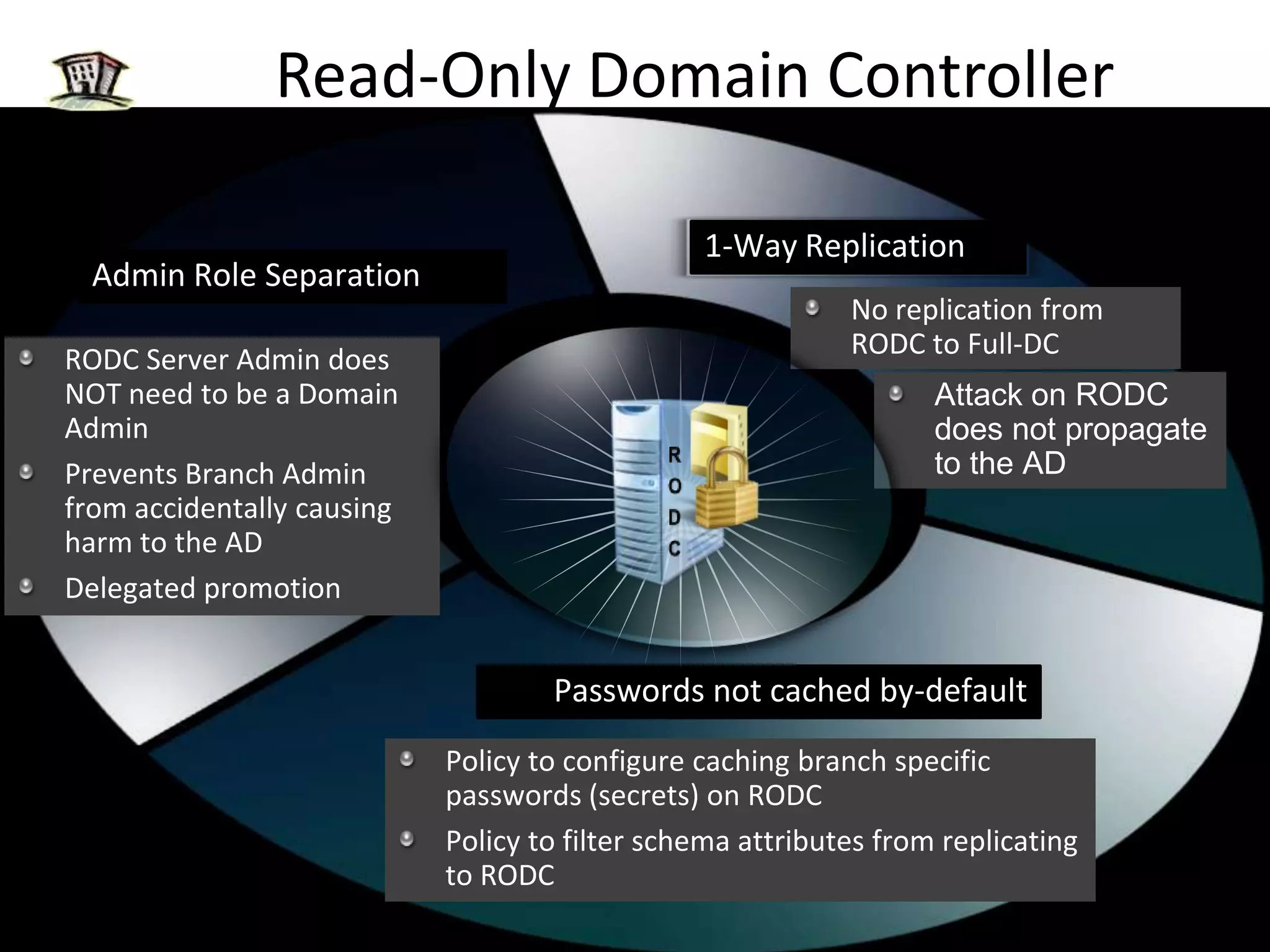
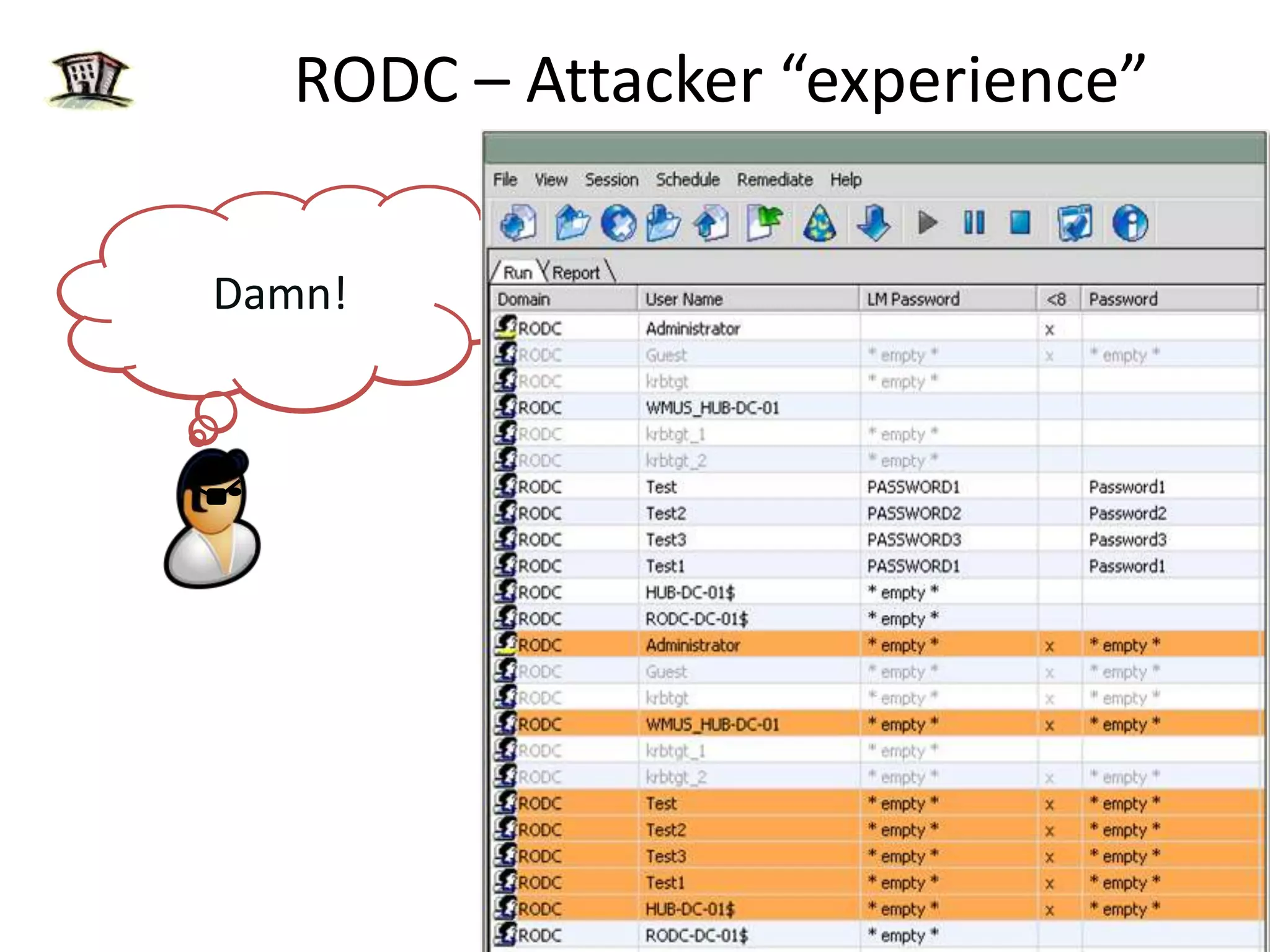
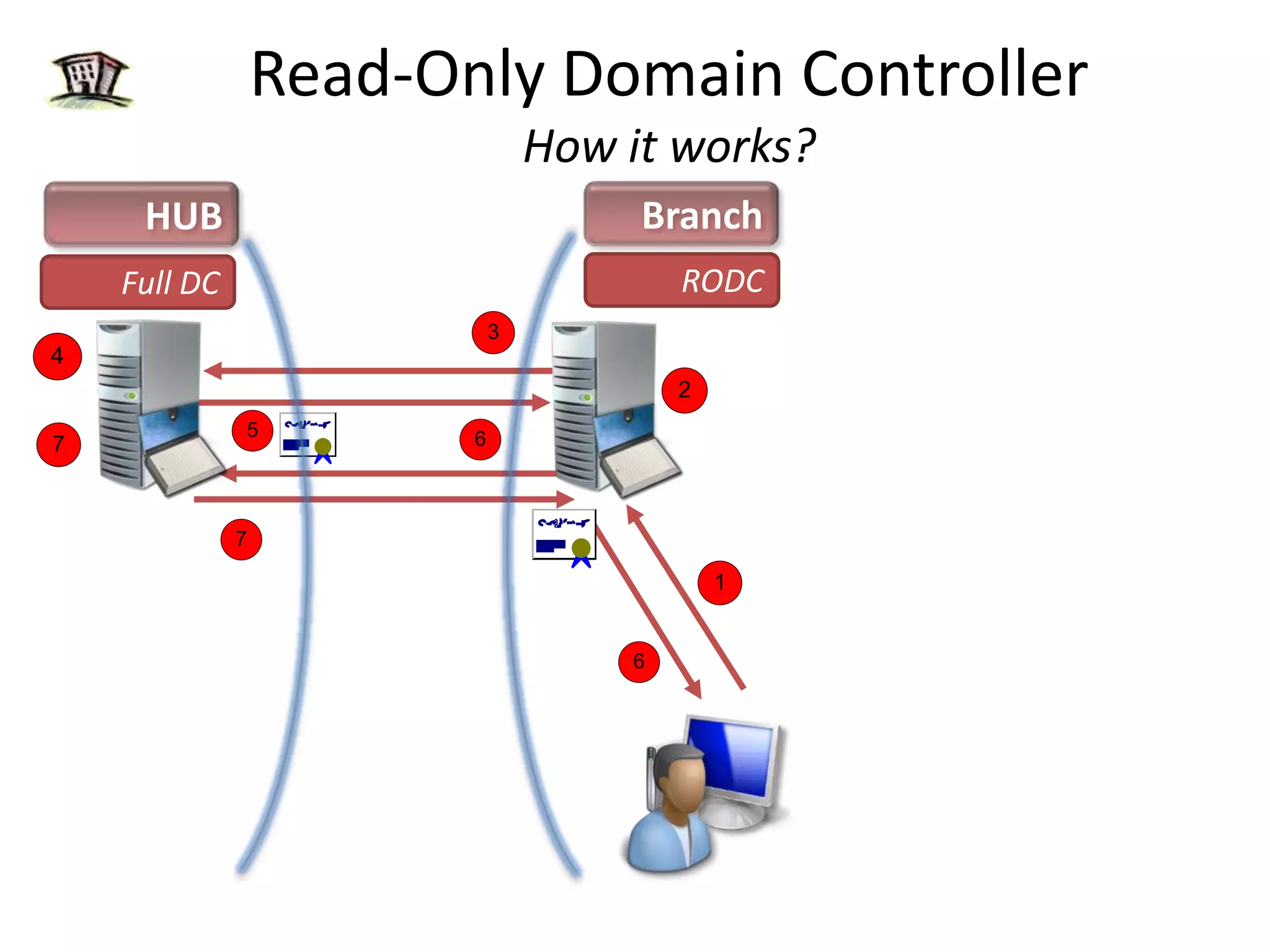
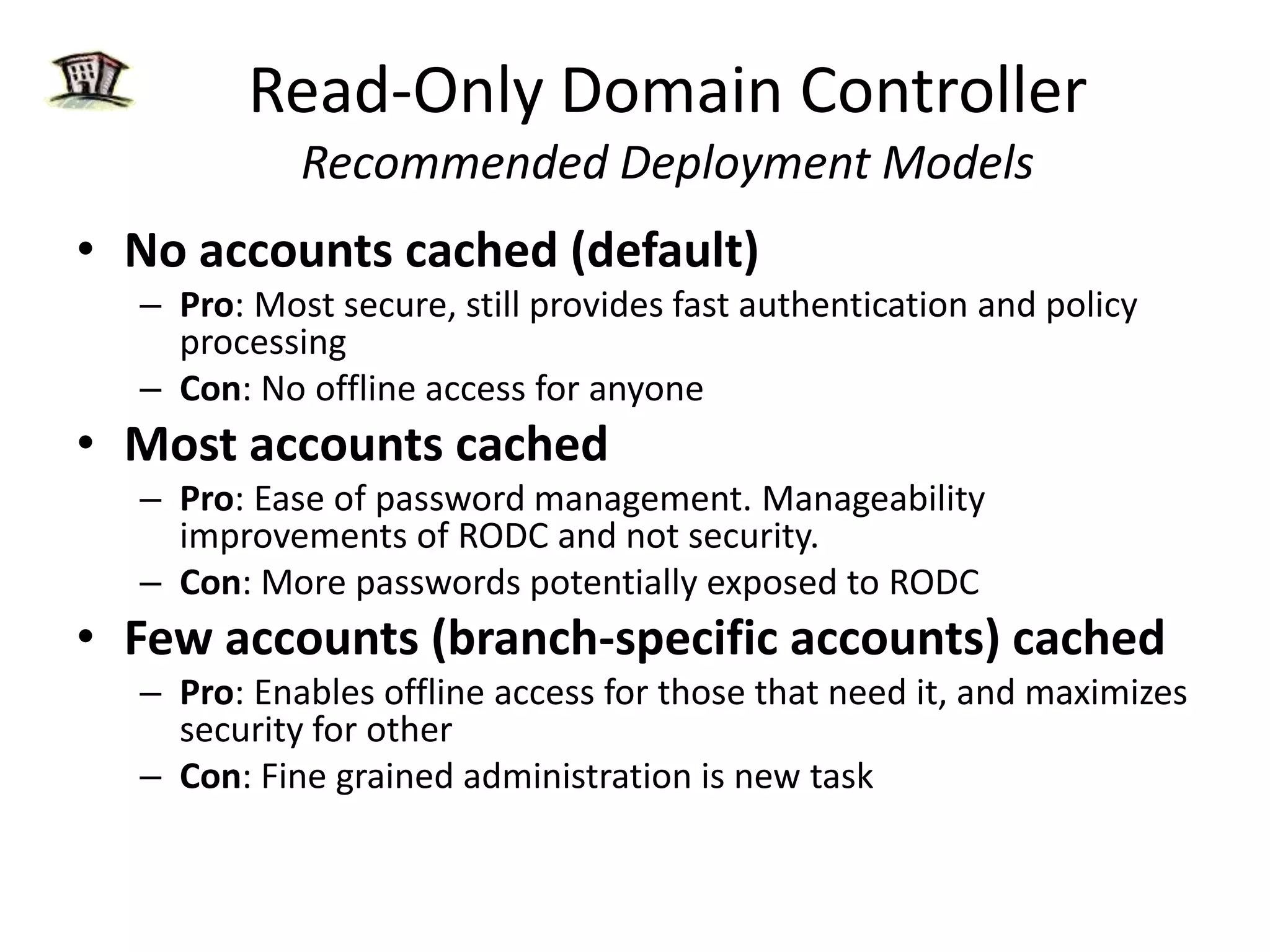
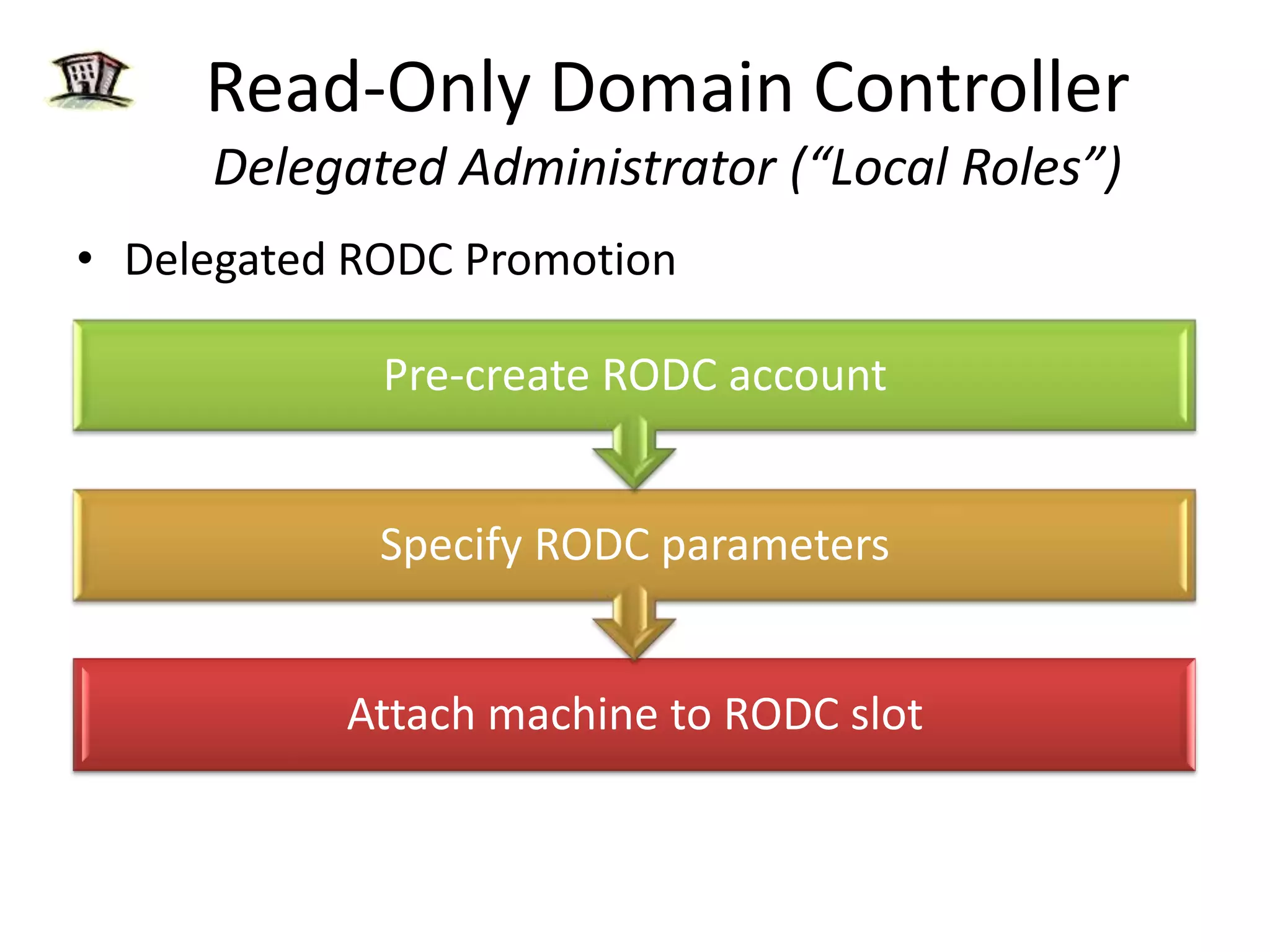
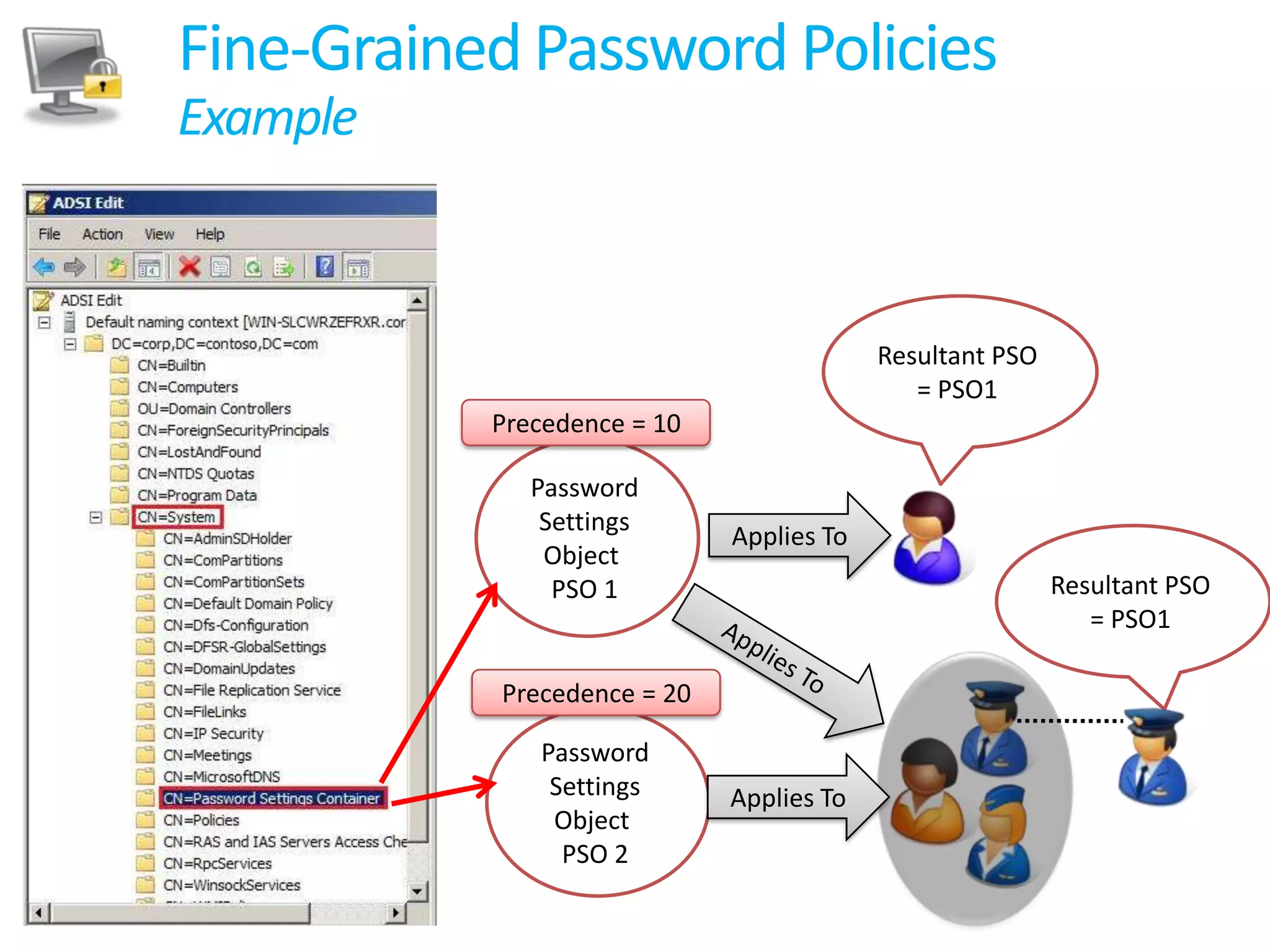
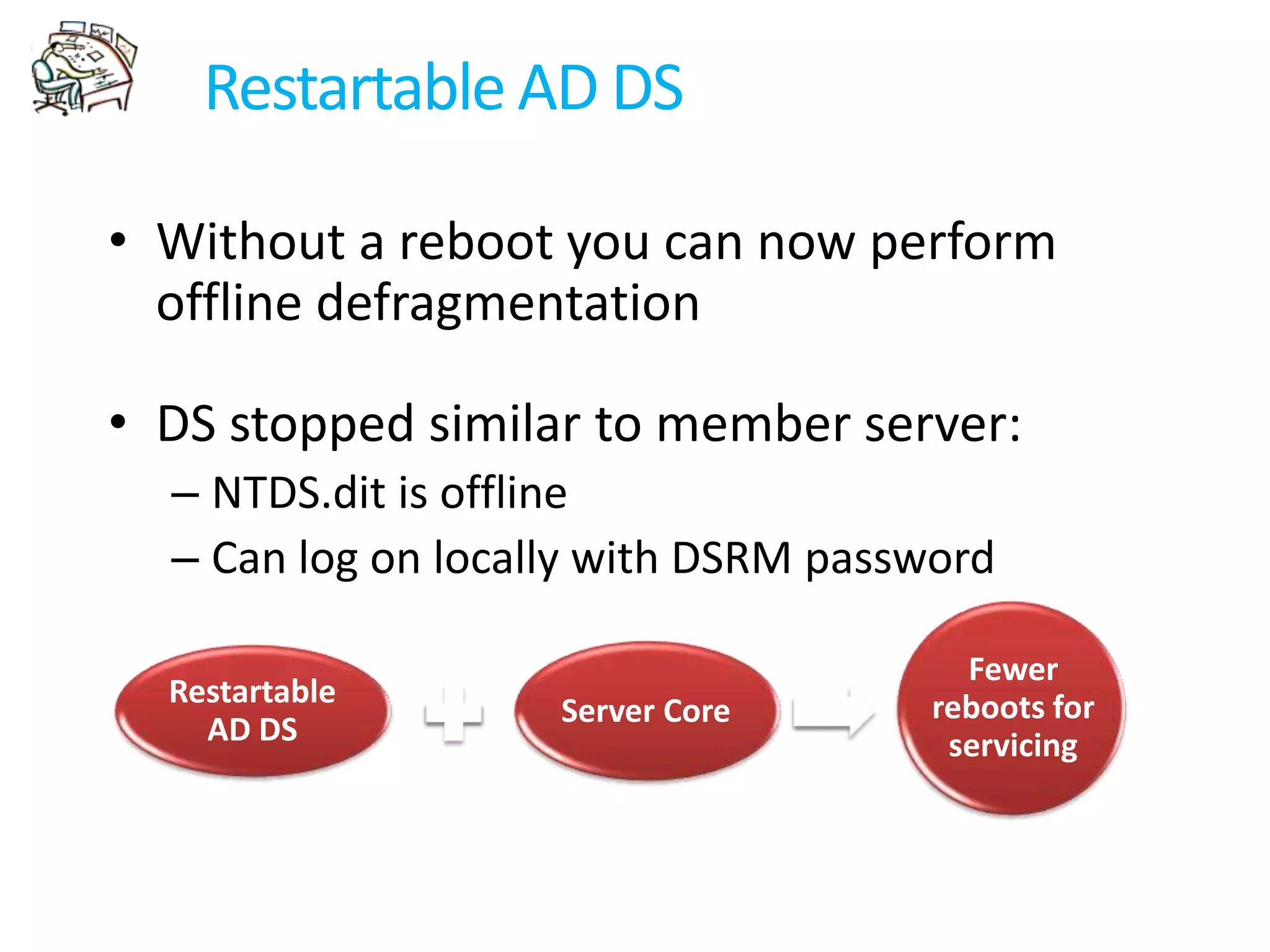
Windows 2008 Active Directory includes several new features to improve management of branch offices and security. It introduces Read-Only Domain Controllers that allow placing a domain controller in a branch office without compromising security if it is compromised. It includes fine-grained password policies that allow customizing password policies for different groups. Enhanced auditing capabilities provide more detailed auditing of directory service changes. Other features like restartable AD DS and DFS-R replication improve manageability.