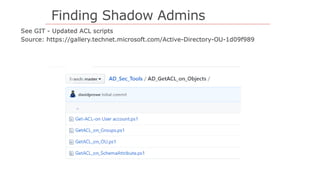
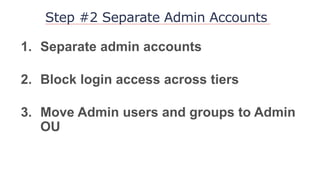
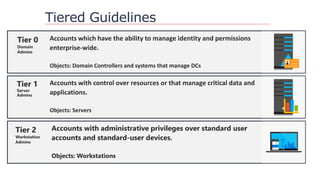
The document outlines strategies to secure Active Directory without financial investment, emphasizing the importance of access control and the risks of privilege creep. It details Microsoft's Enhanced Security Administrative Environment (ESAE) approach through three stages and fourteen steps to mitigate administrative credential compromises. The document also highlights the importance of auditing, alerting, and managing cached credentials to prevent unauthorized access and maintain security integrity.
![Secure Active Directory
in one day without spending
a single dollar
1
David Rowe @customes
david_rowe [@] Harvard.edu
#infosec #nercomp #security
©2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nercomp-2019-adsectools-esae-190604175520/75/Secure-Active-Directory-in-one-Day-Without-Spending-a-Single-Dollar-1-2048.jpg)


















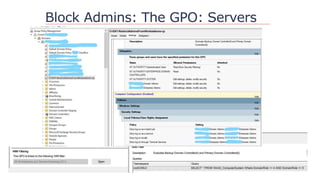

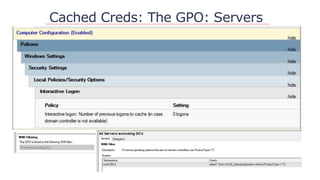
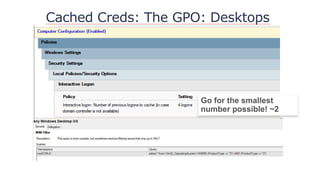
![Cached Creds Defined
Computer level setting:
Interactive logon: Number of previous logons to cache
[store in memory] (in case domain controller is not
available) 1
Value indicates stored users credentials on device – (10)
Default stored as RC4 hash on system](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nercomp-2019-adsectools-esae-190604175520/85/Secure-Active-Directory-in-one-Day-Without-Spending-a-Single-Dollar-26-320.jpg)


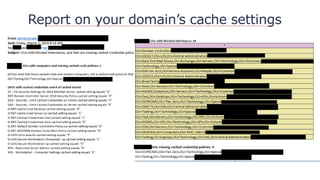


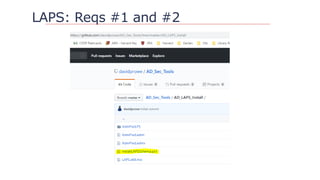
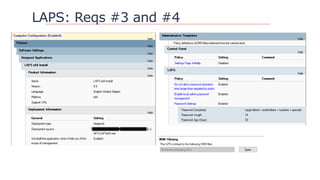

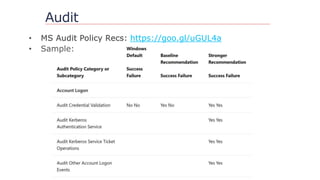




![Questions?
https://github.com/davidprowe/AD_Sec_Tools
@customes
david_rowe [@] Harvard.edu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nercomp-2019-adsectools-esae-190604175520/85/Secure-Active-Directory-in-one-Day-Without-Spending-a-Single-Dollar-43-320.jpg)
