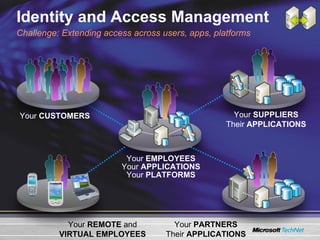
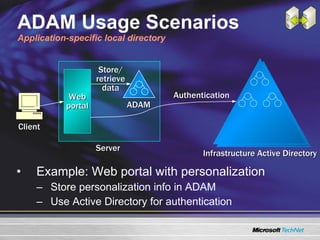
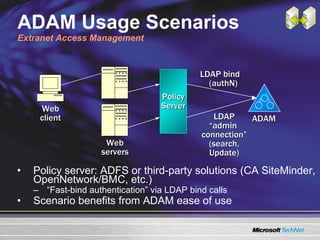
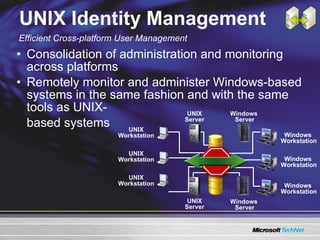
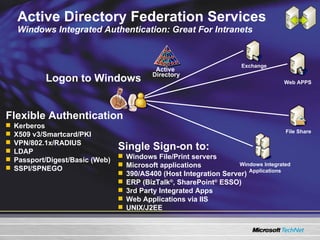
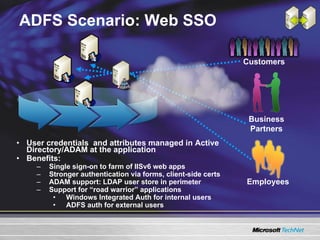
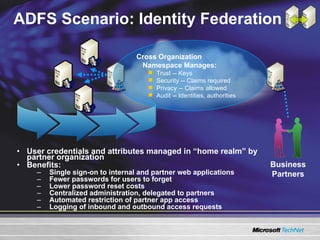
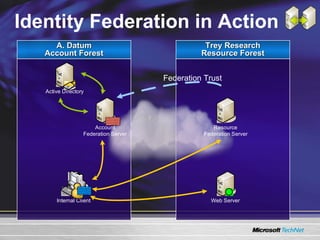
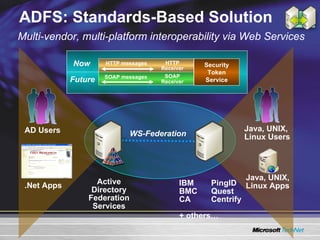
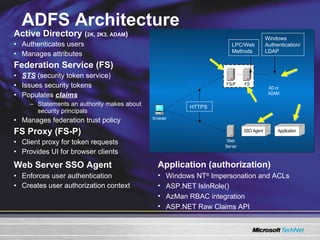
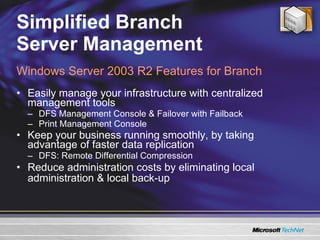
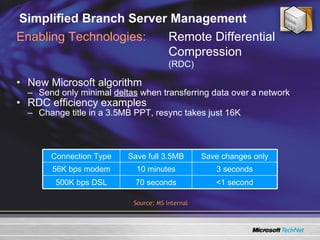
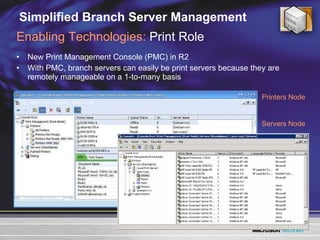
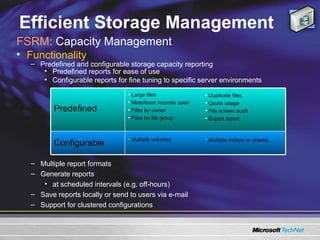
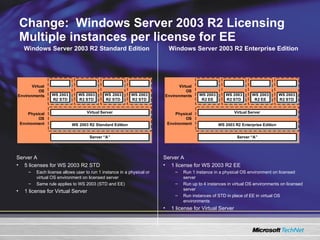
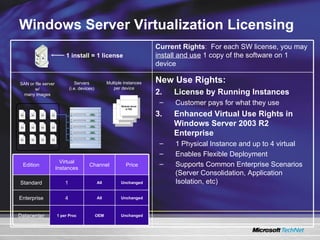
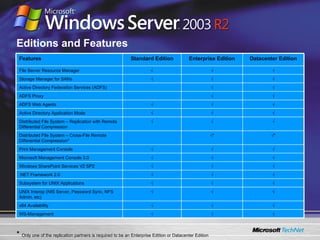
The document discusses features in Windows Server 2003 R2 that help with identity and access management, simplified branch server management, and efficient storage management. It describes capabilities like Active Directory Application Mode, UNIX identity management, Active Directory Federation Services, the security configuration wizard, distributed file system replication, remote differential compression, and the new print management console. These features aim to provide centralized management across platforms, simplify administration of branch offices, and help manage growing storage needs.