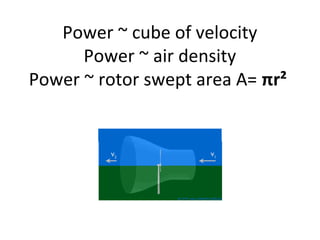
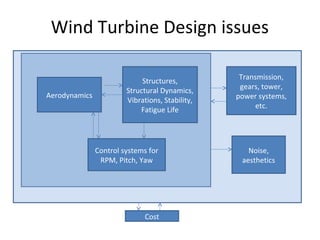
This document provides an overview of wind turbine engineering. It discusses key concepts such as how wind power depends on air volume, velocity, mass, and flux. It explains that turbine power output is a function of air density, wind velocity cubed, and rotor swept area. The Betz limit establishes that the maximum possible power coefficient for a conventional wind turbine is 59% efficiency. The document also outlines the major subsystems of a wind turbine and important design considerations such as aerodynamics, structures, control systems, and costs. Key parameters that must be chosen for a wind turbine design are also summarized.