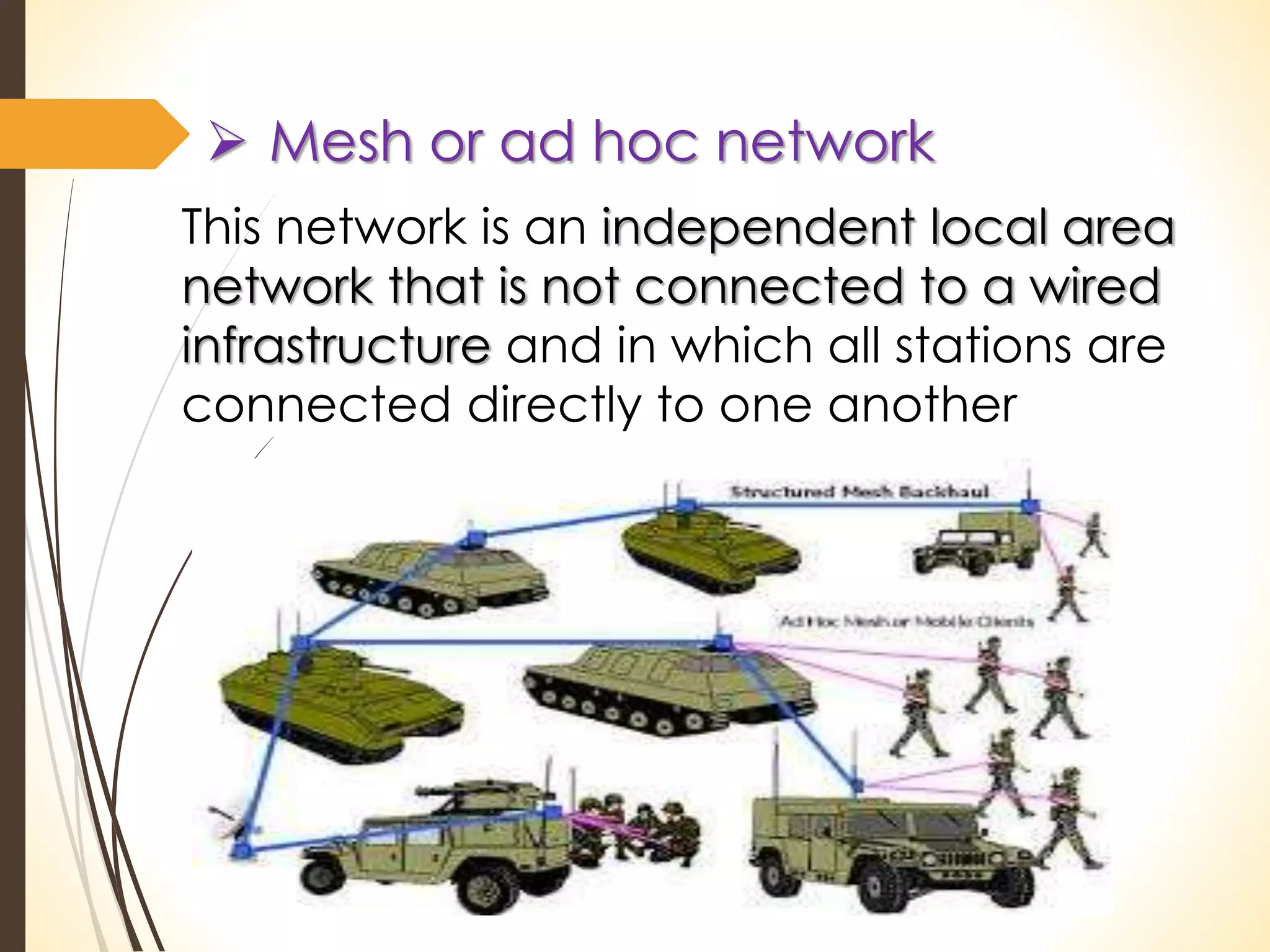
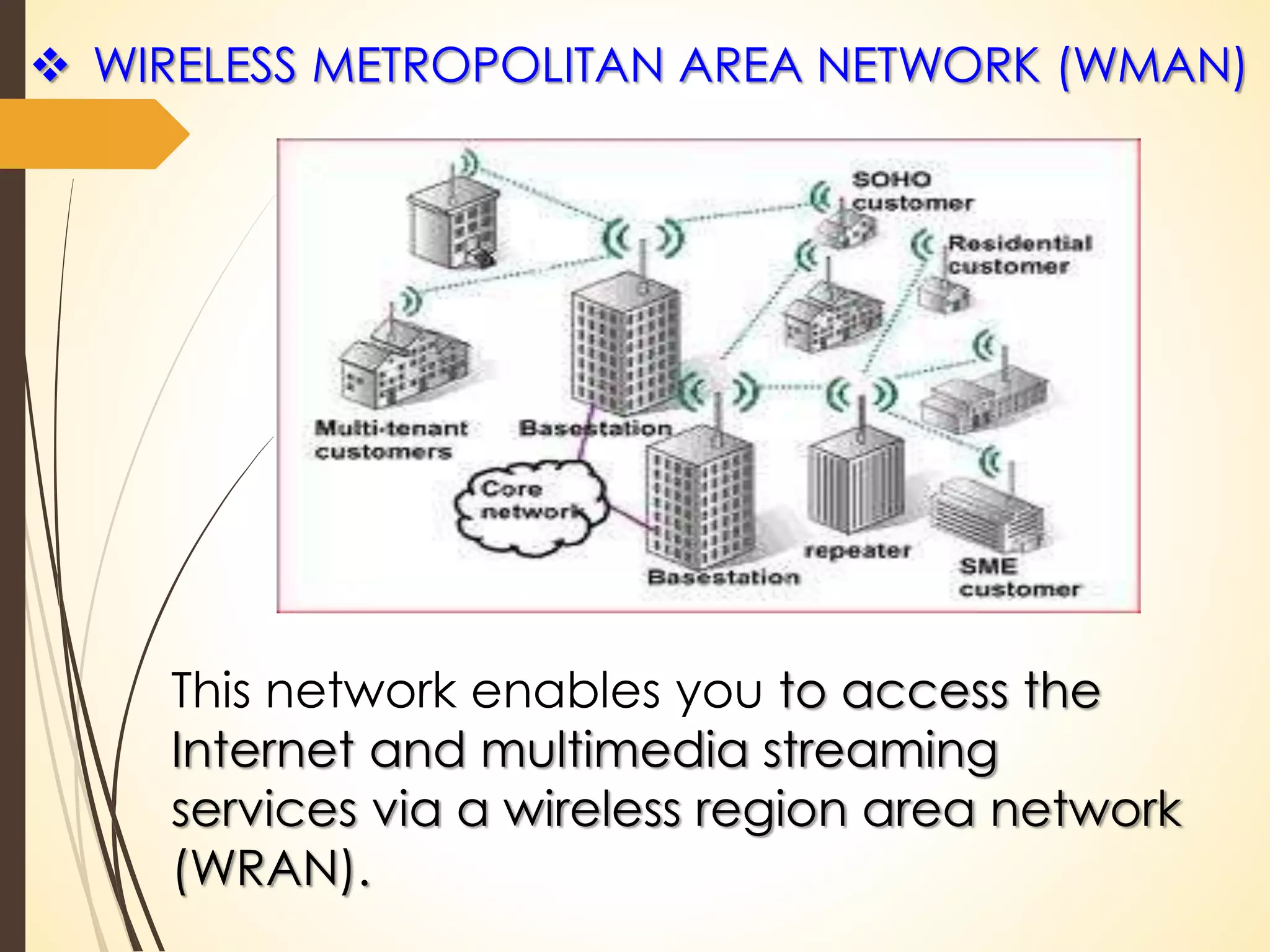
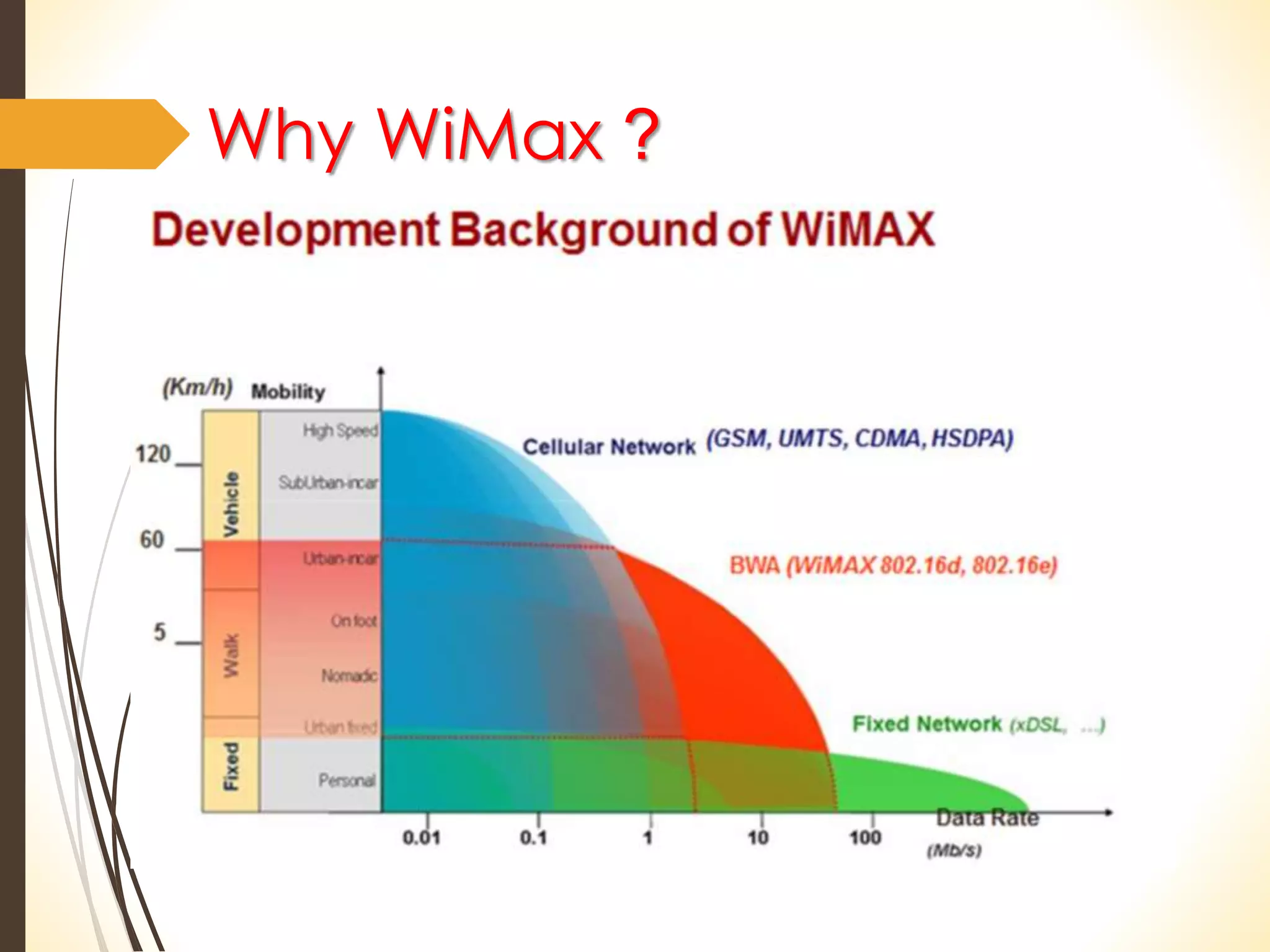
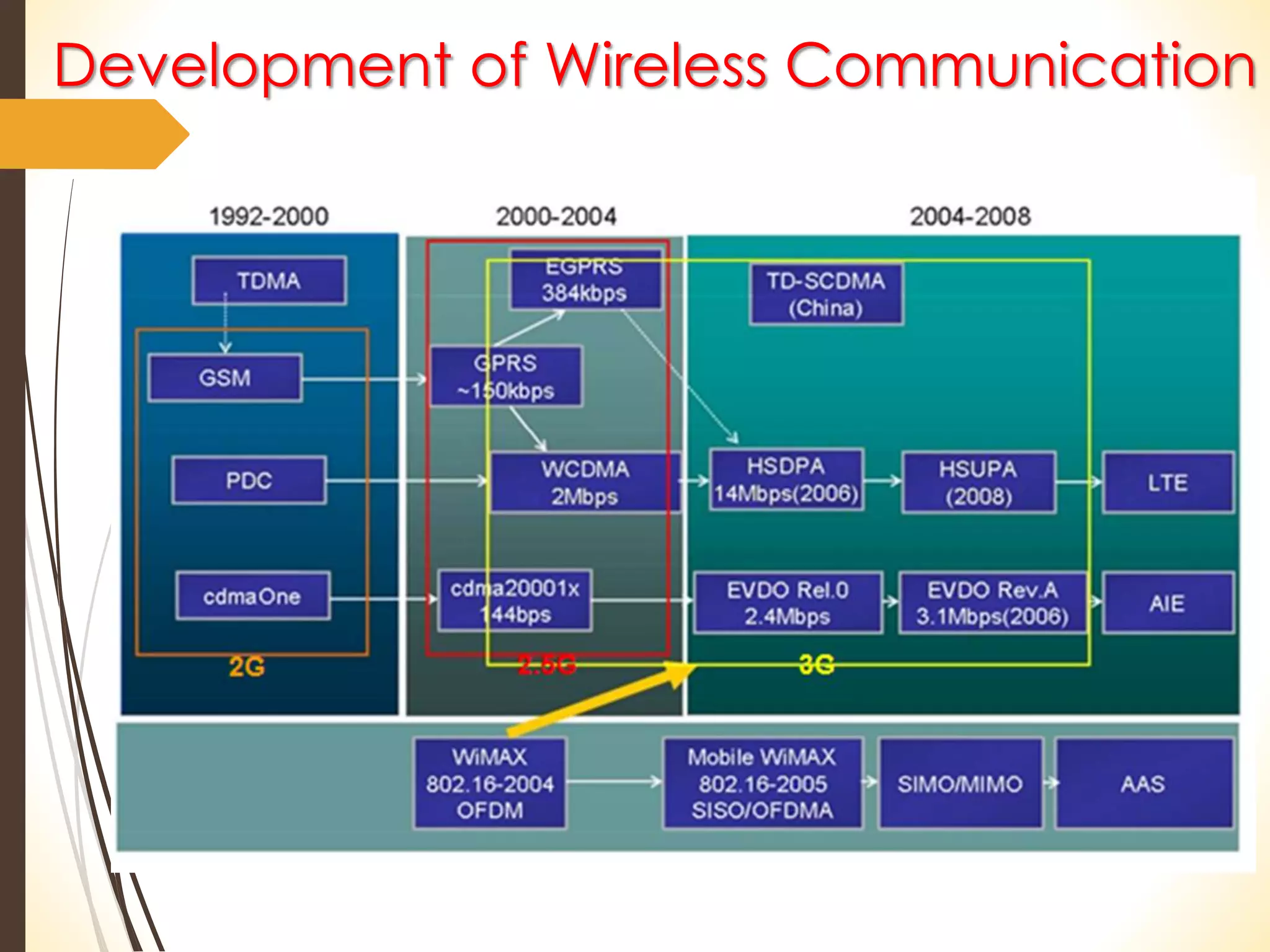
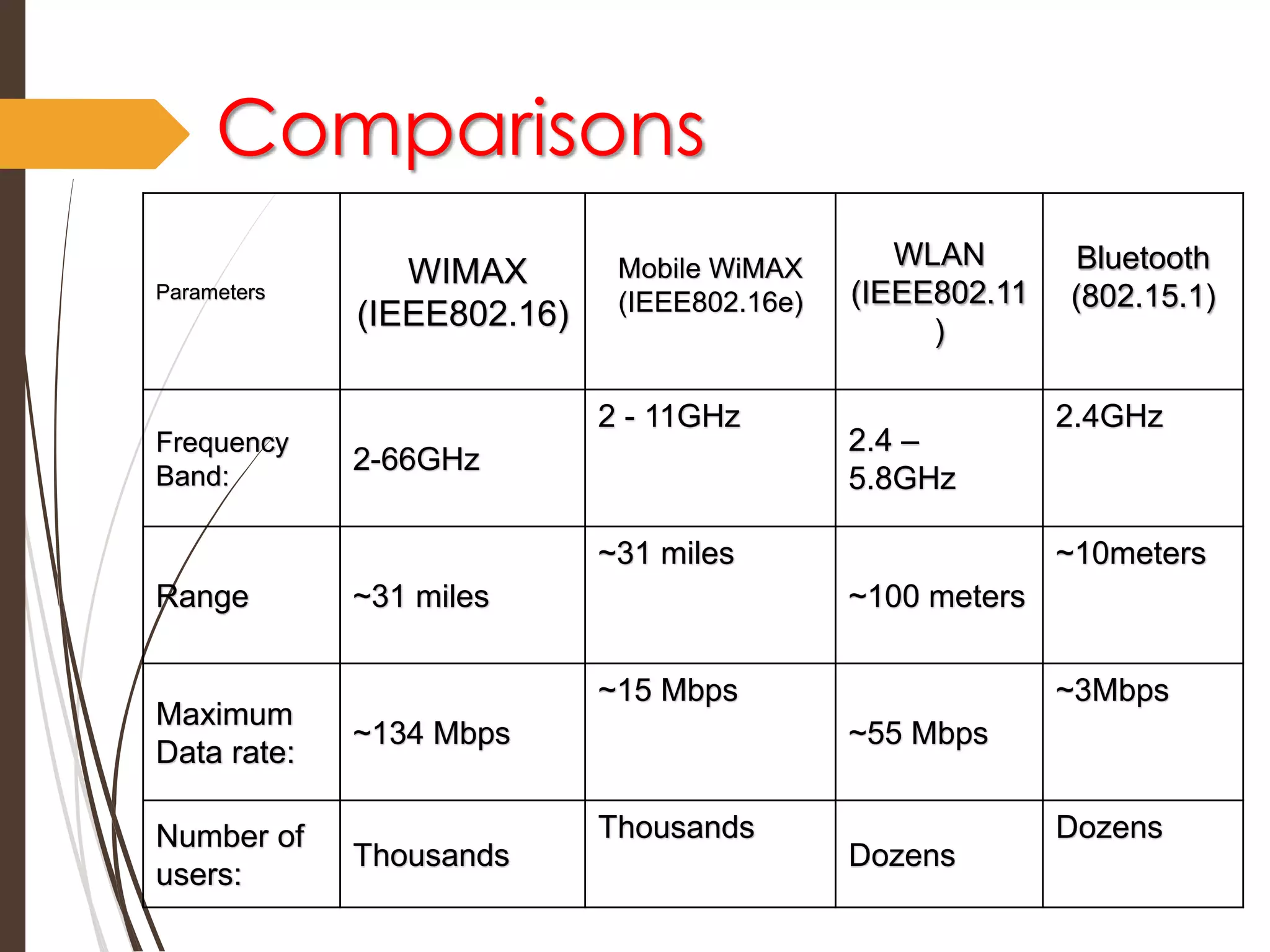
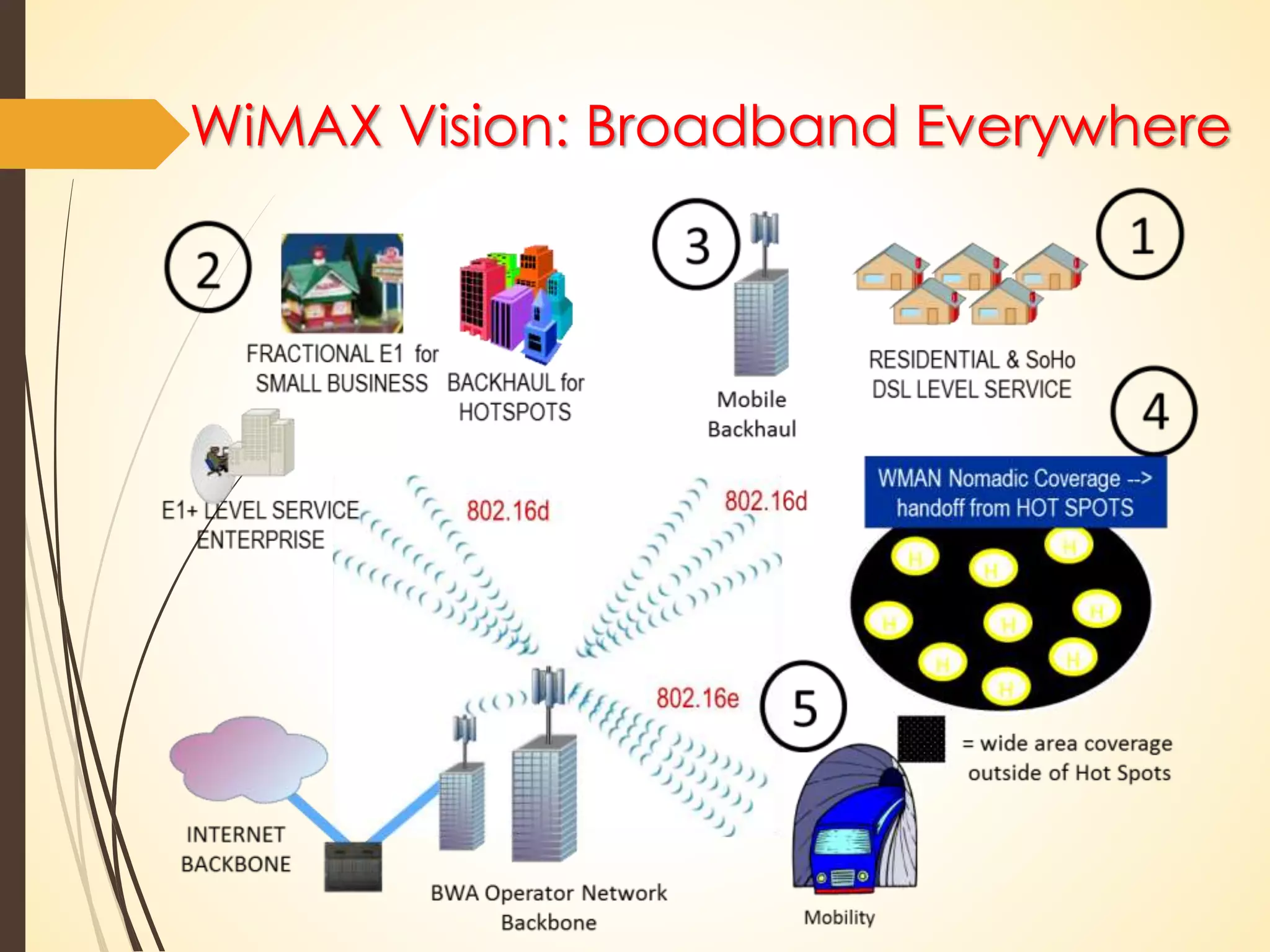
This document discusses wireless technology and WiMAX. It begins with an introduction to wireless technology and its characteristics like mobility, reachability, maintainability and simplicity. It then discusses different wireless network topologies and technologies classified by range, including WWAN, WPAN, WLAN and WMAN. The document introduces WiMAX as a wireless broadband technology based on the IEEE 802.16 standard that supports broadband speeds up to 75 Mbps within a range of up to 50 km. It compares WiMAX to other wireless technologies and discusses WiMAX's vision of providing broadband everywhere as well as its benefits like replacing copper wire networks and providing high-speed connectivity.