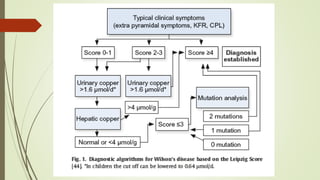
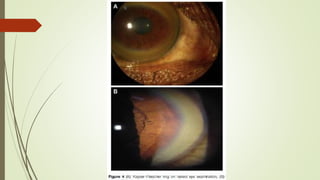
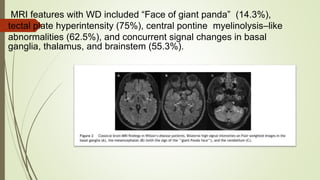
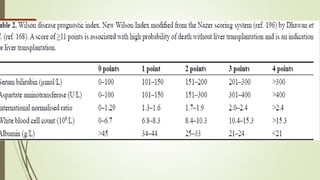
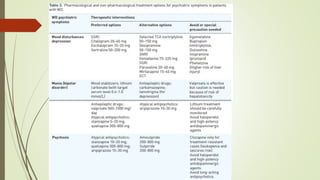
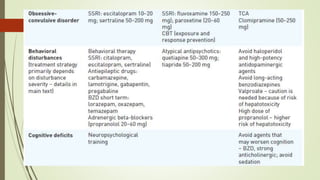
Wilson disease is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder that causes copper accumulation in tissues. It typically presents in the first and fourth decades of life with hepatic, hemolytic, neurological or psychiatric symptoms. Neurological symptoms include tremors, dystonia, parkinsonism and psychiatric issues like psychosis. Diagnosis involves tests of copper levels in blood, urine and liver. Treatment aims to reduce copper levels lifelong using chelating agents like penicillamine or zinc salts. Close monitoring is needed due to potential side effects or copper deficiency from treatment.