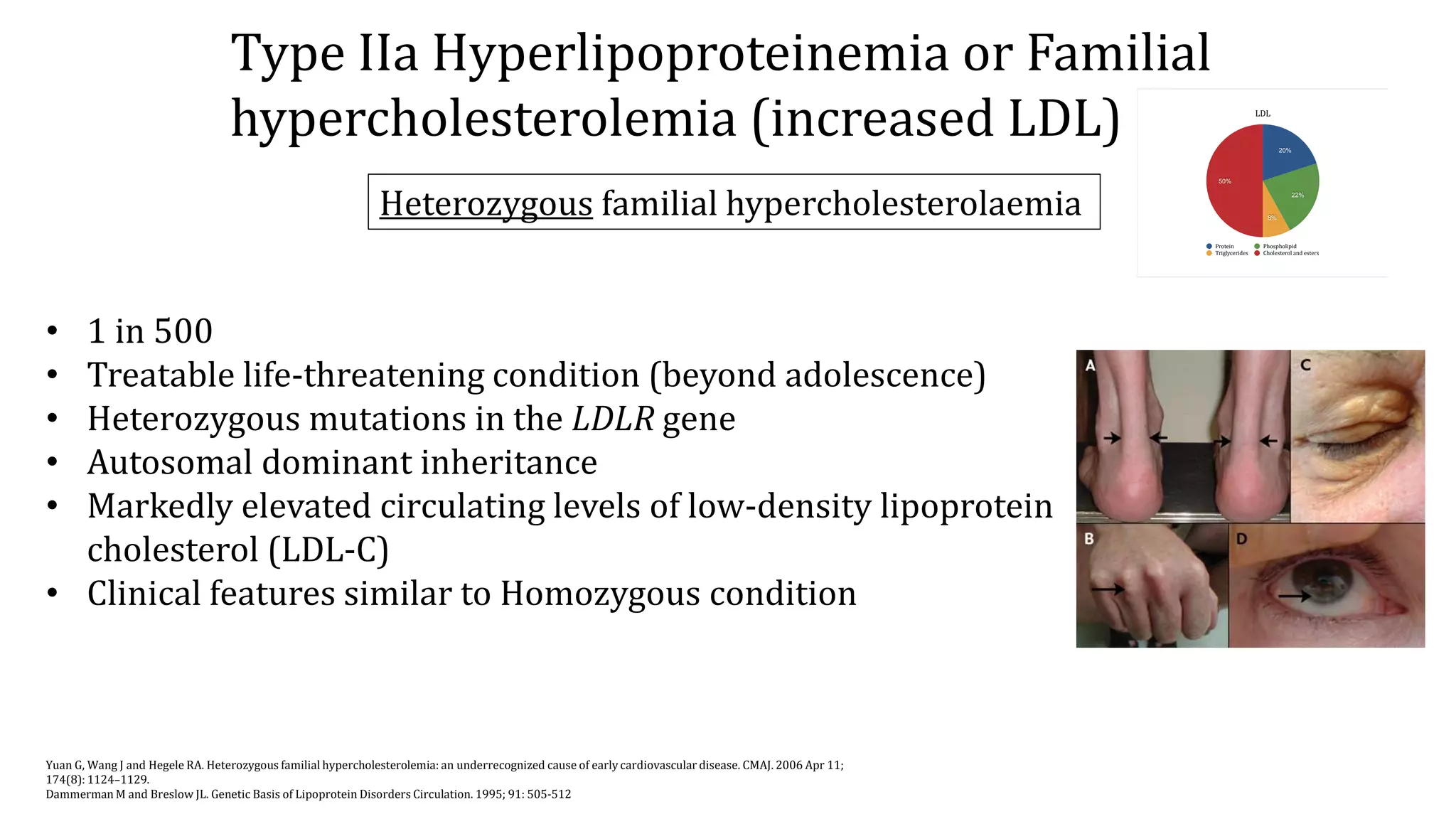
Hyperlipidemia refers to elevated levels of lipids in the blood, including triglycerides and cholesterol. There are several types of hyperlipidemia based on the elevated lipoprotein, including types I-V. Type I is caused by deficiencies of lipoprotein lipase or ApoC-II, resulting in an inability to remove chylomicrons from the blood. Type IIa, or familial hypercholesterolemia, is caused by mutations in the LDL receptor gene and results in markedly elevated LDL cholesterol. It can be either homozygous or heterozygous. Both forms increase the risk of premature cardiovascular disease if not properly treated.












![Source: Feingold KR, Grunfeld C. Introduction to Lipids and Lipoproteins. [Updated 2015 Jun 10]. In: De Groot LJ, Beck-Peccoz P, Chrousos G, et al., editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000-.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK305896/?report=reader#_NBK305896_pubdet_ Accessed on 04/22/2016
Source: Lipids and lipoproteins: metabolism and its violations.
http://intranet.tdmu.edu.ua/data/kafedra/internal/distance/classes_stud/English/2%20course/Elective%20course%20(Modern%20Methods%20of%20Diagnosis)/08.%20Lipids%20and%20lipoproteins%20metabolis%20and%20its%20violatios.htm
Accessed on 04/22/2016
Vaverkova H. LDL-C or apoB as the Best Target for Reducing Coronary Heart Disease. Should Apob be Implemented into Clinical Practice? Clin Lipidology. 2011;6(1):35-48.
Composition of Lipoproteins](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyperlipidemiaetiologyepidemiologyclinicalfeatures-191005154018/75/Hyperlipidemia-etiology-epidemiology-clinical-features-13-2048.jpg)