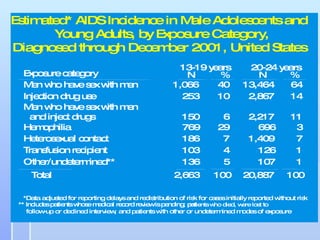
This document discusses HIV/AIDS, how it is transmitted, symptoms, and statistics. It explains that HIV attacks immune cells, leading to AIDS if untreated. HIV can be transmitted via unprotected sex, needle sharing, or from mother to child during pregnancy, birth or breastfeeding. Early symptoms may include flu-like illness, but many have no symptoms for years. Later, AIDS develops as the immune system weakens. The document provides data on HIV/AIDS cases in West Virginia and risk behaviors in the state's population. It emphasizes preventing transmission, especially among youth.