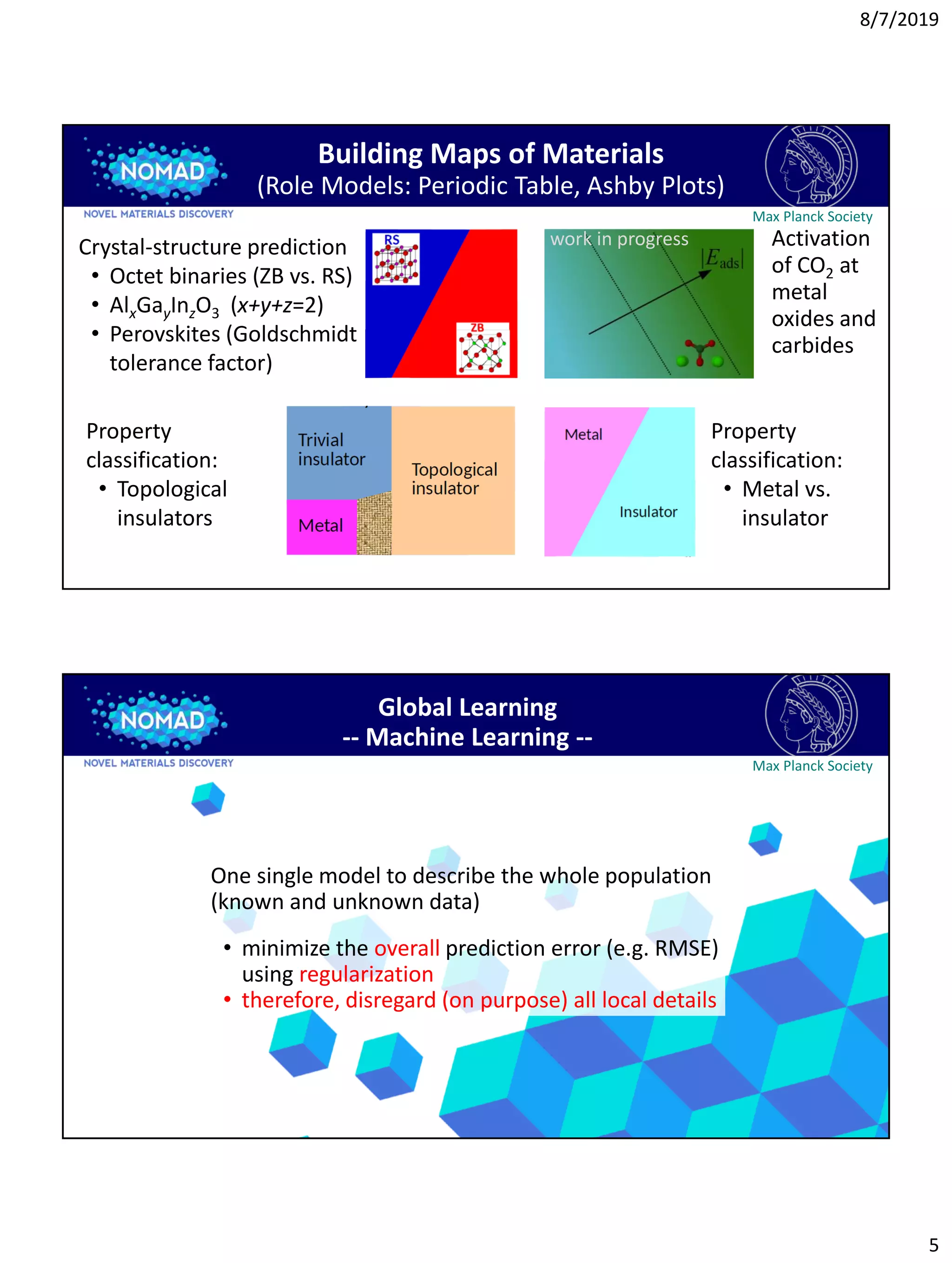
1) The document discusses challenges in using machine learning and data analytics for materials science research. Specifically, most materials are irrelevant for a given purpose, so models need to identify statistically exceptional subgroups rather than averaging all data.
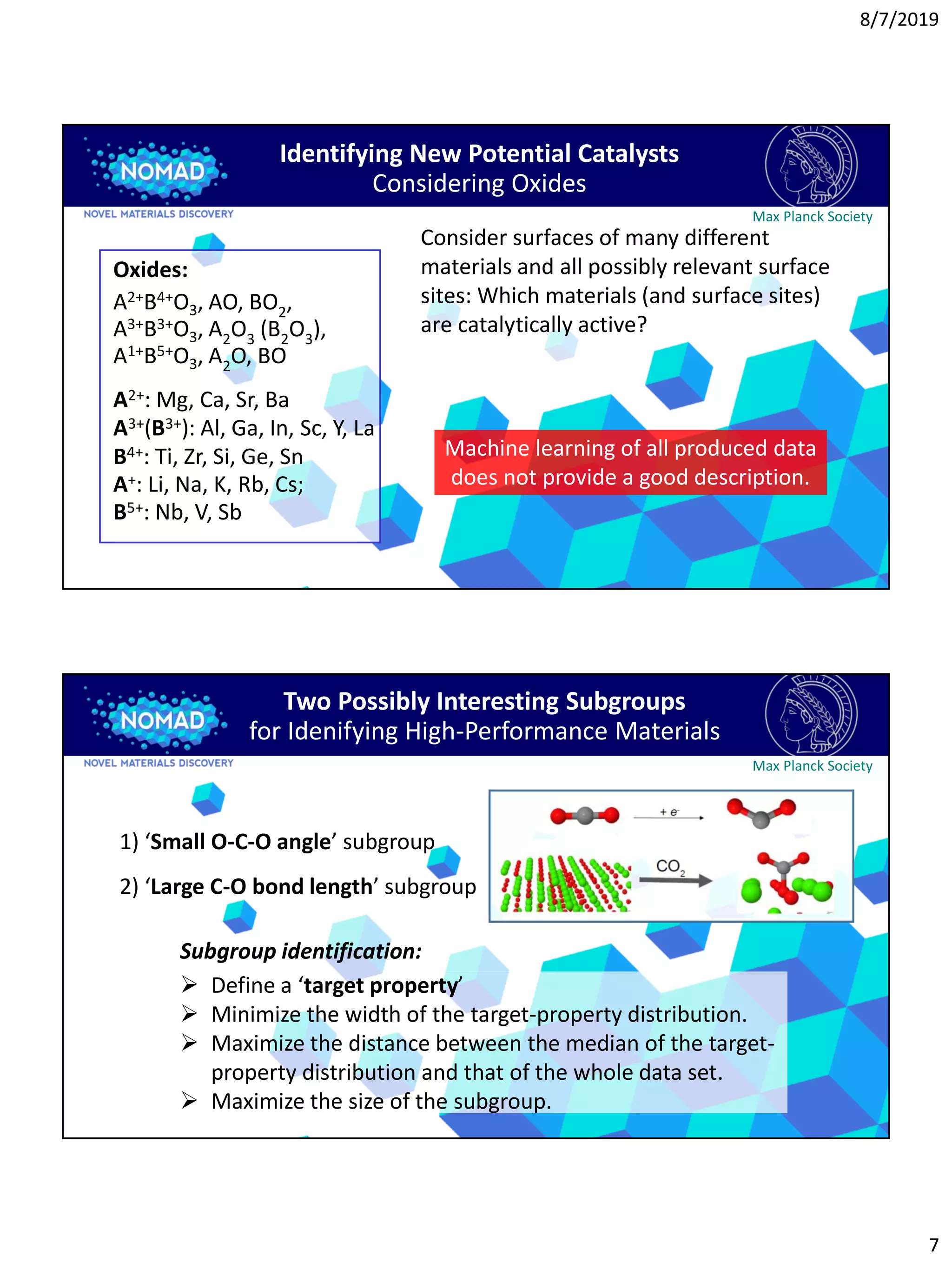
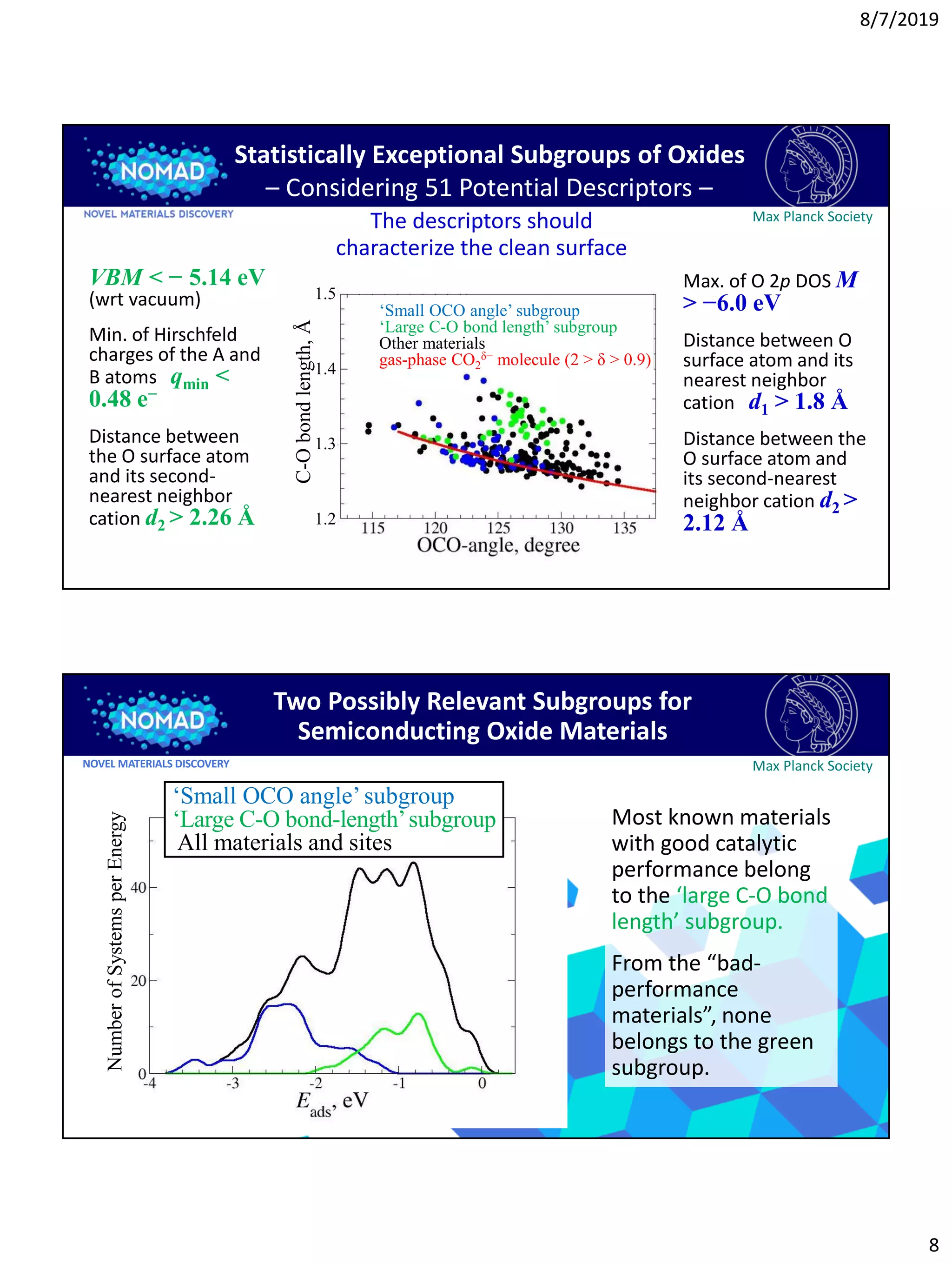
2) Two potential methods for identifying promising subgroups are discussed: focusing on materials with small oxygen-carbon-oxygen angles or large carbon-oxygen bond lengths for catalysis applications.
3) The concept of a model's domain of applicability is introduced, wherein models perform best when applied only to similar data they were trained on, rather than all data globally. Identifying these reliable domains is important.
![8/7/2019
1
Max Planck SocietyMax Planck Society
When The New Science Is in The Outliers
When The New Science Is In The Outliers
Matthias Scheffler
Fritz-Haber-Institut der Max-Planck-Gesellschaft, 14195 Berlin, Germany, and Physics Department and IRIS
Adlershof, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, 12489 Berlin, Germany
Several issues hamper progress in data-driven materials science. In particular, these are a missing FAIR [1]
data infrastructure and appropriate data-analytics methodology [2].
Significant efforts are still necessary to fully realize the A and I of FAIR. Here the development of metadata,
their intricate relationships, and data ontology need critical attention. Obviously, a FAIR data infrastructure
– for being accepted by the community – should work without bureaucratic hurdles or the needs for special
training. In this talk, I will discuss the challenges and progress, focusing on computational materials science.
Concerning the data-analytics, we note that the number of possible materials is practically infinite, but only
10 or 100 of them may be relevant for a certain science or engineering purpose. In simple words, in
materials science and engineering, we are often looking for “needles in a hay stack”. Fitting or machine-
learning all data (i.e. the hay) with a single, global model may average away the specialties of the
interesting minority (i.e. the needles). I will discuss methods that identify statistically-exceptional
subgroups in a large amount of data, and I will discuss how one can estimate the domains of applicability of
machine-learning models. [3]
1. FAIR stands for Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Re-usable. The FAIR Data Principles;
https://www.force11.org/group/fairgroup/fairprinciples
2. C. Draxl and M. Scheffler, Big-Data-Driven Materials Science and its FAIR Data Infrastructure. Plenary Chapter in Handbook of Materials
Modeling (eds. S. Yip and W. Andreoni), Springer (2019). https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1904/1904.05859.pdf
3. Ch. Sutton, M. Boley, L. M. Ghiringhelli, M. Rupp, J. Vreeken, M. Scheffler, Domains of Applicability of Machine-Learning Models for Novel
Materials Discovery, to be published.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matthias-190826170528/75/When-The-New-Science-Is-In-The-Outliers-1-2048.jpg)