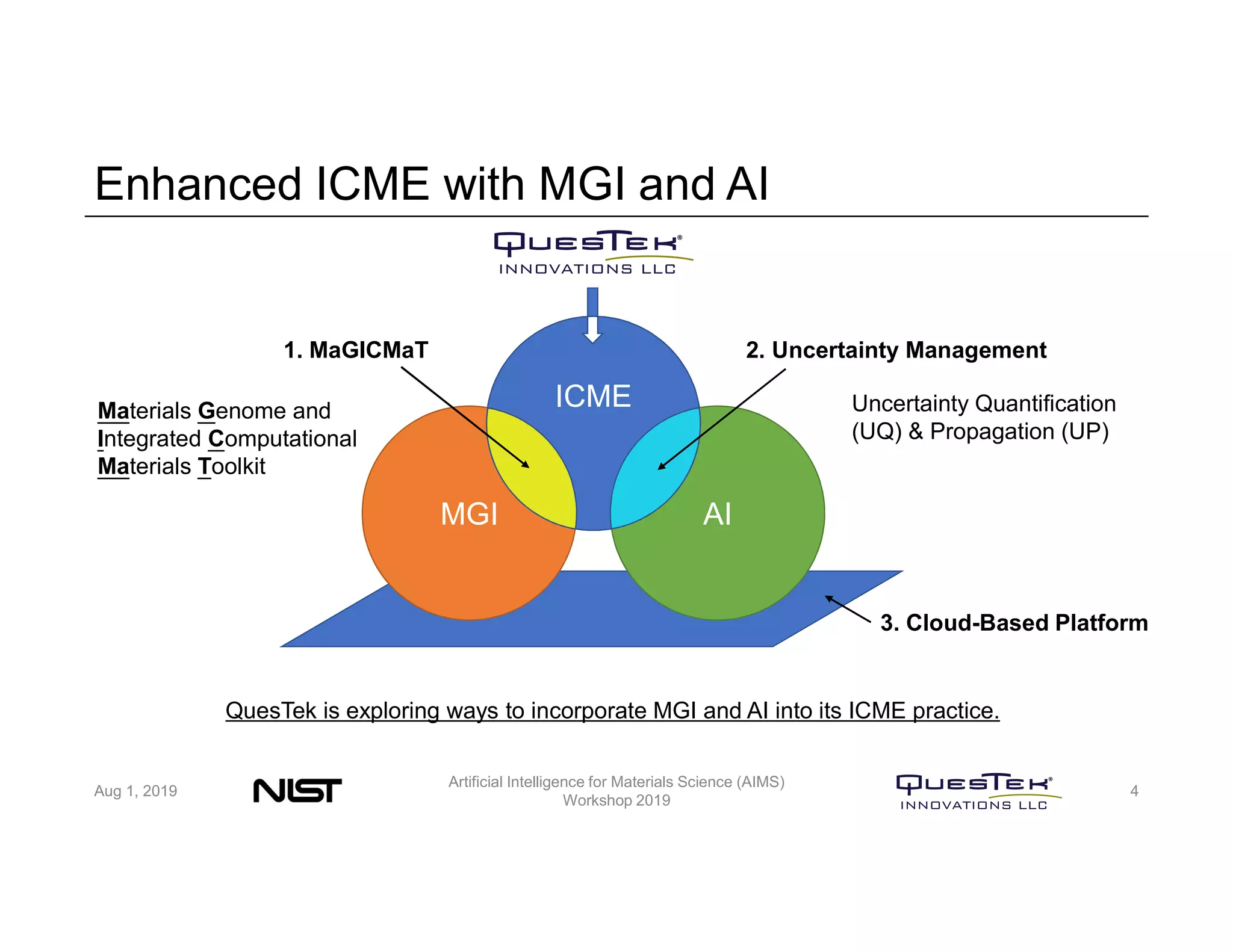
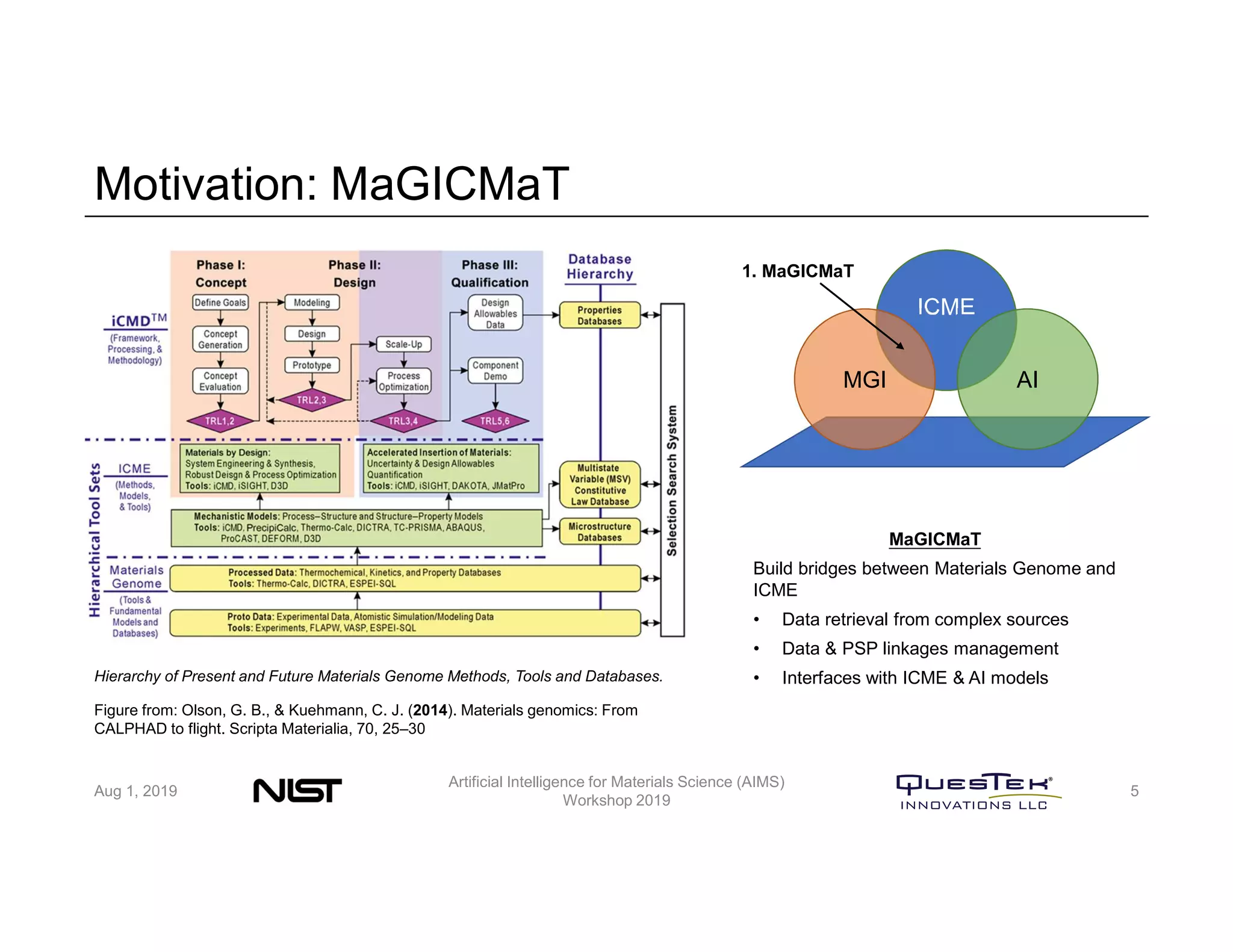
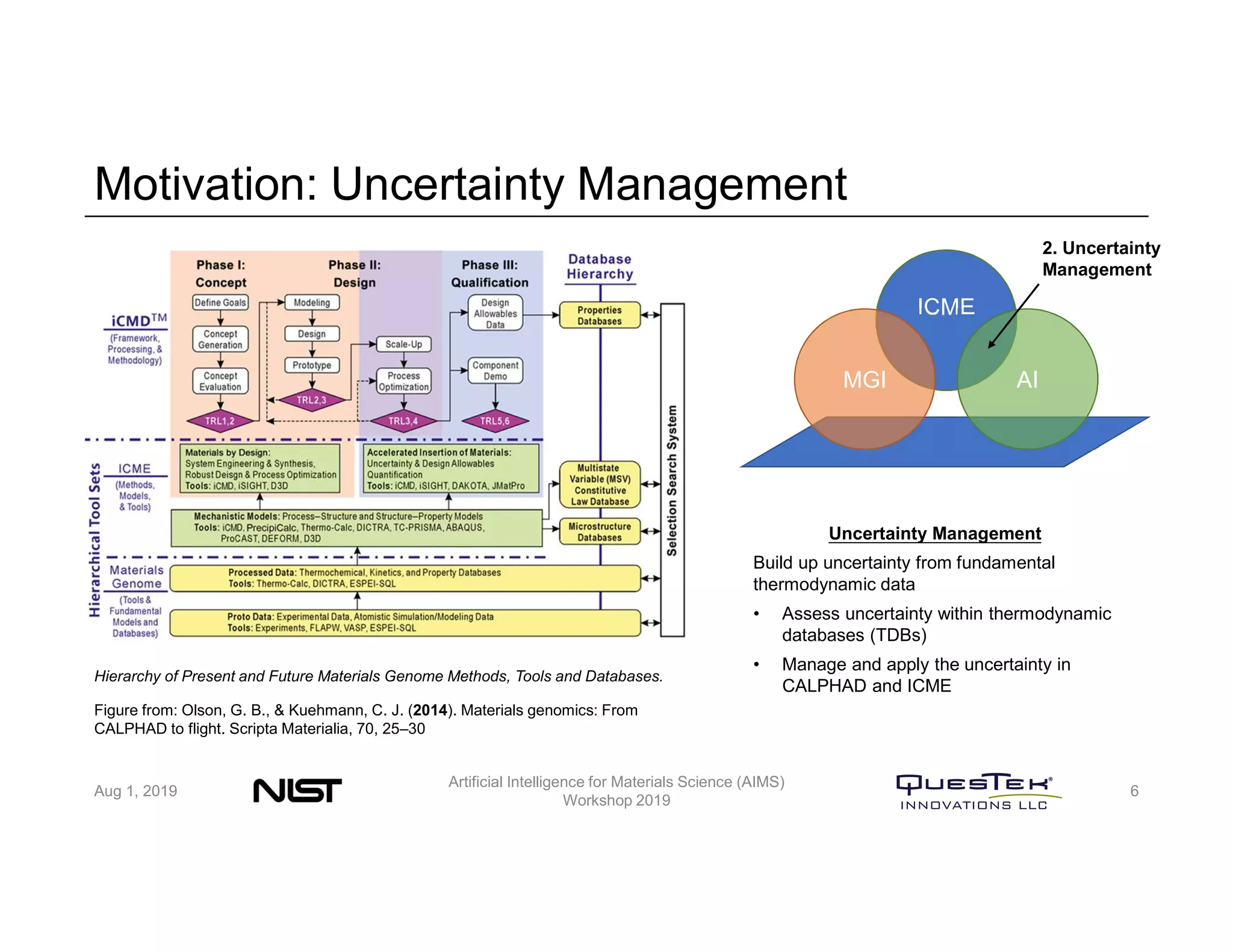
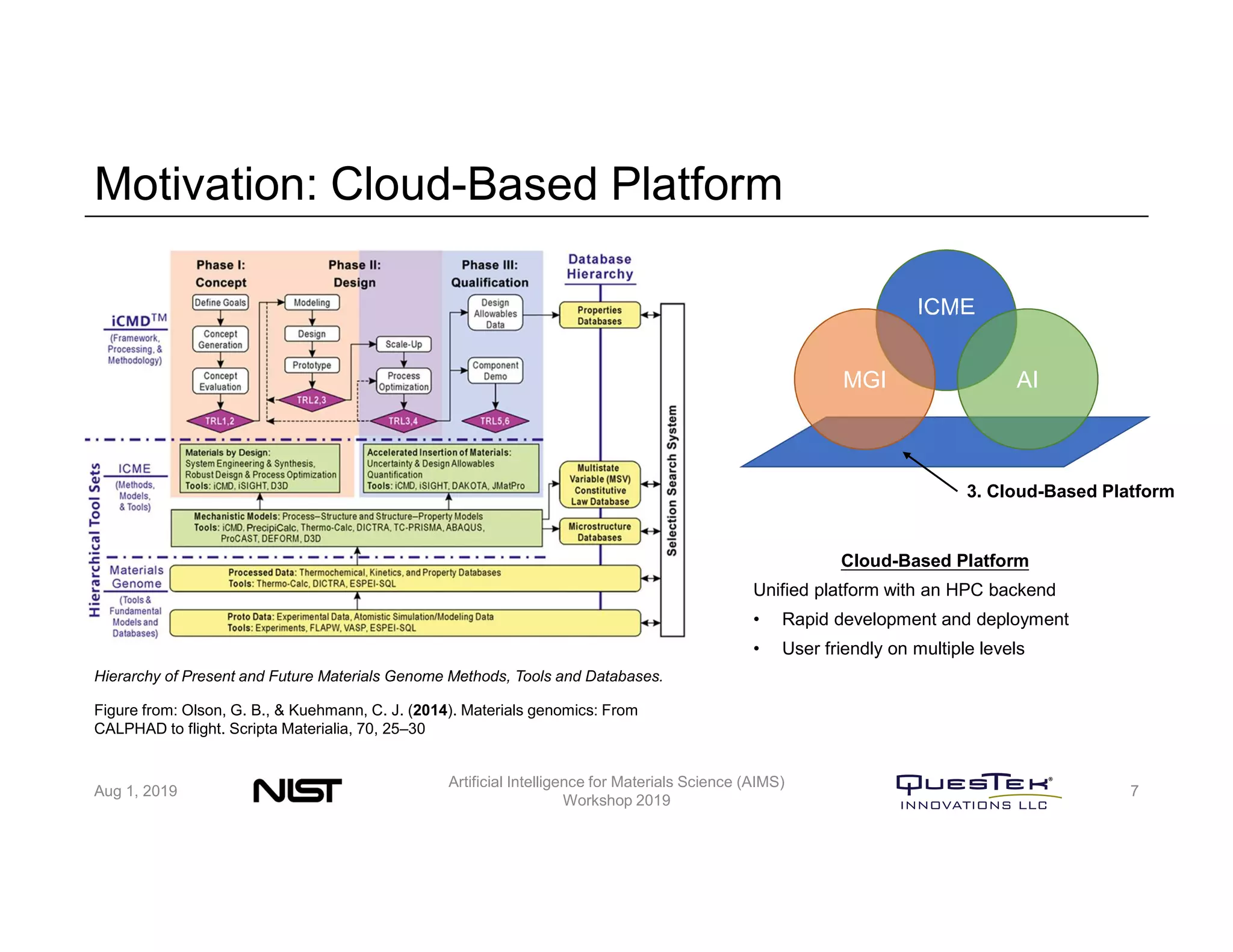
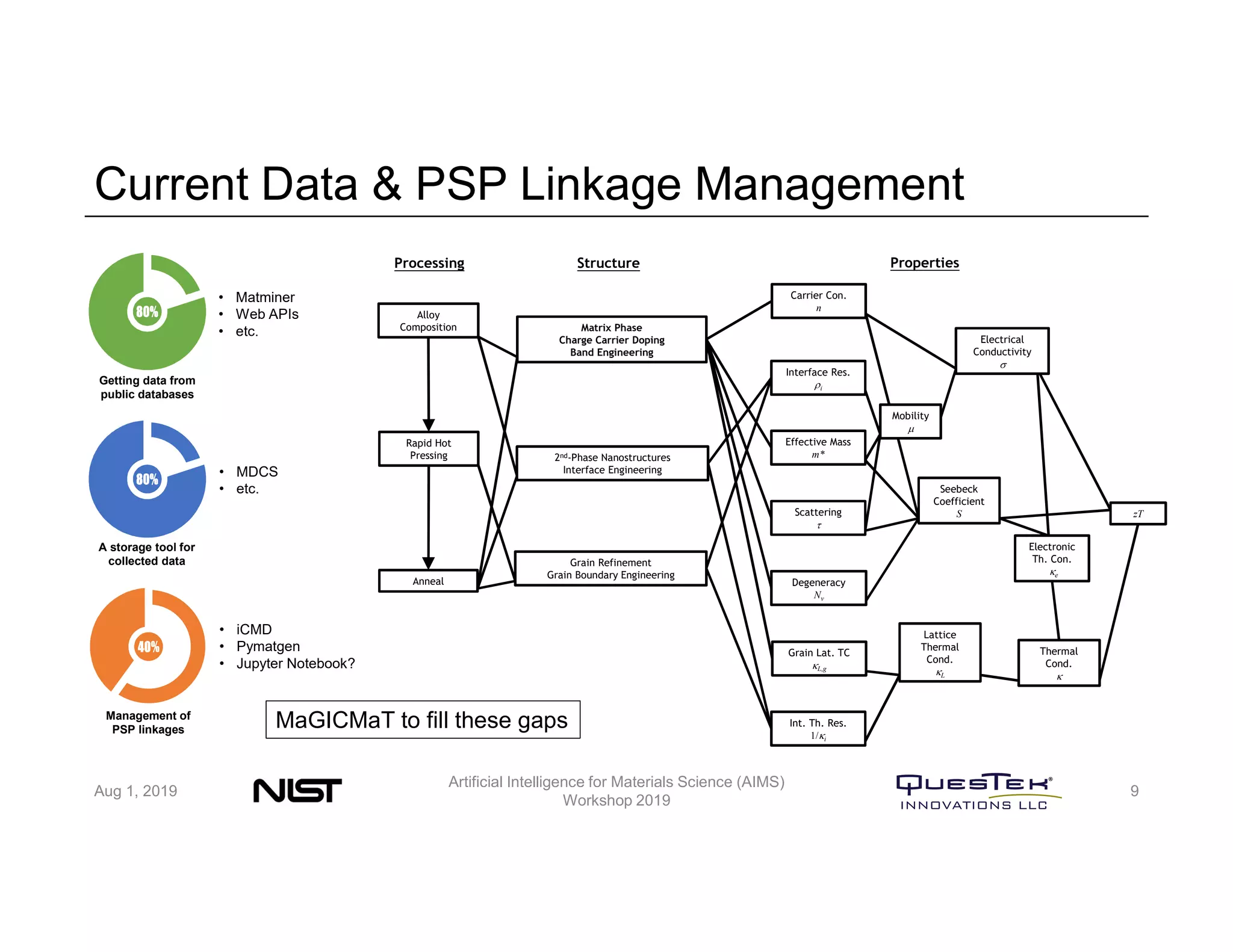
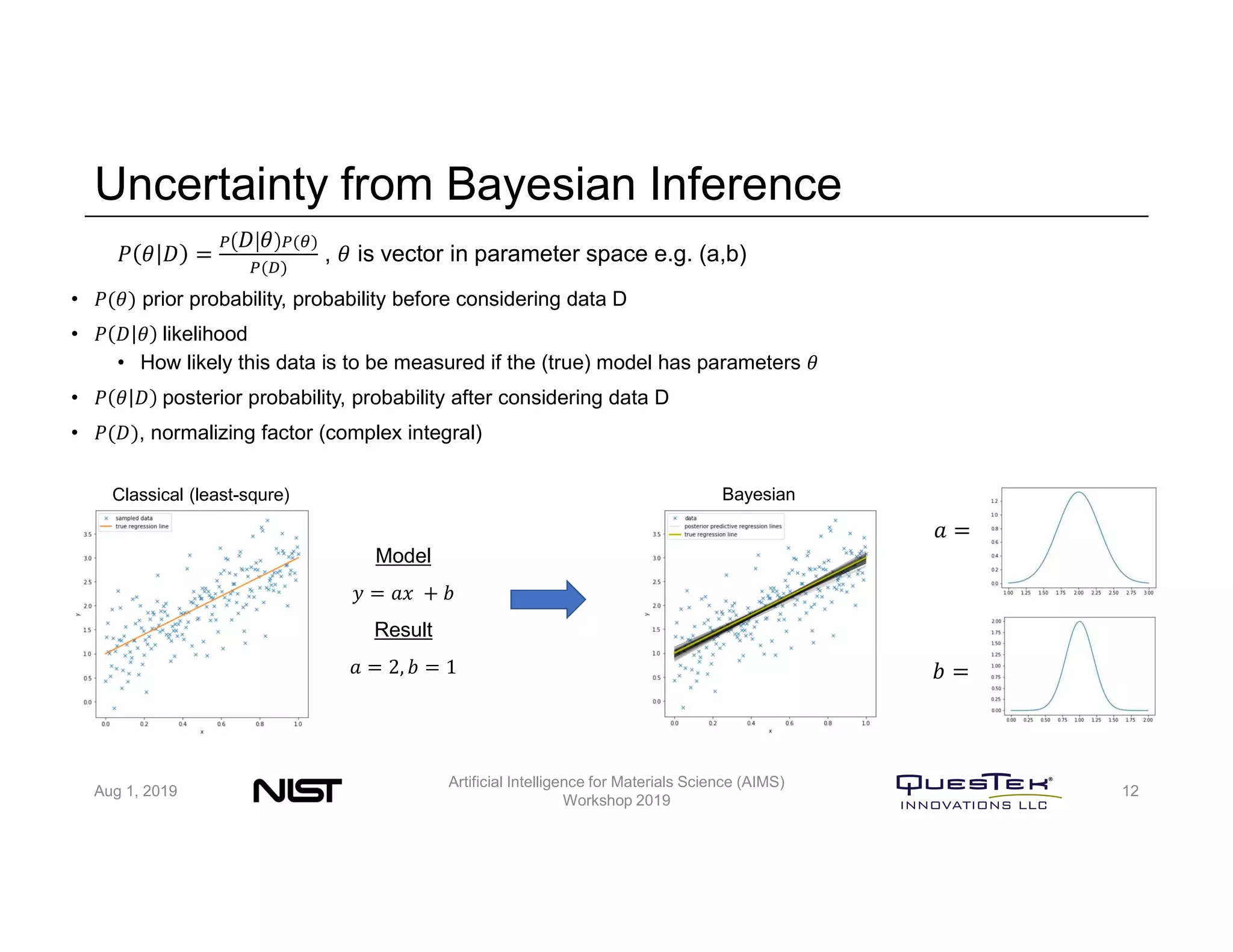
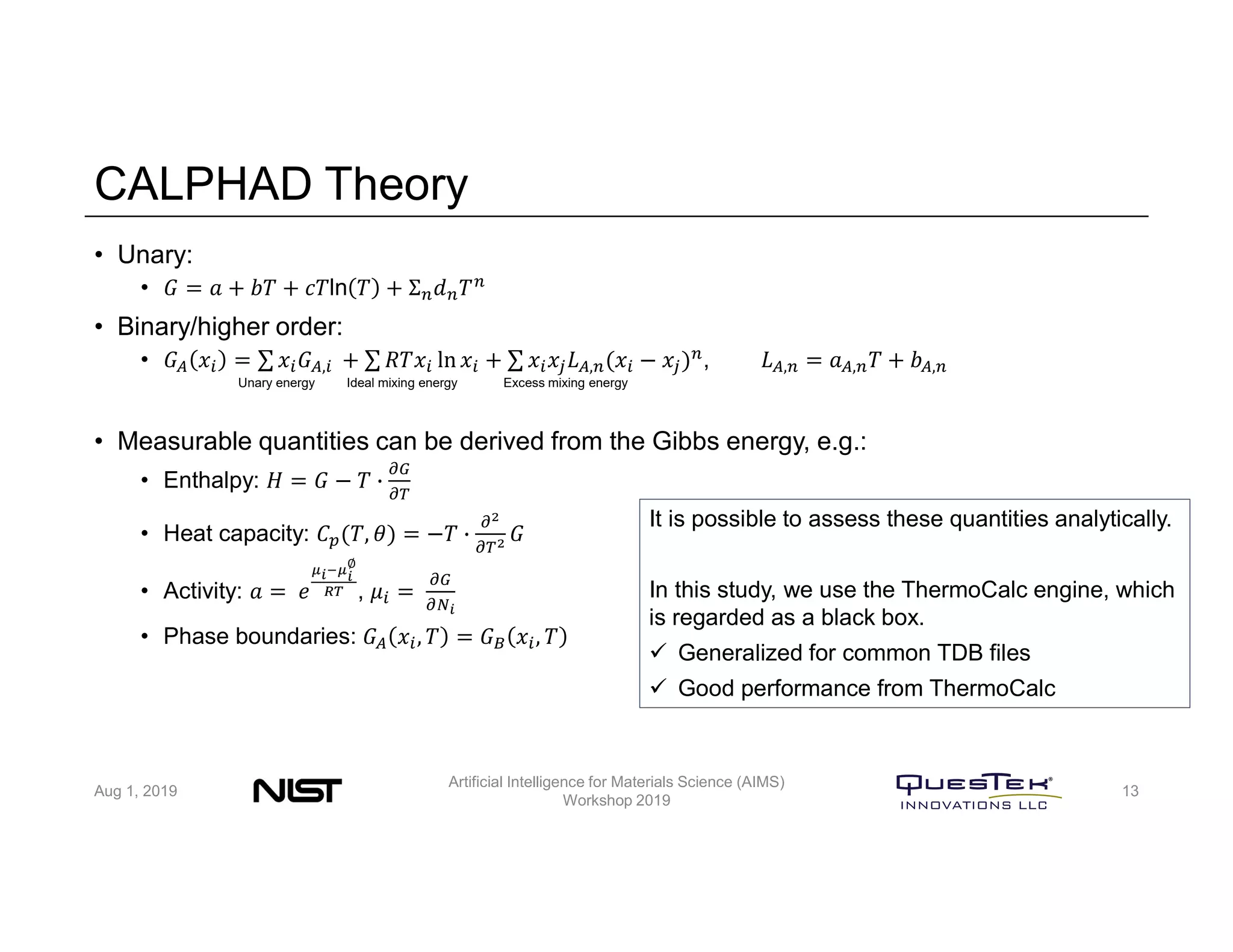
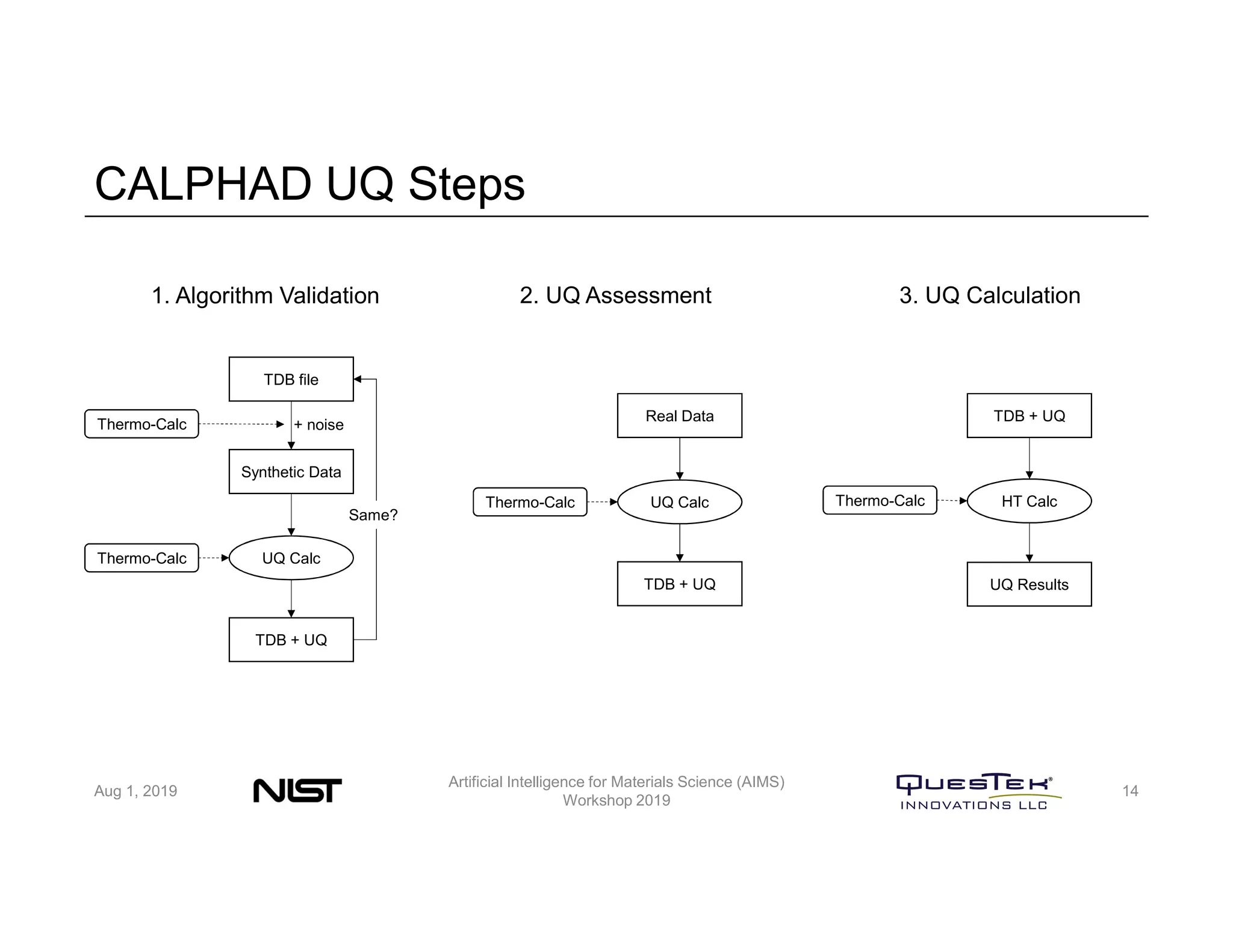
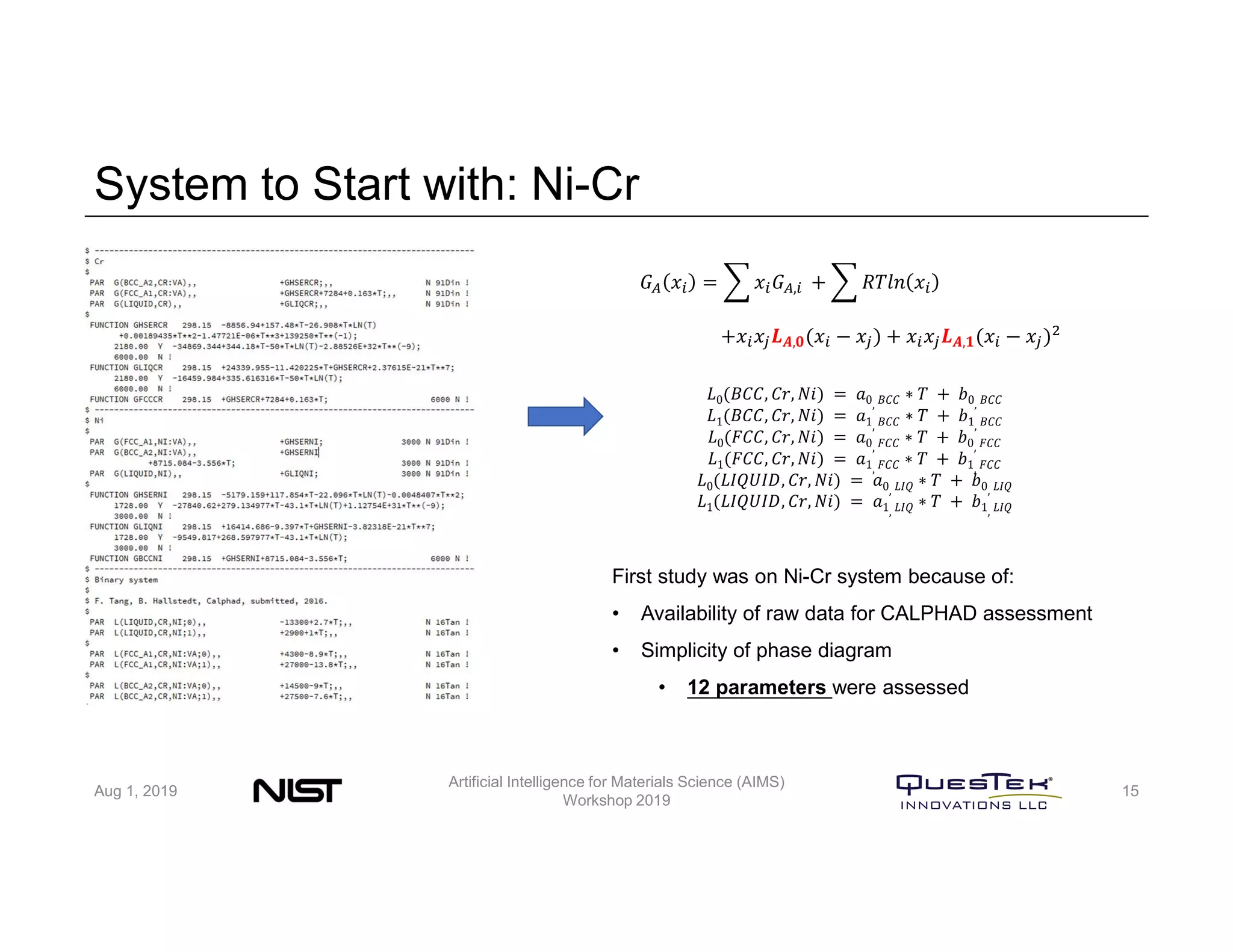
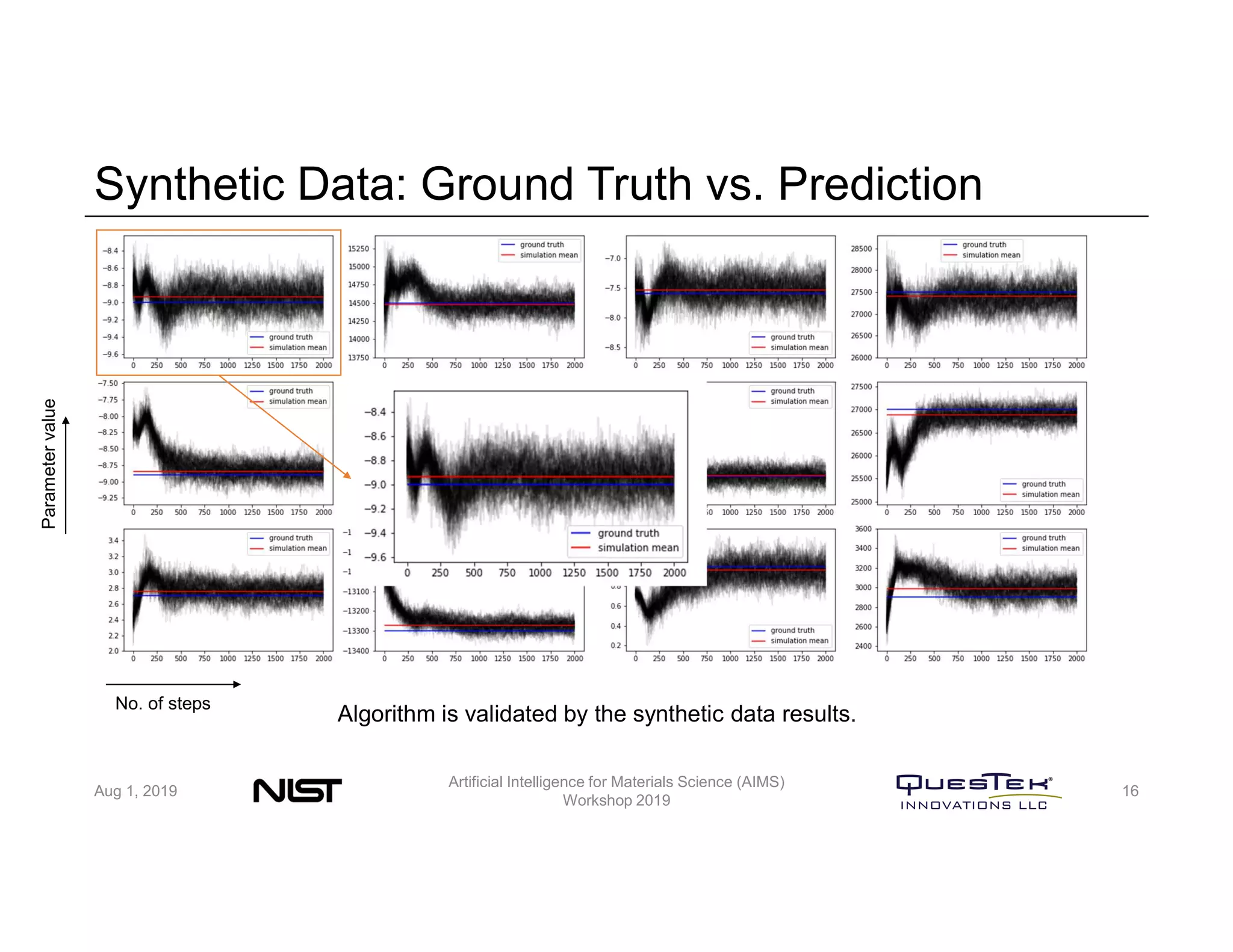
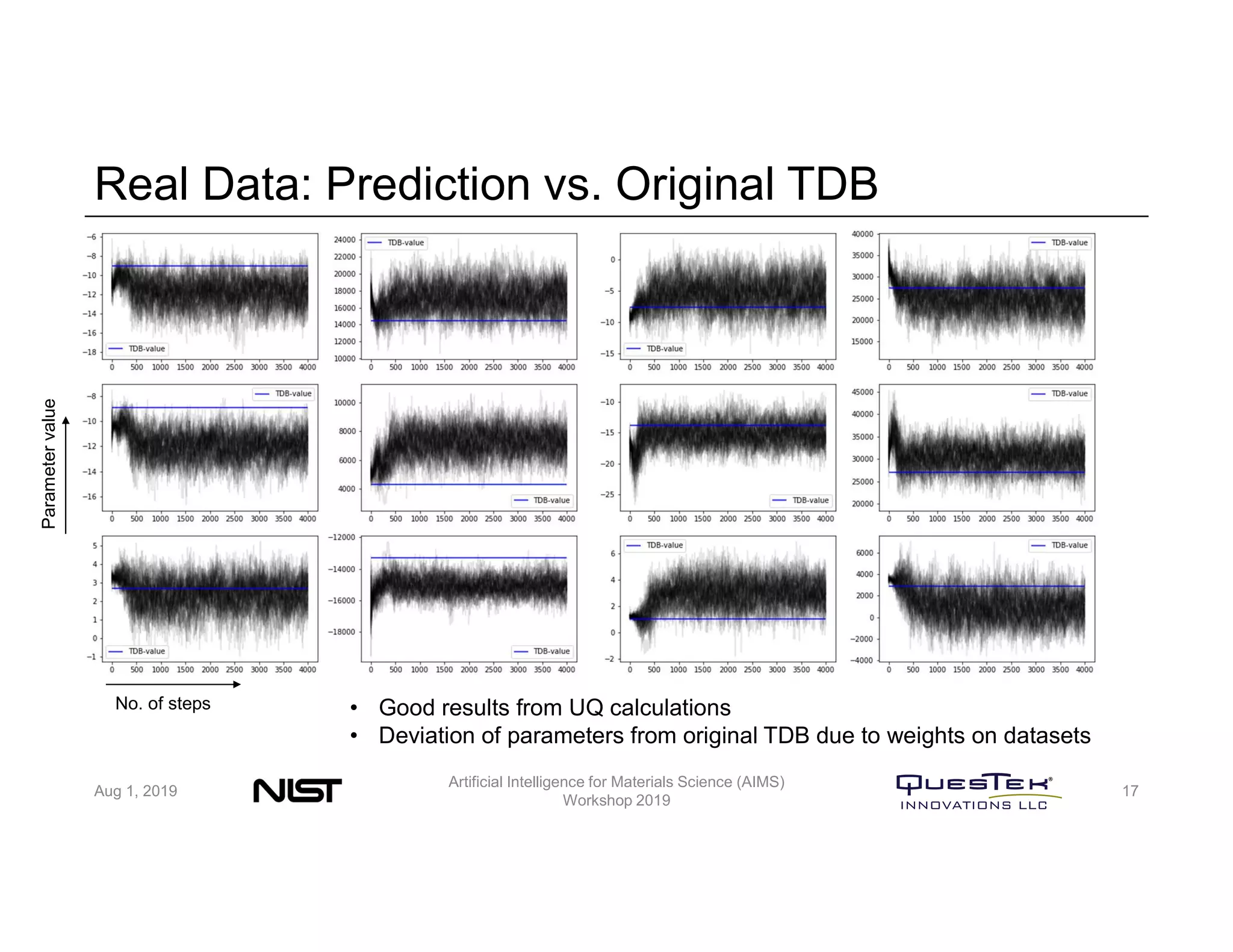
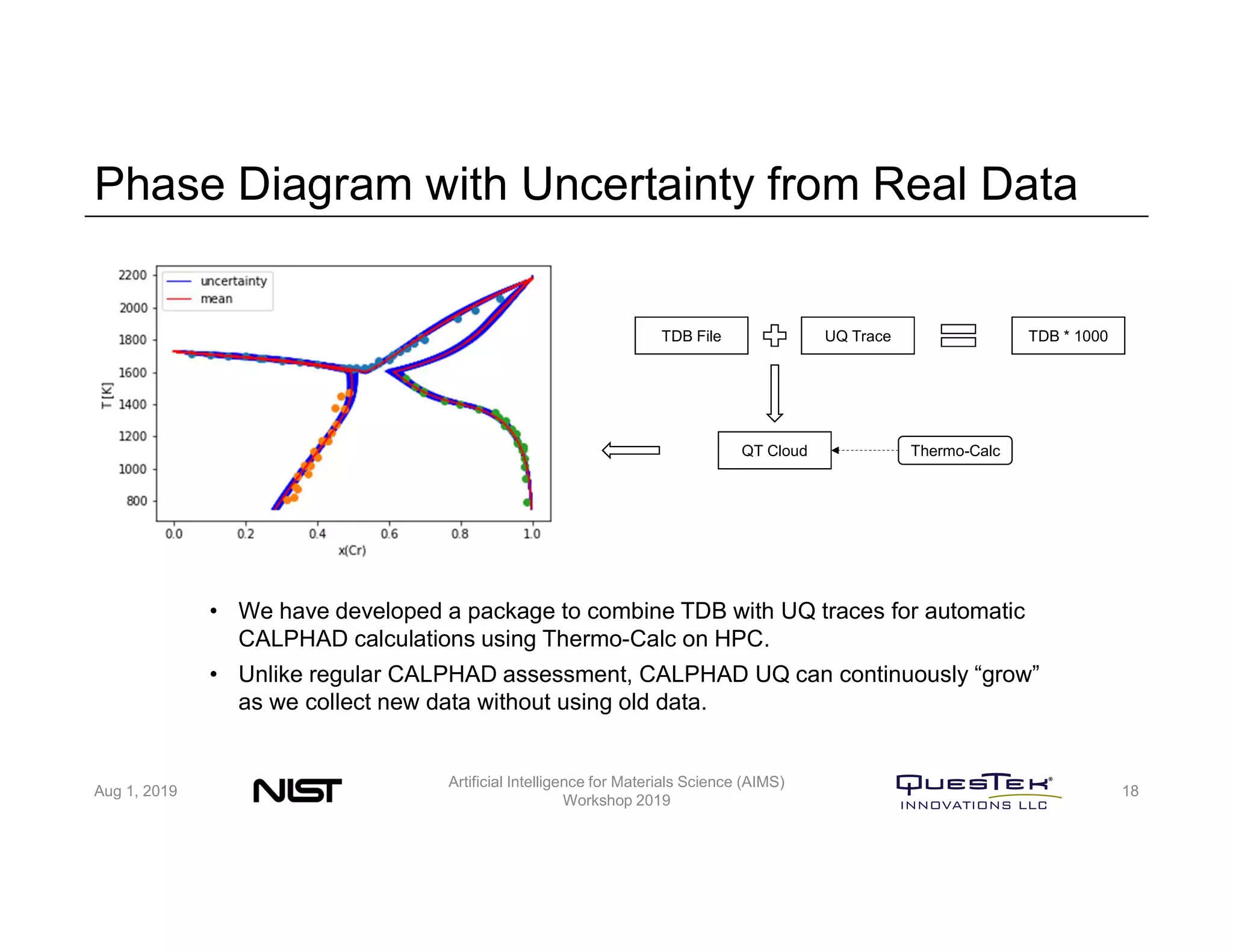
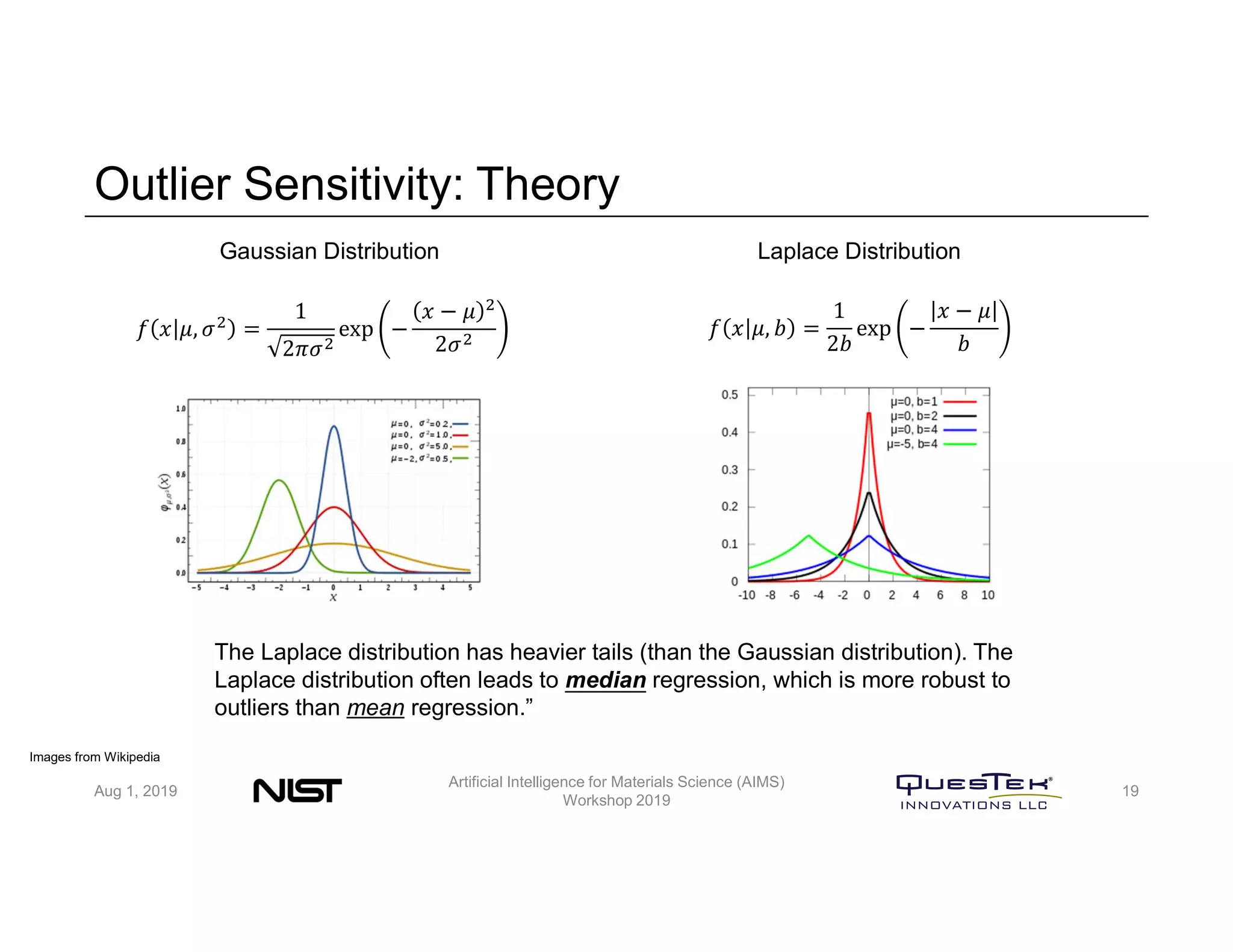
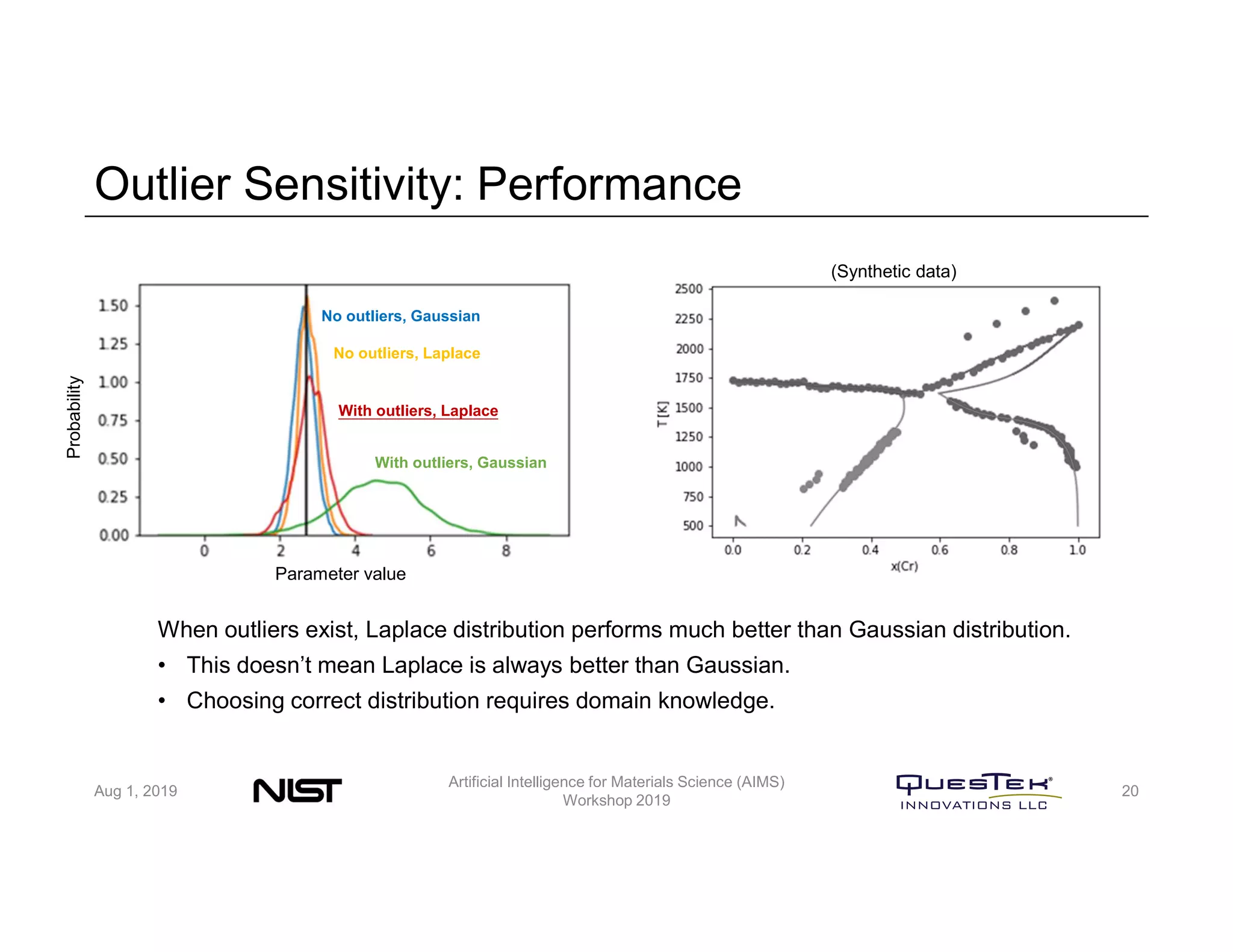
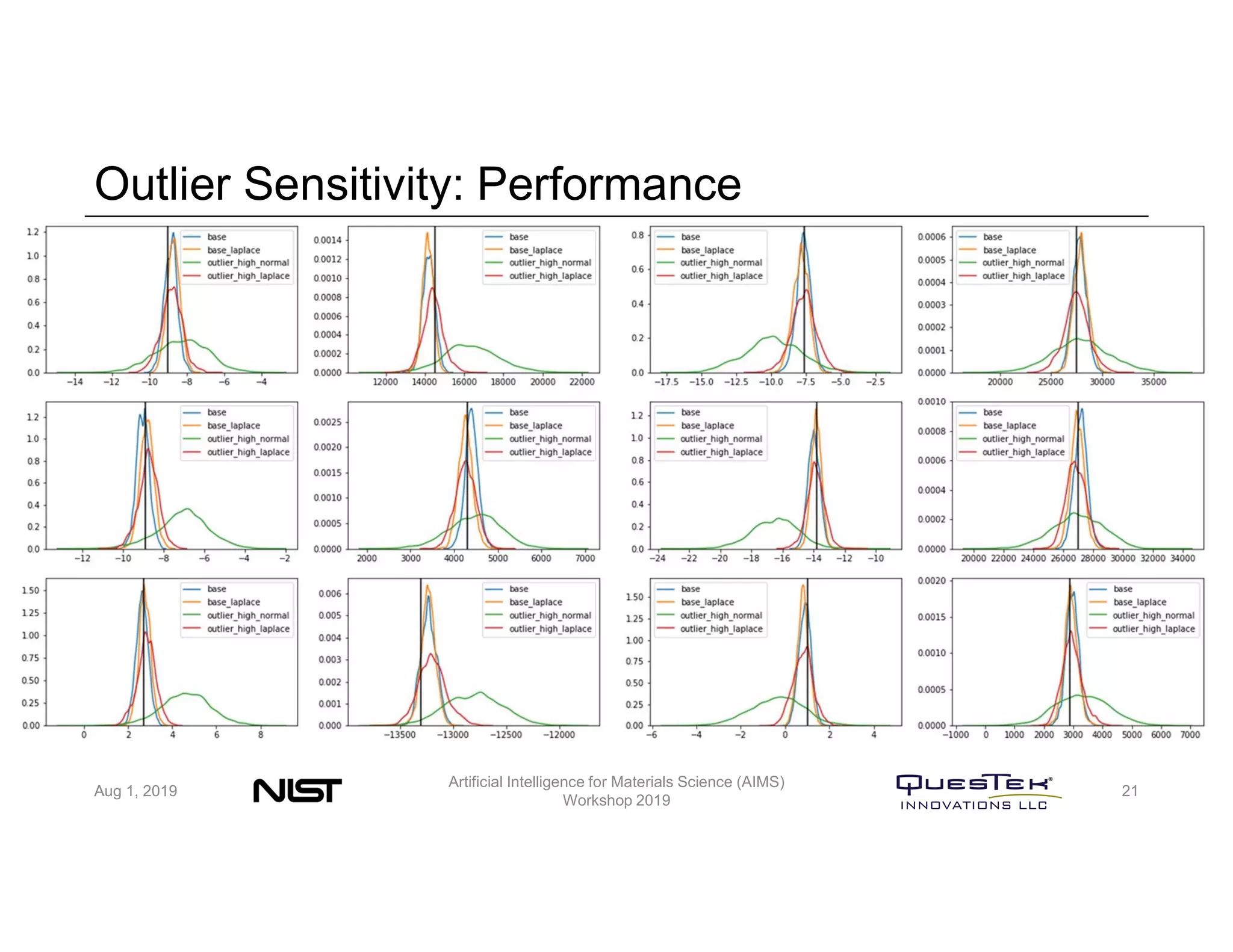
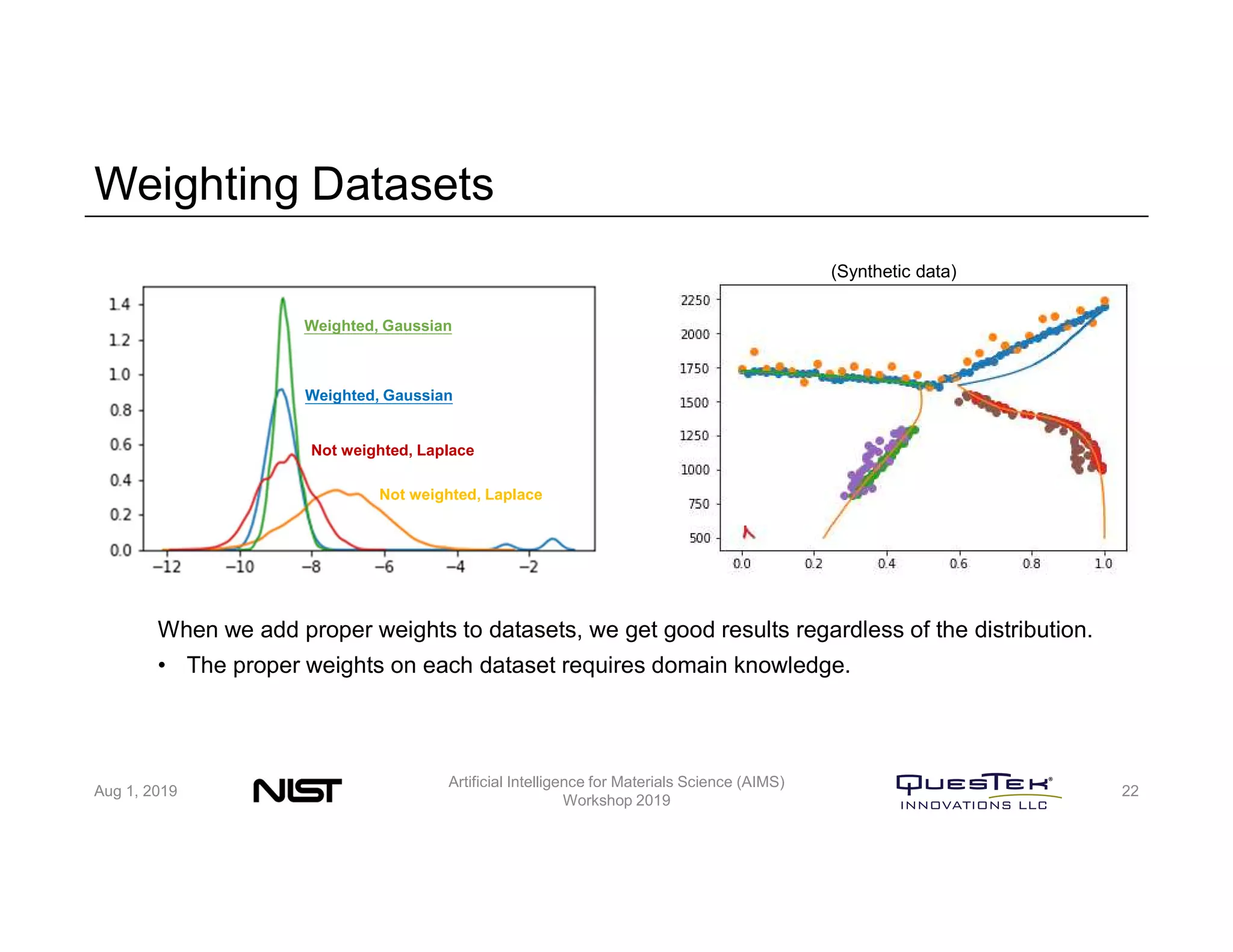
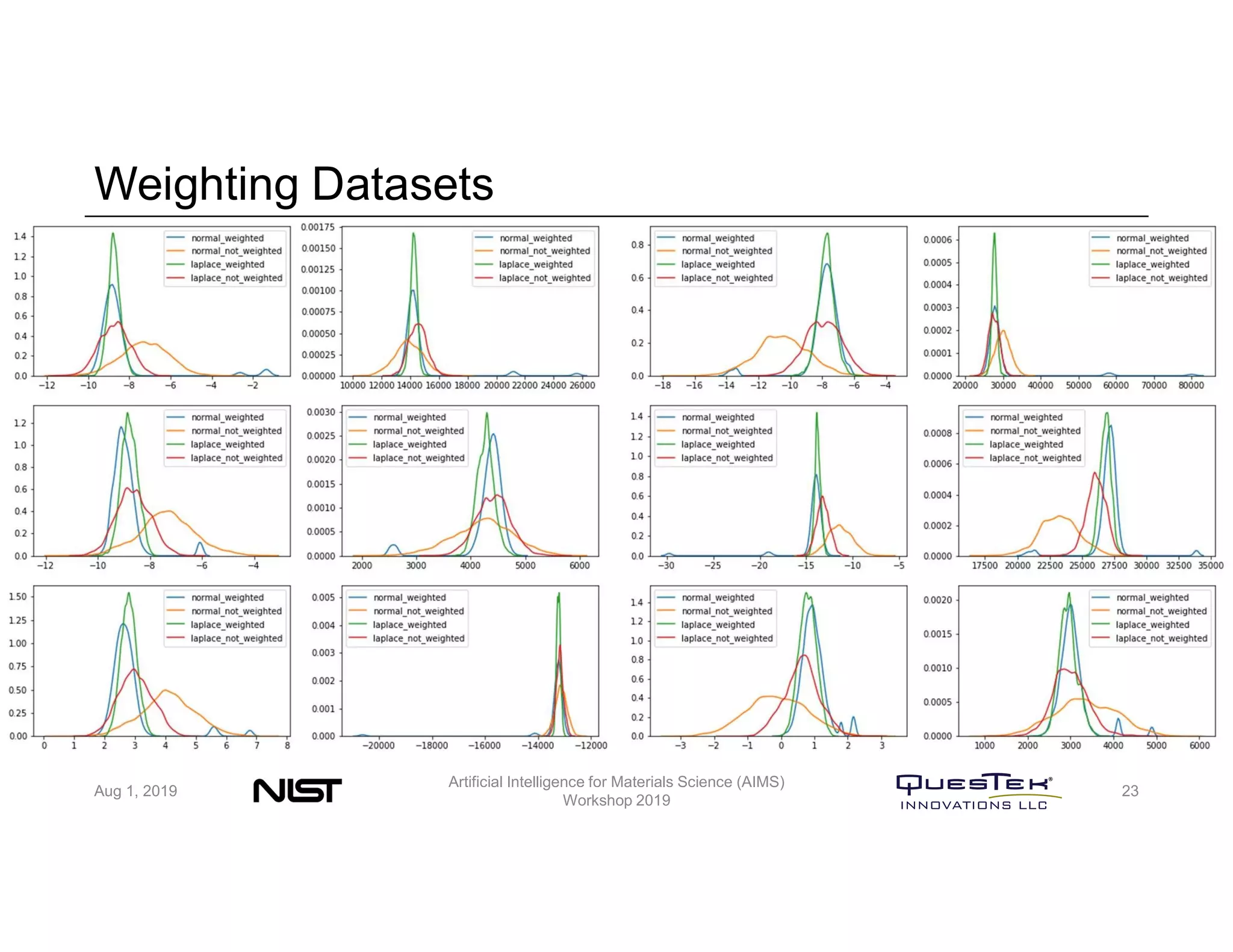
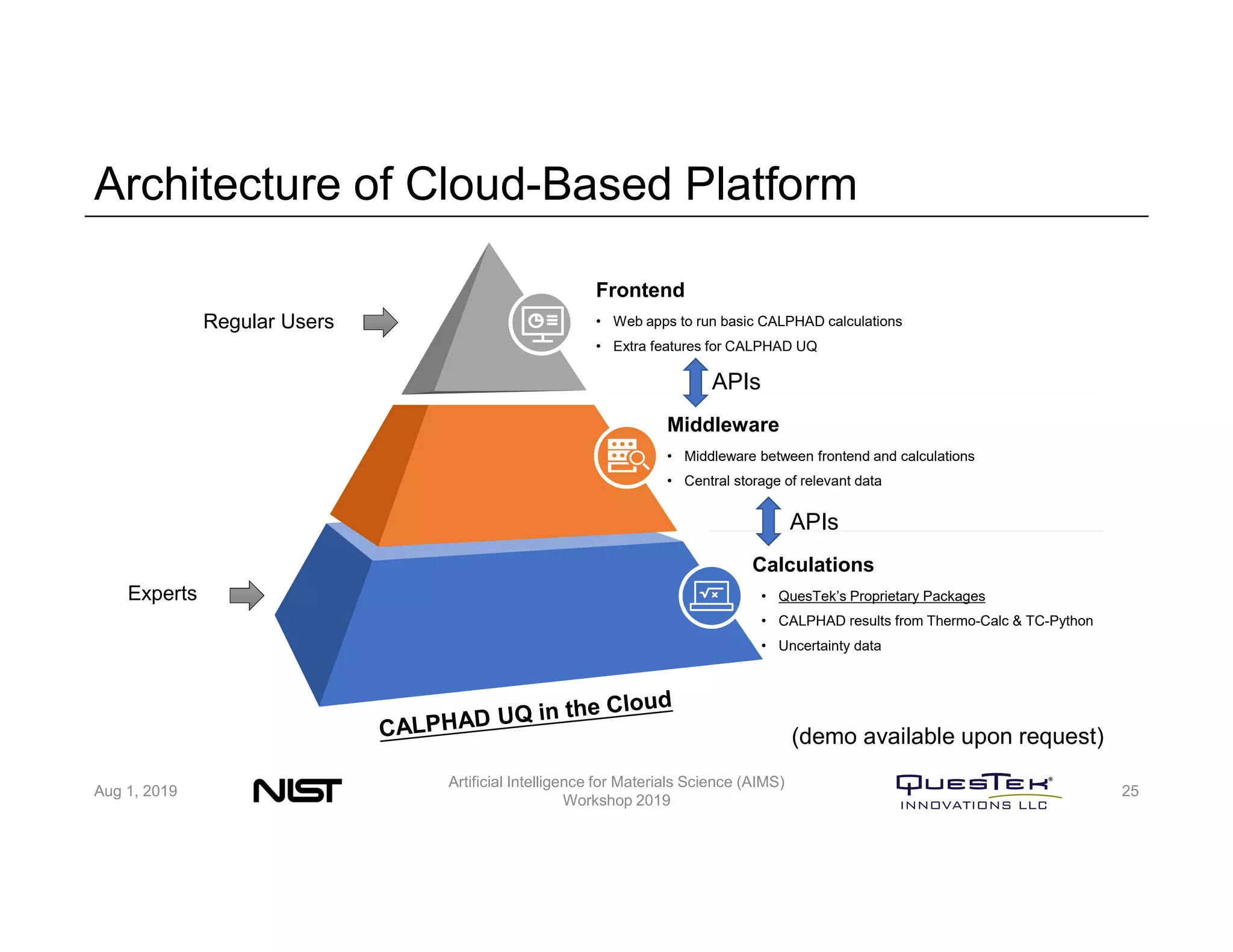
QuesTek Innovations presented a framework to incorporate materials genome initiatives (MGI) and artificial intelligence (AI) into their integrated computational materials engineering (ICME) practice. They discussed three key aspects: (1) MaGICMaT, a materials genome and ICME toolkit to manage data and property-structure-performance linkages, (2) an uncertainty quantification framework for CALPHAD modeling, and (3) a cloud-based platform to enable rapid development and deployment of ICME models with an HPC backend. The presentation provided details on their approaches for each aspect and highlighted opportunities to further enhance ICME with MGI and AI.