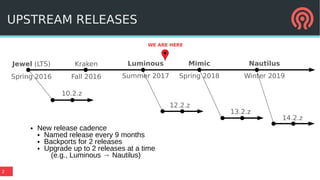
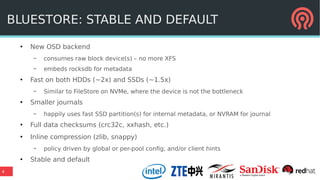
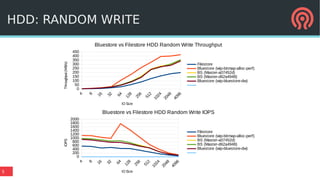
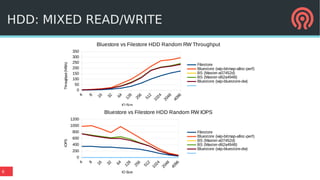
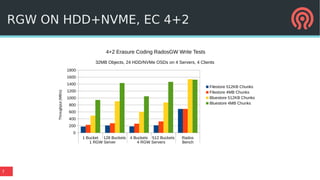
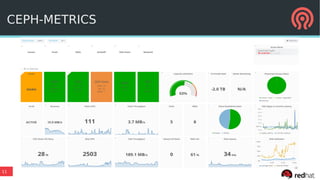
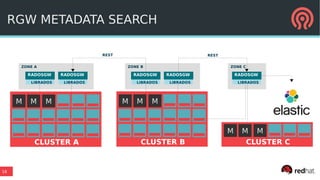
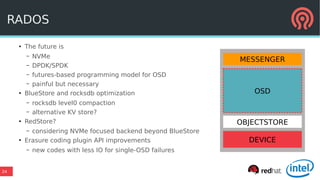
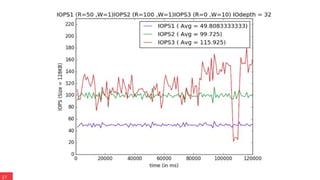
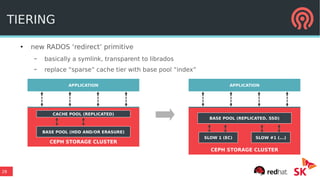
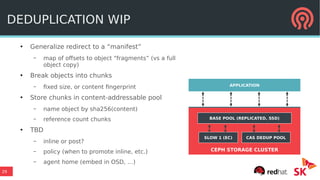
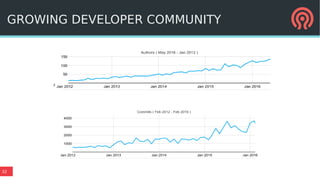
The document discusses the advancements in Ceph's Luminous release, highlighting new features like the Bluestore backend, improved erasure coding, and enhanced management via ceph-mgr. It outlines the new release cadence, performance improvements in storage efficiency, and updates on Ceph's integration with container technologies. Additionally, it emphasizes community engagement and collaboration with various organizations and developers in the Ceph ecosystem.