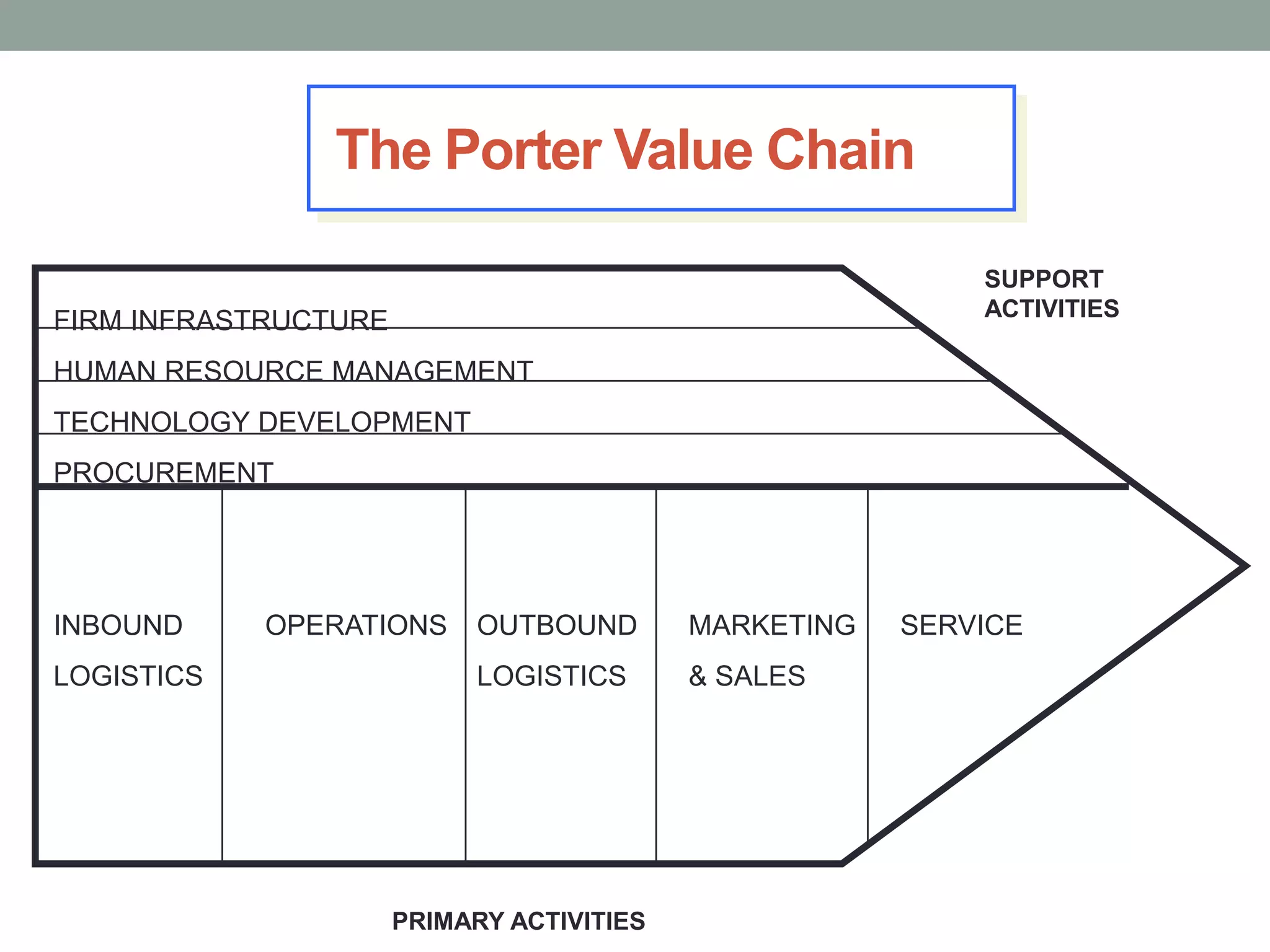
1. Strategy is the overall plan for deploying resources to establish a favorable position, while tactics are specific maneuvers. Strategic decisions are important, involve significant commitments, and are not easily reversible.
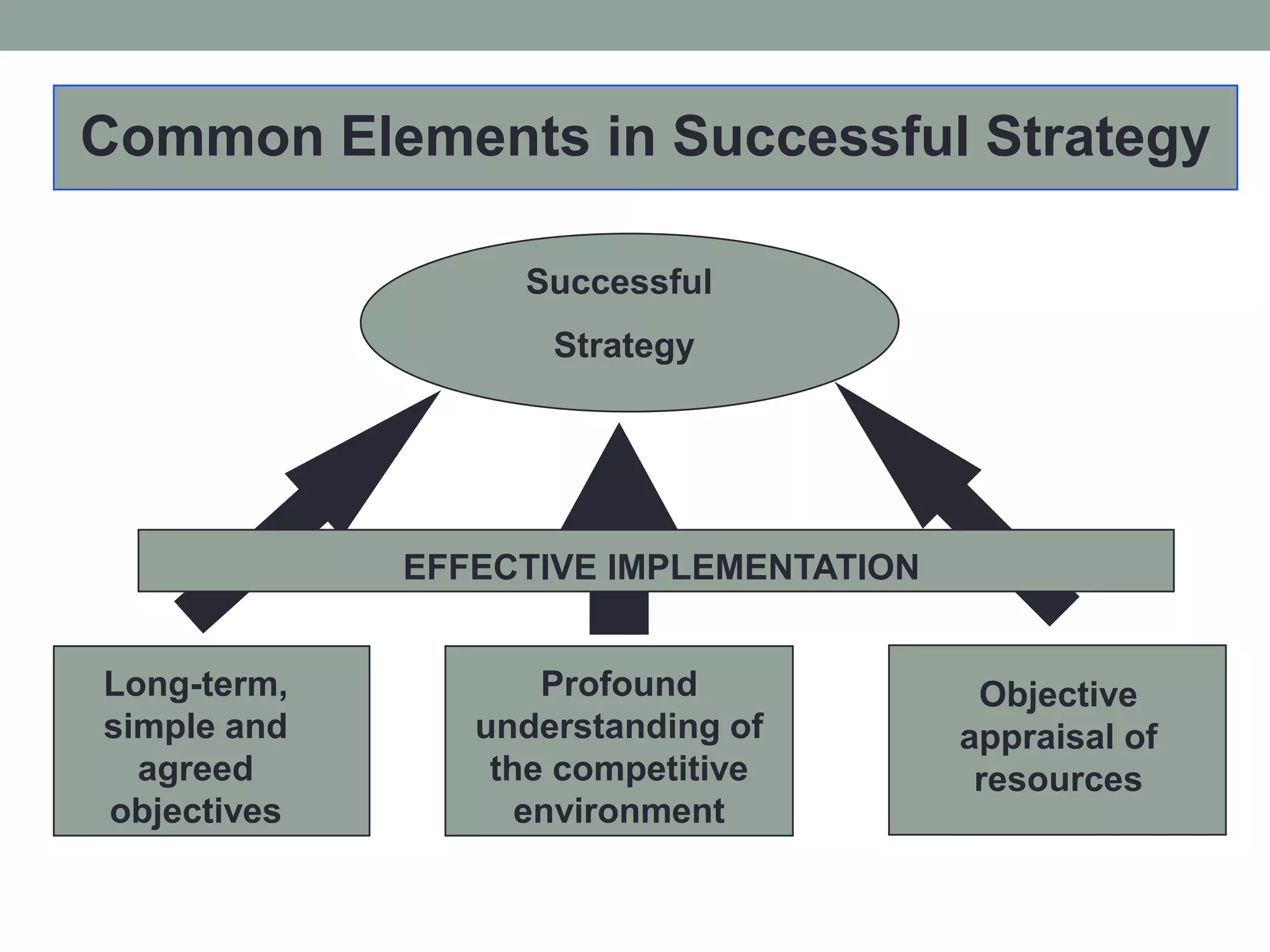
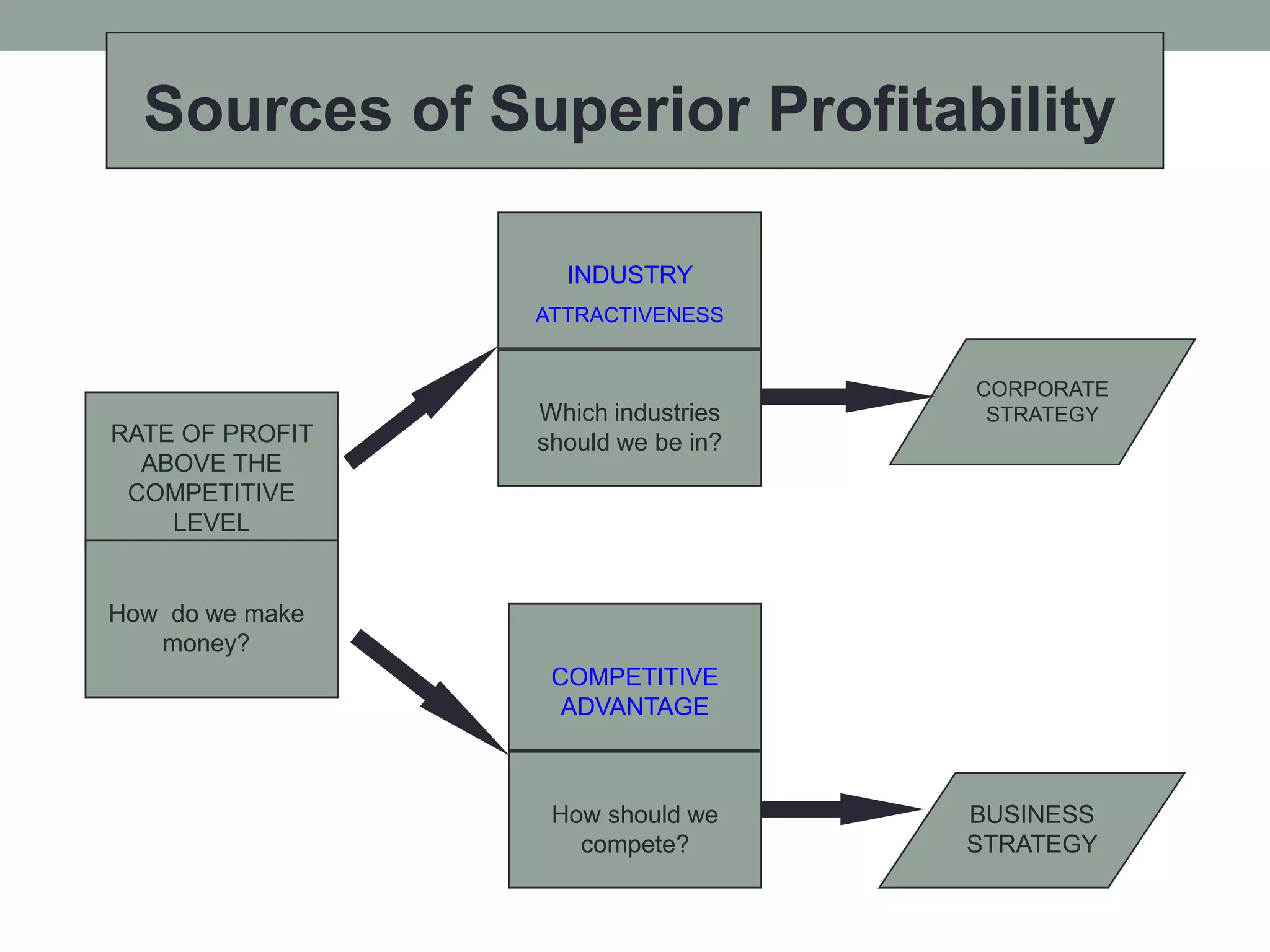
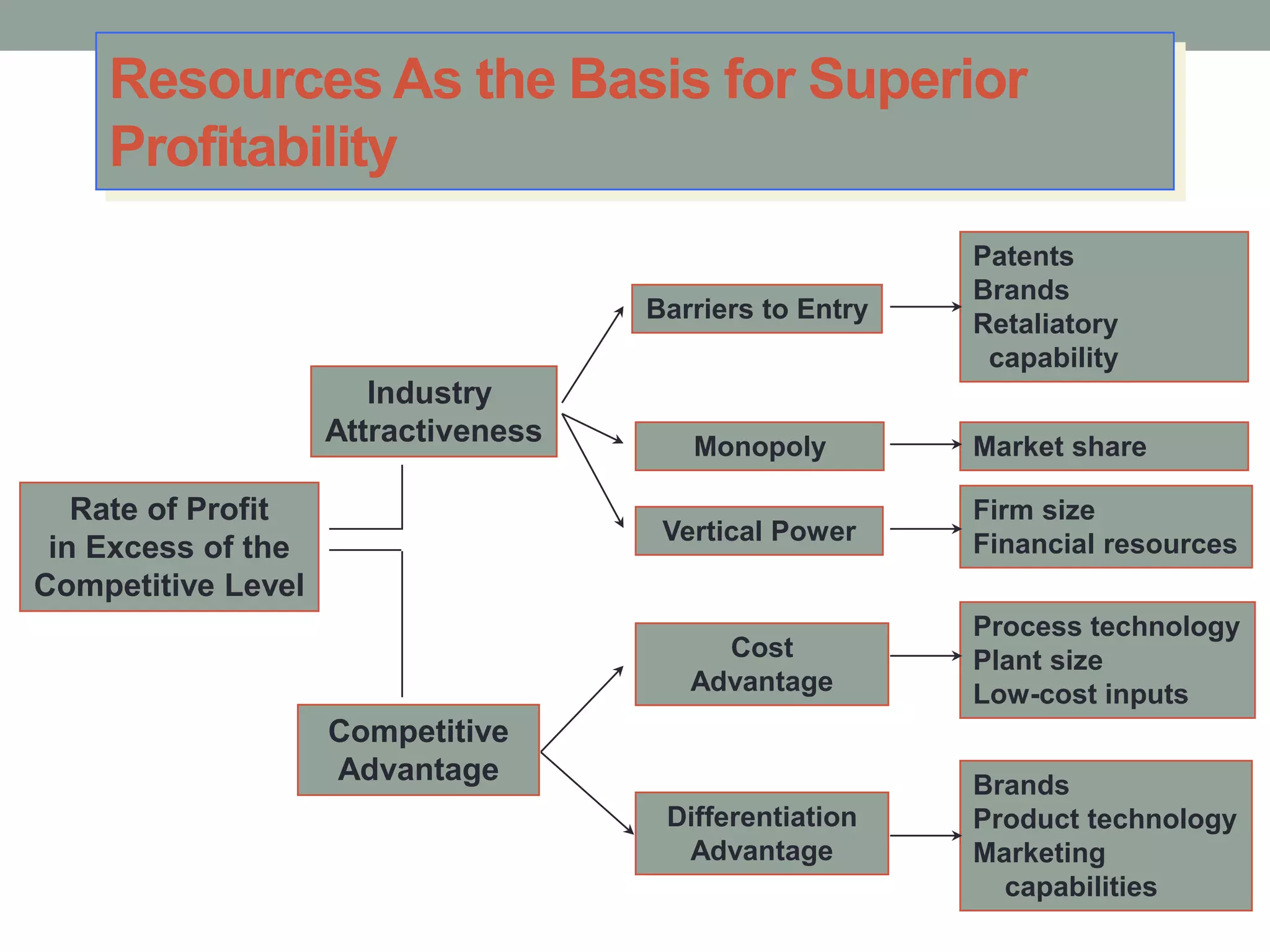
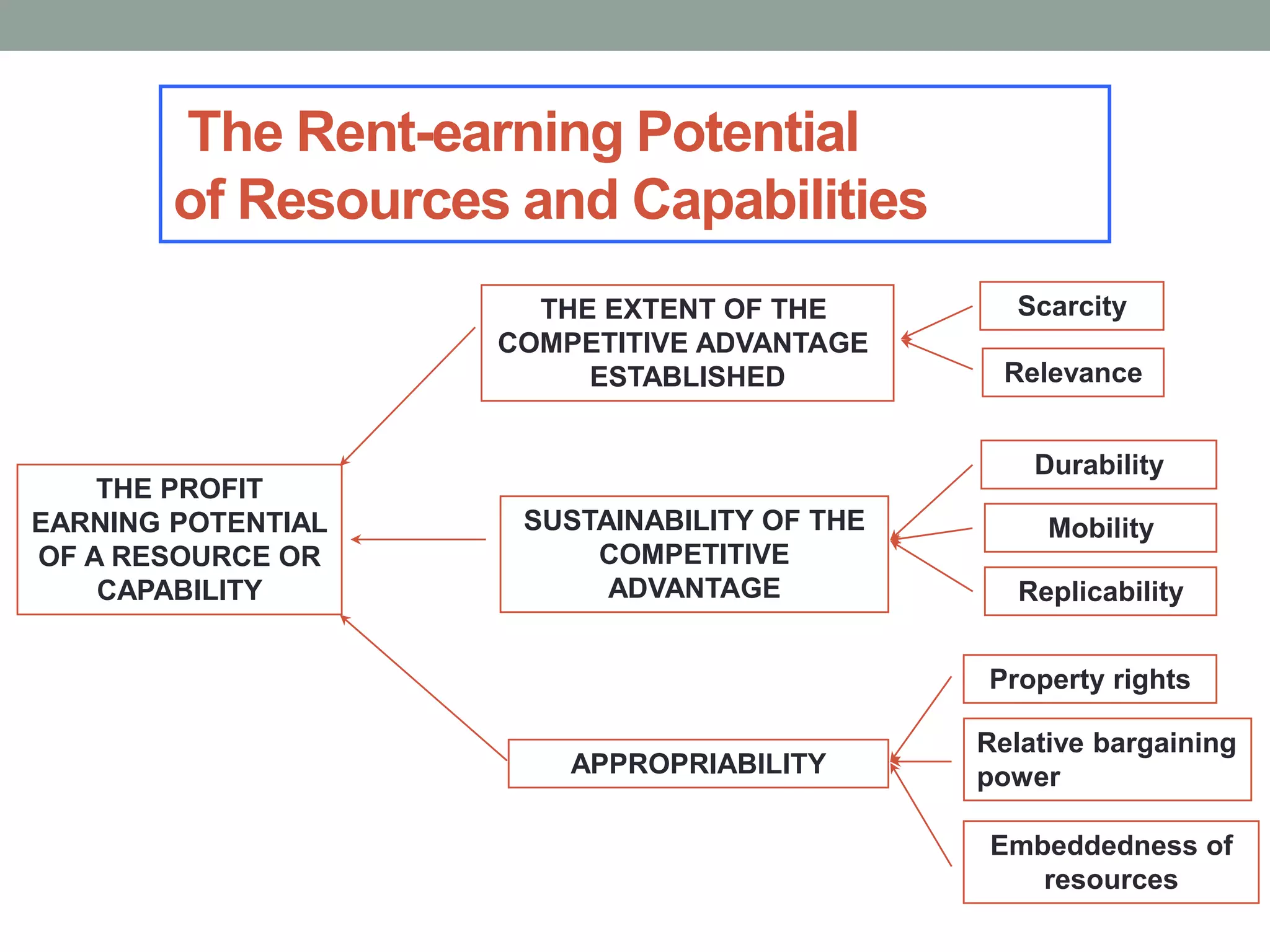
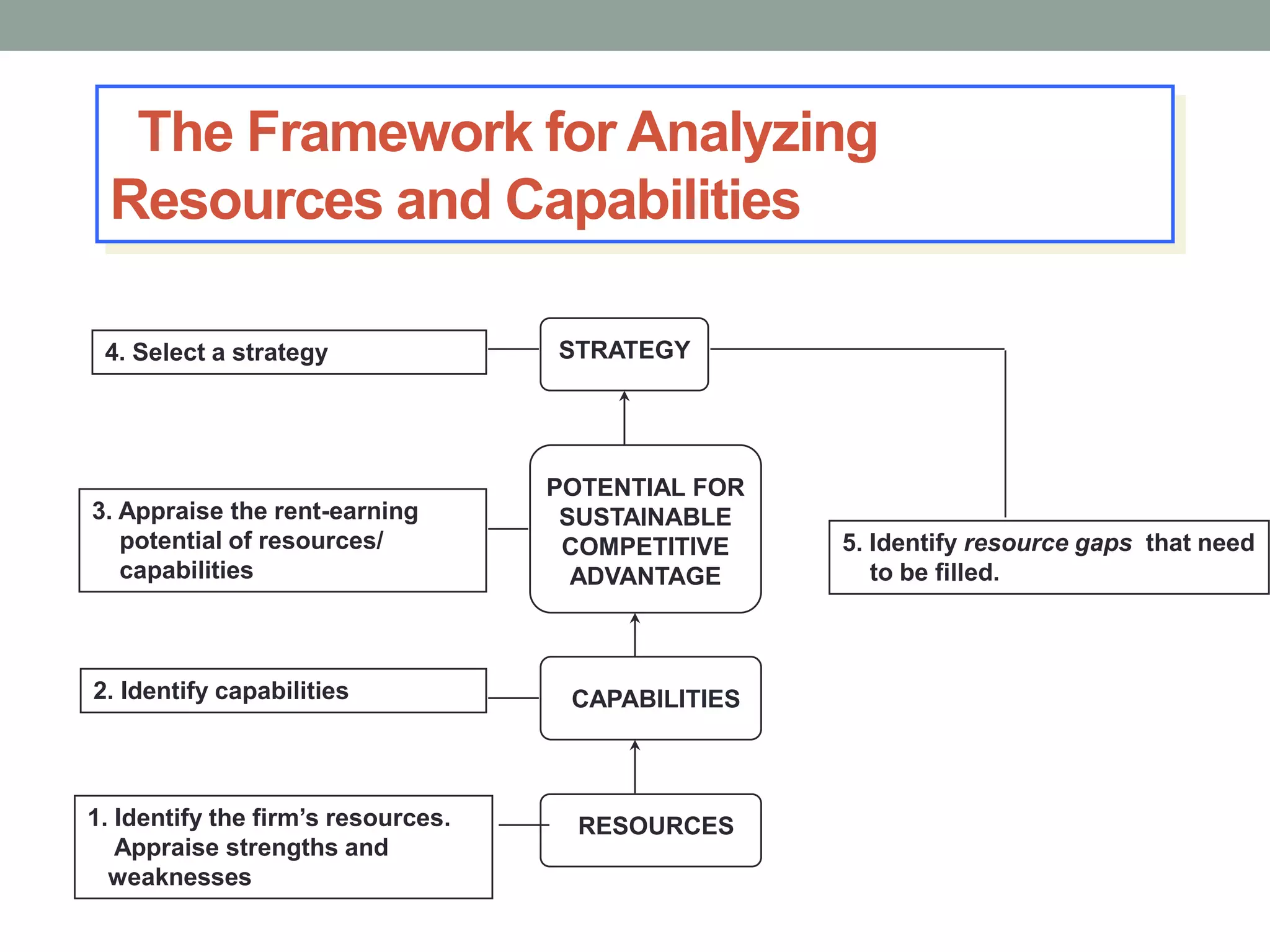
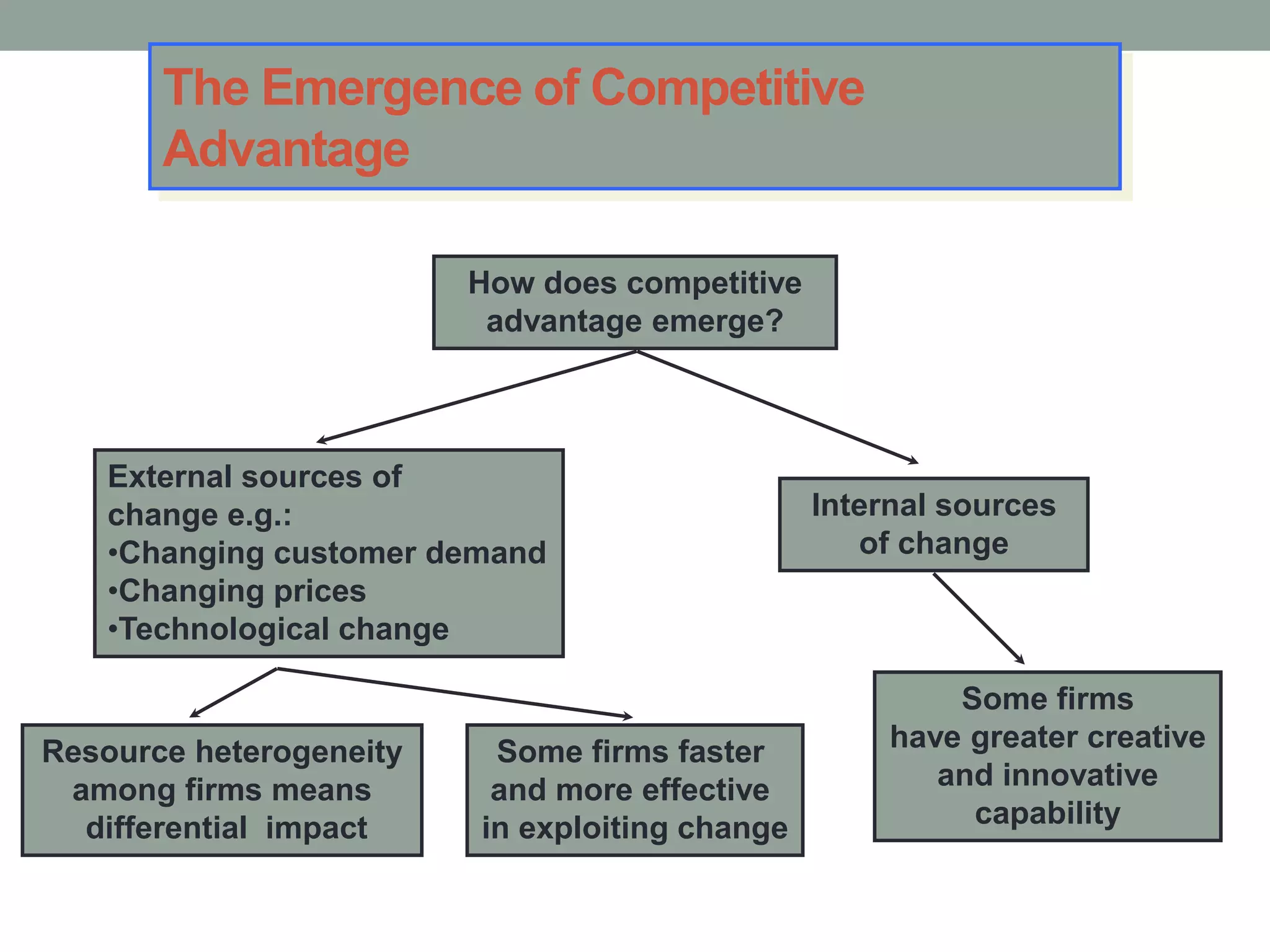
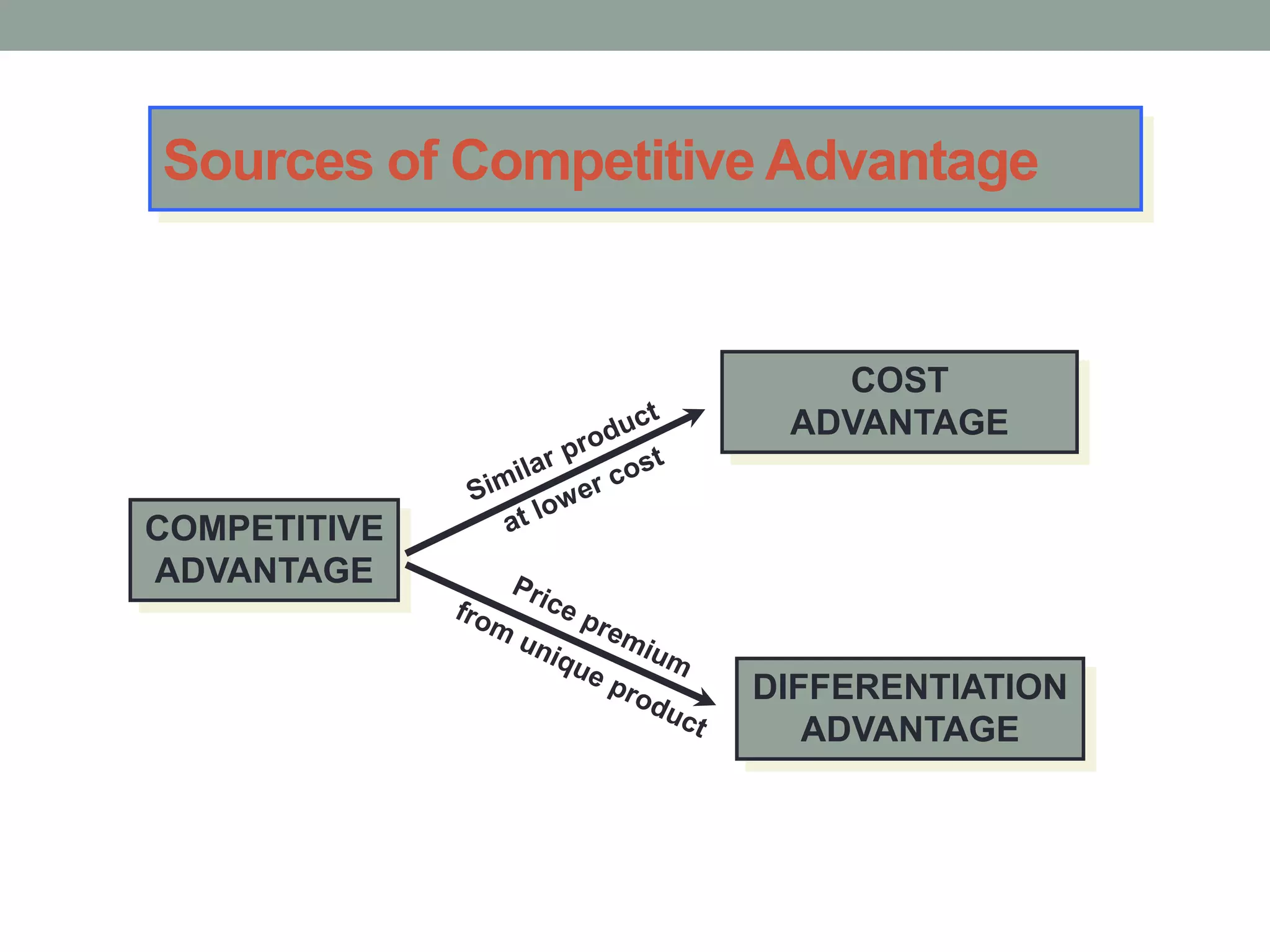
2. Successful strategies have long-term simple objectives, a profound understanding of competition, and an objective appraisal of resources. Resources and capabilities that are scarce, relevant, durable, immobile, and difficult to replicate can provide competitive advantages like differentiation or lower costs.
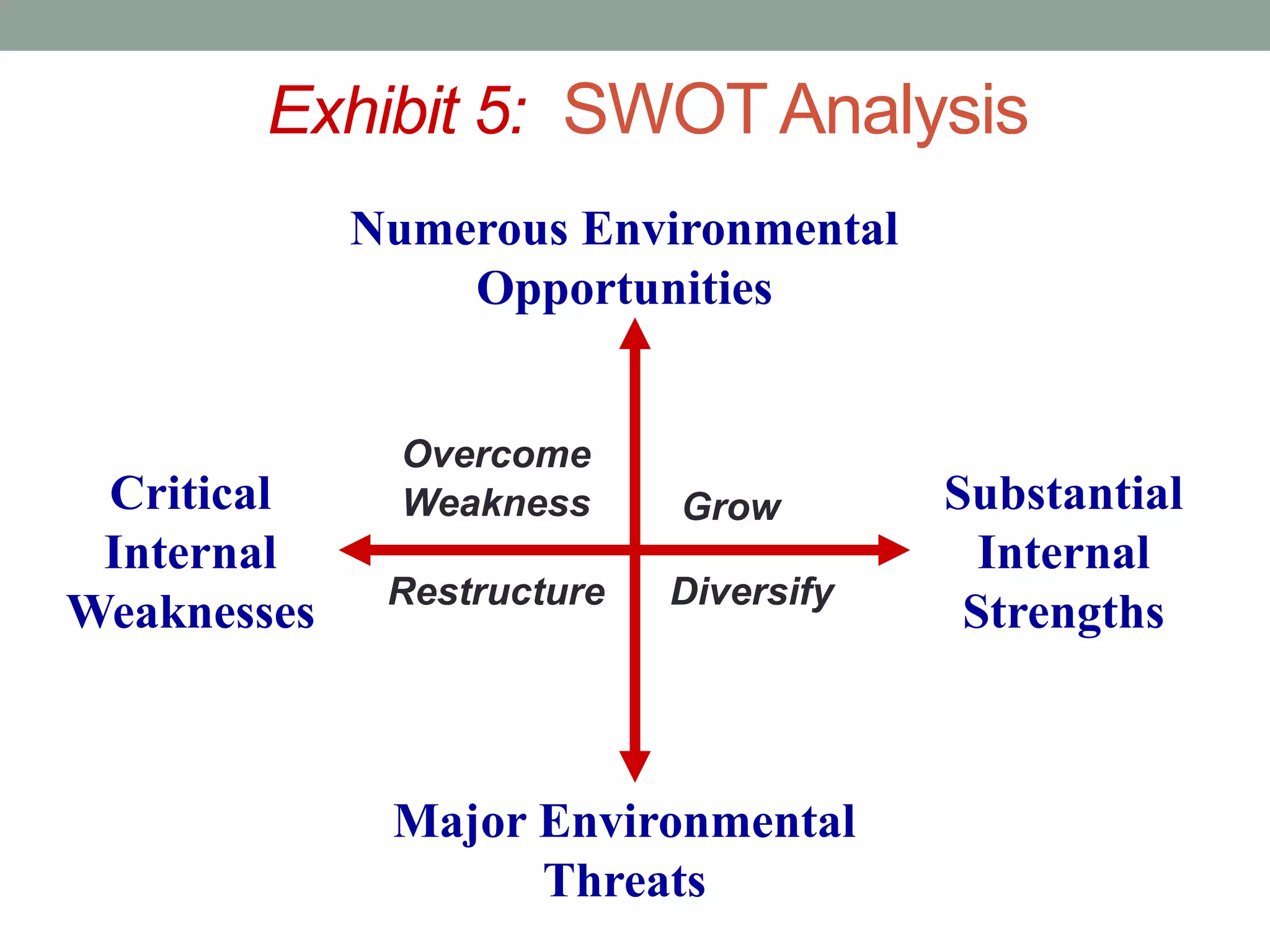
3. Firms conduct SWOT analyses to evaluate their internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats to determine how to overcome weaknesses, diversify, restructure, or grow based on their positioning.