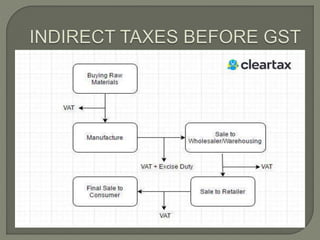
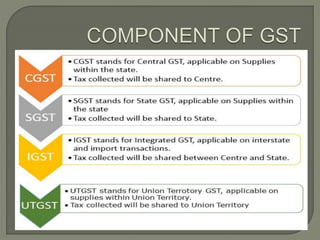
The document discusses Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. Some key points:
- GST replaced many indirect taxes and came into effect on July 1, 2017 following passage of the GST Act in March 2017.
- GST eliminates the cascading effect of taxes, provides a simple online procedure, and regulates the unorganized sector.
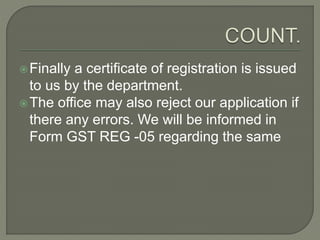
- Individuals and businesses above certain turnover thresholds must register for GST through the online portal by providing documents like PAN, address proof, and bank statements.