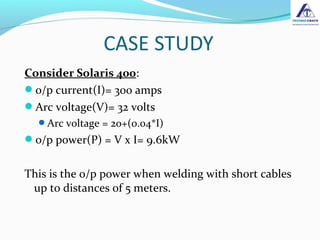
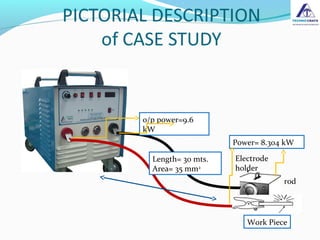
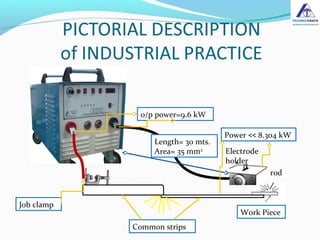
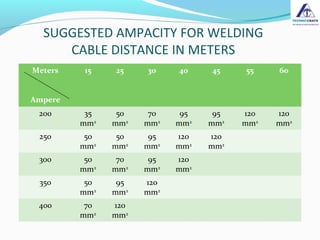
The document discusses the importance of selecting the appropriate size of welding cables to minimize power losses during welding operations. It highlights how insufficient cable size can lead to inadequate performance and increased power dissipation, particularly in longer cable lengths. The calculations provided demonstrate the relationship between cable length, cross-sectional area, and resistance, ultimately advising users to choose larger cable sizes to ensure efficiency and reduce power losses.